Supply chain management (SCM) coordinates the entire production flow of goods, involving a variety of concerted workflows.
A core aim of SCM is to optimize the transformation of raw materials into finished goods: improving efficiency, reducing costs, minimizing waste, eliminating delays, and enhancing customer satisfaction – all based on gathering and analyzing data.
Enter barcodes. In this article, we explore where in SCM workflows these versatile data carriers come into play, and why mobile barcode scanning is the most efficient way of processing them.
Core areas of supply chain management
Supply chain management is more than the manufacturing and shipping of products. Let’s begin with a brief breakdown of its core tasks.
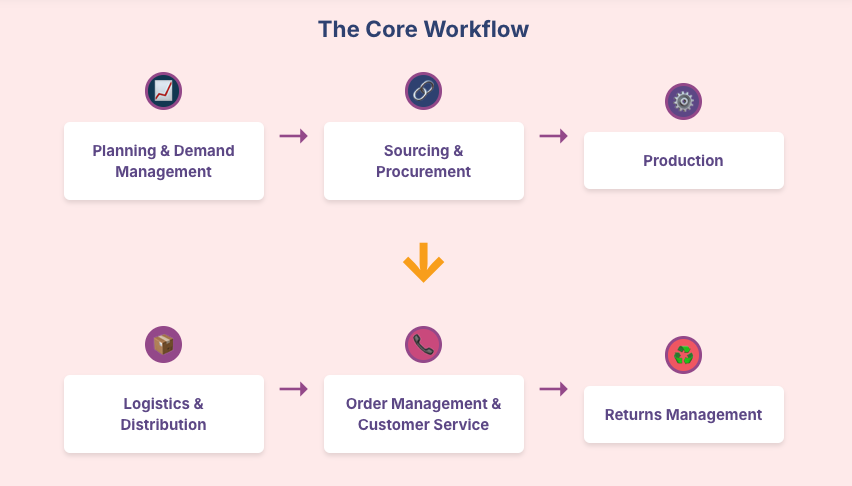
- Planning and demand management
Planning is the foundation for all production and supply chain decisions. By analyzing market trends and forecasting customer demand, businesses can plan production schedules, manage inventory sizes, and anticipate potential disruptions.
- Sourcing and procurement
For a given production run, suitable suppliers are selected, and raw materials, components, and consumables are purchased.
- Production
This is where the raw materials are transformed into finished products. Regular quality control and process optimization measures maintain a smooth production process and ensure regulatory compliance. Manufacturing has to be aligned with intake, inventory, and distribution capacity.
- Logistics and distribution
Effective warehousing, transportation, and order fulfillment operations are crucial in moving products from factories to warehouses, and from distribution centers to customers.
- Order management and customer service
Customer service ensures that customers have a good experience with all order processing, tracking, and fulfillment touchpoints.
- Returns management
Comprehensive customer service includes the return of defective or unwanted products. Efficient returns management involves processing returned products, updating inventory levels, and tracking the returned items in the warehouse to ensure smooth restocking.
- Inventory management
Constant inventory level monitoring helps ensure that the right amount of stock – whether components or finished goods – is available at the right time.
- Monitoring
Monitoring all processes is crucial for identifying potential bottlenecks and improving operations. This reduces costs, improves efficiency, minimizes disruptions, and thus increases customer satisfaction.
Where do barcodes come into play?
The different areas of SCM utilize similar workflows. After all, raw materials have to be shipped, tracked, and stored just as much as finished goods do.
That’s why a standardized system, such as barcoding, has uses for a wide range of supply chain management processes.
It facilitates the exchange of product information, such as quality checks or expiry dates, between different stakeholders. Another major benefit is enhanced traceability.
But how exactly does a barcode system work?
How do barcodes work?
Barcodes are visual representations of data. Each arrangement of black-and-white bars or pixels can represent a unique code.
Barcode scanners decode these patterns and can send this data to backend systems for automatic processing.
For one-dimensional (1D) barcodes with a bar pattern, traditional laser scanners suffice.
Two-dimensional (2D) barcodes, however, require more modern scanning technology. With their complex encoding and characteristic pixel patterns, camera-based scanners are the tool of choice.
And this includes smartphone-based scanning.
Where can barcodes be used in supply chain management?
Barcodes have several key advantages over other data carrier technologies, such as RFID. Not only are they small enough to fit onto labels and small components, they are also cost-effective. Generating and printing barcodes is inexpensive, and even budget mobile devices can be used for scanning them.
Now, let’s take a look at the main applications of barcode scanning in supply chain management.
Integration across existing systems
Integrated with warehouse management systems (WMS), inventory management systems (IMS), and enterprise resource planning (ERP) systems, barcode scanning enables seamless data processing for automated analytics and management processes.
Inventory management
Scanning barcodes on in- and outgoing products enables real-time updates to inventory levels, ensuring that stock levels are accurate at all times. This reduces the risk of stockouts or overstocking.
Receiving and putaway
When workers scan barcodes on goods as they arrive at the warehouse, they can rapidly verify shipments, record the receipt of goods, and move items to their correct storage locations.
Order picking and packing
Scanning item and location barcodes during picking ensures that only the correct items are picked and automatically updates inventory levels.
Shipping and distribution
Scanning barcodes on shipping labels is used to verify outgoing shipments and update their order status at every stage of their journey. This provides real-time shipment tracking for either the customer or other recipients further along the supply chain.
Returns management
Barcode scanning ensures that returned products are processed correctly in the inventory system, streamlining restocking and disposal processes.
Tracking and traceability
Barcode systems allow stakeholders to track and trace goods throughout the supply chain. This is crucial for swift, targeted recall management and for identifying quality issues.
Compliance with regulations
The regulations to observe in supply chain management are as varied as its operations – and they are tightening. Take the EU’s Digital Product Passport (DPP), for instance. Every product on the EU market, regardless of origin, will have to have a digital record accessible through a data carrier, such as a barcode.
Advanced barcode scanning solution: mobile barcode scanners for supply chain management
Barcode scanner software leverages image processing technology and modern smart device cameras to turn ordinary smartphones or tablets into powerful barcode scanners.
They can scan both 1D and 2D barcodes, even when these are damaged or poorly lit. Today’s mobile scanner solutions deliver incredible scanning speed and accuracy.
The Scanbot Barcode Scanner SDK can be integrated into any mobile and web app within hours, thanks to its Ready-to-Use UI Components. After that, a quick download turns any smart device into a powerful barcode scanner.
The SDK comes with several specialized scan modes and features useful for supply chain management workflows.
With Batch Scanning, you can scan several barcodes consecutively, without having to restart the scanning process. And Multi Scanning lets you capture multiple barcodes simultaneously.
Find & Pick will visually highlight and scan only barcodes with the desired values, ideal for warehouse picking workflows. The Scan & Count feature is useful for inventory management tasks: It enables employees to count multiple items in one go.
The Scanbot Barcode Scanner SDK allows for high flexibility thanks to its fixed-price model. A flat annual fee for unlimited scanning – without user or device tracking – lets it grow with your business.
Experience it yourself in our free barcode scanner demo apps. If you have any questions, we are happy to answer them at sdk@scanbot.io.



