Software solutions based on optical barcode recognition (barcode OCR) have emerged as a more versatile and efficient alternative to traditional barcode scanners, particularly as the world moves on to 2D barcodes and automated document processing.
In this article, we’ll explore what barcode OCR is, and what distinguishes it from traditional scanning methods.
Understanding barcodes
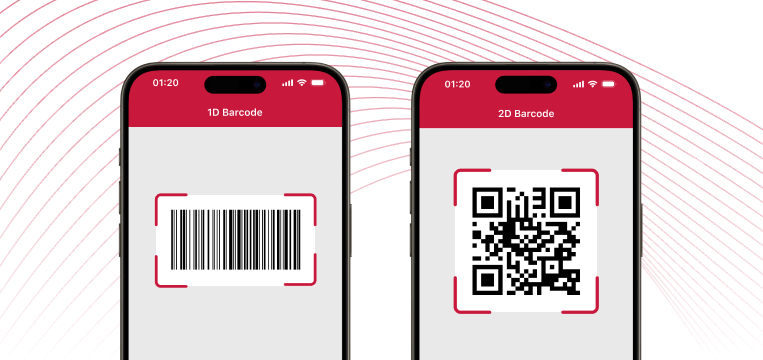
A barcode is a visual, machine-readable representation of data. Generally, there are two distinct types of barcodes: 1D and 2D barcodes. The key difference is in how they store data – and in how they are read.
1D barcodes
One-dimensional (1D) barcodes use black-and-white bars of varying width. Among the best-known 1D barcodes is the UPC, the first one to be used commercially in the 1970s. Today, it is typically found on the packaging of retail products.
A barcode scanner typically reads this pattern from left to right, translating the unique sequence of wide and narrow bars and spaces into a numeric or alphanumeric string. The barcode scanner will often use this string to look up more detailed information in a connected database. A point-of-sale terminal can, for instance, query the store database for price and stock level information.
2D barcodes
Two-dimensional (2D) barcodes represent data in geometric patterns of black-and-white pixels or dots. Most people are familiar with QR Codes as a result of a combination of technological advancements – smartphones capable of scanning barcodes – and changes in consumer behavior, accelerated by the COVID-19 pandemic.
2D barcodes are read both horizontally and vertically, which allows them to hold significantly more data than 1D barcodes. This can eliminate the need to reference an external database.
Why barcodes are so important
Barcodes are everywhere. They are an incredibly versatile backbone technology for countless industries. As a fast, accurate, and standardized method of data capture, they are indispensable for a variety of applications.
| Industry | Common applications |
| Retail | Point-of-sale, inventory and shelf management, returns management |
| Healthcare | Positive patient identification, medication administration, medical device tracking, lab specimen labels |
| Manufacturing | Tracking and traceability, warehouse receiving |
| Logistics | Supply chain management, fleet management, cold chain logistics |
| Entertainment, hospitality, and travel | Ticketing for events and transportation, check-in |
Traditional barcode scanning vs. barcode OCR
Traditionally, barcodes were read with single-purpose scanners that use LED light sources or lasers. However, as these scanners can only read 1D barcodes, they often fall short of modern demands.
Meanwhile, the more versatile 2D barcodes are becoming increasingly important through initiatives such as GS1 Sunrise 2027, GS1 Digital Link, and the EU’s Digital Product Passport. Businesses that seek a competitive advantage should therefore adopt solutions that can scan all barcode types.
Image-based barcode scanners meet this demand by capturing the entire barcode from an image, rather than reading it in a single line from left to right. This enables fast scanning of both 1D and the more complex 2D barcodes. They are also far more reliable in the face of barcode damage.
Thanks to advances in image processing technology, even ordinary smart devices can become enterprise-grade barcode scanners – once equipped with modern barcode scanner software. Consequently, more and more businesses are switching from expensive dedicated devices to more versatile smart devices.
This shift to smart devices also introduces an additional benefit: The ability to use optical barcode recognition, or barcode OCR.
What is barcode OCR?
Barcode OCR solutions combine barcode scanning software with optical character recognition (OCR) techniques. This allows them to scan barcodes not only from physical surfaces, but also from digital documents and images.
Such software identifies the barcode within the image, decodes it, and extracts the information for various purposes, such as sorting a document. Usually, this workflow involves several steps.
- Image creation or import: The software takes a picture of the barcode using the device camera. Alternatively, it imports an existing image or document.
- Image preprocessing: The image is prepared for barcode detection by applying methods such as skew correction, background noise removal, and contrast adjustment.
- Barcode detection: The software scans the image to detect and locate barcodes.
- Decoding: Once a barcode is located, the software decodes its data by interpreting its unique visual pattern.
- Data extraction: The decoded information from the barcode is then extracted and returned.
Where is barcode OCR used?
Optical barcode recognition is particularly valuable in industries that deal with high volumes of barcoded documents, such as healthcare, finance, and legal businesses.
Barcode OCR solutions drastically reduce manual labor and, consequently, human error in tasks such as document indexing, filing, and data entry. No dedicated scanner device is needed, either – any computer or smart device can be enhanced with a barcode OCR app.
Barcode OCR vs. traditional barcode scanning at a glance
| Feature | Barcode OCR (Optical barcode recognition) | Traditional barcode scanning |
| Input source | Digital images, PDFs, and scanned documents | Physical objects with printed barcodes |
| Hardware | Generic computer or smart device | Dedicated handheld or stationary barcode scanners |
| Application | Automated document processing, sorting, and data extraction | Single barcode scanning |
Barcode OCR: Start scanning today
Barcode OCR represents a significant evolution in barcode technology. It offers a highly versatile and efficient solution for businesses ready to embrace image-based scanning and the broader adoption of 2D barcodes.
Modern software development kits make this easy: You can set up a fully functional Barcode OCR web app with just a few lines of code – even in a single, self-contained HTML file, thanks to the Scanbot Web Barcode Scanner SDK.
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8" />
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0, maximum-scale=1.0, user-scalable=0" />
<title>Scan barcodes from an image</title>
</head>
<body style="margin: 0">
<input class="file-picker" type="file" accept="image/jpeg,image/png" />
<p id="result"></p>
<script type="module">
import "https://cdn.jsdelivr.net/npm/scanbot-web-sdk@7.0.0/bundle/ScanbotSDK.ui2.min.js";
const sdk = await ScanbotSDK.initialize({
enginePath:
"https://cdn.jsdelivr.net/npm/scanbot-web-sdk@7.0.0/bundle/bin/barcode-scanner/",
});
document.querySelector(".file-picker").addEventListener("change", async (e) => {
e.preventDefault();
const file = e.target.files[0];
if (!file) return;
const reader = new FileReader();
reader.readAsDataURL(file);
reader.onload = async () => {
try {
const result = await sdk.detectBarcodes(reader.result);
const resultContainer = document.getElementById("result");
if (result?.barcodes?.length > 0) {
// Clear previous results
resultContainer.innerHTML = "";
// Display all detected barcodes
result.barcodes.forEach((barcode, index) => {
const barcodeElement = document.createElement("p");
barcodeElement.innerText =
`Barcode ${index + 1}:\n` +
`Type: ${barcode.format}\n` +
`Content: "${barcode.text}"\n\n`;
resultContainer.appendChild(barcodeElement);
});
} else {
resultContainer.innerText = "No barcodes detected.";
}
} catch (error) {
console.error("Error detecting barcodes:", error);
document.getElementById("result").innerText = "Error detecting barcodes.";
}
};
});
</script>
</body>
</html>Feel free to copy the code into an HTML file and open it in your browser. When moving to production, we recommend you download the SDK and host it on your server instead of using a CDN.
The Scanbot Barcode Scanner SDK leverages advanced machine vision technology to deliver high-quality input images and enterprise-grade OCR scan accuracy. All processing happens on-device, which is crucial for handling documents with sensitive information.
If you have any questions, please message scanbot@sdk.io. Our solution experts are always happy to discuss your use case.