Supply chain fraud has emerged as a critical issue for businesses worldwide, particularly in the freight sector. The ongoing digital transformation of supply chains has created new vulnerabilities that criminals are quick to exploit. Fraudsters are employing increasingly sophisticated methods, e.g., fictitious pickups, double brokering scams, and impersonation of legitimate carriers.
To combat these issues, companies are implementing various strategies, including improved vetting processes, compliance automation, and email security tools to detect impersonation attempts. One critical strategy gaining traction is supply chain mapping, which serves as a comprehensive tool for visualizing and understanding the intricate networks of suppliers, manufacturers, distributors, and customers involved in the production and delivery of goods.
Supply chain mapping involves creating a detailed visual representation of the flow of materials, information, and finances throughout the supply chain. This process allows businesses to identify key stakeholders and their relationships, which is essential for optimizing efficiency and managing risks effectively. By mapping out every component of the supply chain, organizations can pinpoint inefficiencies, potential bottlenecks, and areas susceptible to disruptions.
How supply chain mapping can help combat supply chain fraud
Understanding the intricacies of your supply chain can help identify vulnerabilities and implement targeted measures to mitigate risks. Supply chain mapping involves identifying all the stages of a product’s journey, from raw materials to the end consumer. This comprehensive view allows companies to pinpoint weak points in the chain that are particularly susceptible to fraud.
For instance, a company might discover that a particular supplier has a history of unethical practices or that a specific geographic location is known for counterfeit production. By understanding these specific vulnerabilities in their supply chain, companies can then develop targeted strategies to mitigate risks. This might include implementing stricter quality control measures at certain stages, diversifying suppliers to reduce reliance on a single source, or using technology to track products more effectively.
Supply chain mapping also promotes transparency by making the origins and movements of products more visible. This increased visibility allows for better monitoring and oversight, making it harder for fraudulent activities to go undetected. If a company can trace a product back to its source, it can more easily verify its authenticity and identify any potential points where counterfeiting or adulteration might have occurred.
Comprehensive supply chain mapping is a complex endeavor, especially for large companies with intricate global networks. However, the insights gained from this process are crucial for building a more secure and resilient supply chain, reducing the risk of fraud and protecting both the company’s reputation and its consumers’ interests.
The role of barcode technology in mapping supply chains
One of the most effective ways to track and trace products throughout their journey is using barcodes to encode standardized information. This information can then be used to create a comprehensive map of the supply chain, identifying all the stages and stakeholders involved.
Barcodes, particularly those using the GS1 standard, assign unique identifiers to individual products, enabling precise tracking. Unlike generic barcodes that only identify a product type, GS1 barcodes allow companies to track each specific unit, making it possible to trace its path through the supply chain. This granular level of identification is essential for creating a detailed supply chain map, as it provides a digital fingerprint for every item.
Scanning an item’s barcode enables automatic data capture at various points in the supply chain, from manufacturing and warehousing to distribution and retail. Each time a barcode is scanned, it records the product’s location and status, creating a digital trail. This data can be integrated into supply chain management systems, providing real-time visibility into product movements. By analyzing this data, companies can identify bottlenecks, optimize routes, and improve overall supply chain efficiency.
Supply chain management using barcode scanning software
Traditionally, those involved in the supply chain had to rely on dedicated hardware scanners to capture items’ data. However, barcode scanning software has since become the preferred option due to its adaptability and expandability. By integrating an SDK into a mobile or web app, companies can easily provide scanning functionalities to all participants in the supply chain.
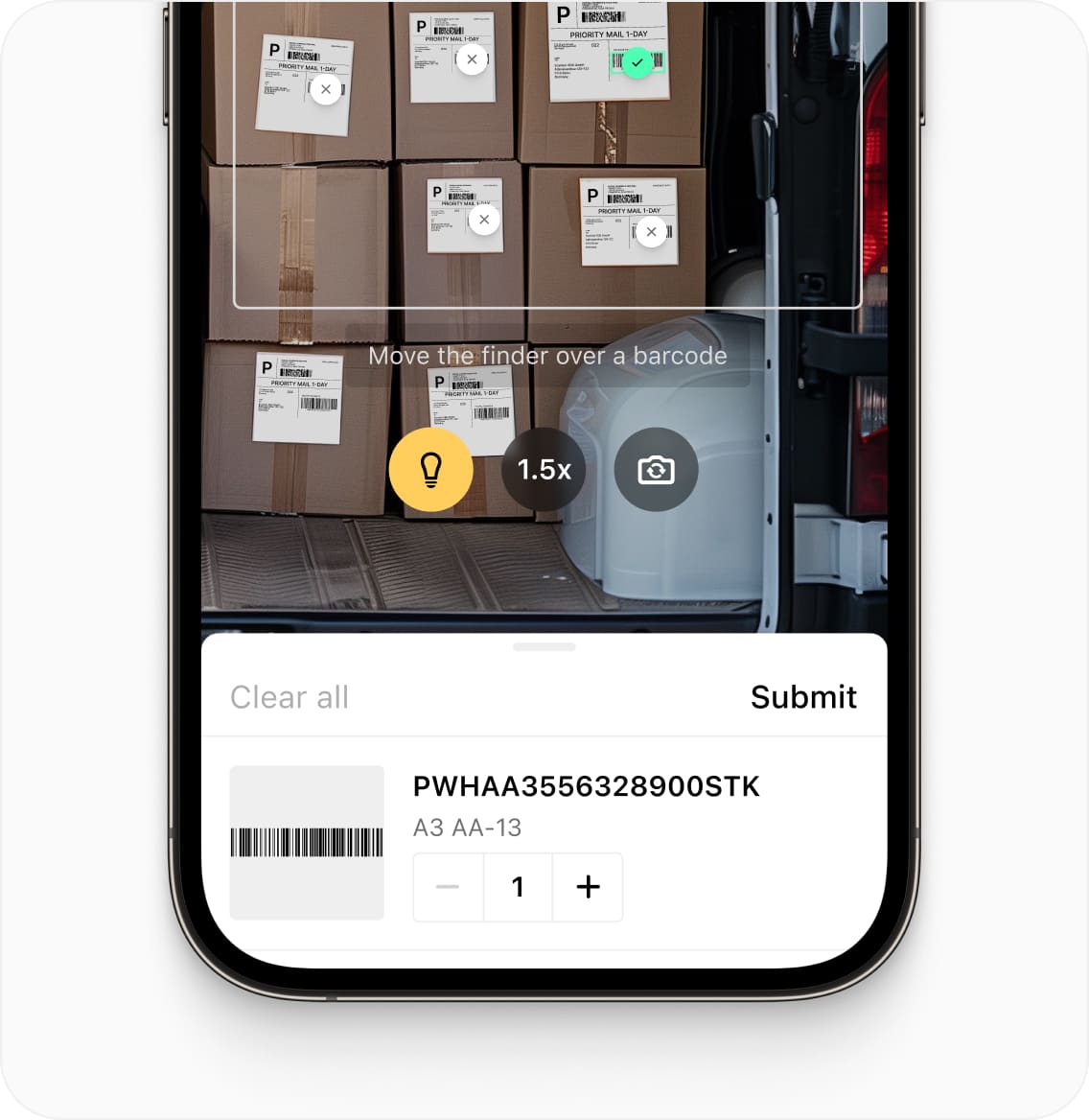
We’ve developed the Scanbot Barcode Scanner SDK with the complex requirements of enterprise use cases in mind. This powerful barcode scanning software is available for Android, iOS, Web, Windows, and Linux and supports various cross-platform frameworks, including React Native, Flutter, and .NET MAUI. Its wide availability ensures it can interface with any supply chain management system.
The Scanbot SDK reliably scans all common 1D and 2D barcodes, even when they are damaged, poorly lit, very small, or far away. It operates entirely offline and never connects to third-party servers, ensuring maximum data privacy and security. Thanks to its built-in ready-to-use UI components, you can set up a barcode scanning interface in minutes while having complete control over its look and feel. Its in-depth documentation and free integration support cater to the needs of developers and ensure a short time to roll-out.
Experience the SDK yourself by trying our free demo apps or running our example apps for various platforms. If you’d like to test the SDK in your app, generate a free 7-day trial license to start integration immediately.



