Efficient inventory management is crucial for success. If you’re looking to streamline your operations and gain better stock visibility, a barcode system could be a game-changer for your business.
In this article, we’ll guide you through the process of optimizing your inventory management by introducing a barcode system.
Let’s start with the basics: What exactly are barcodes, and how do they help you handle your inventory?
What are barcodes?
Fundamentally, barcodes are visual representations of data. They encode numbers, letters, and other symbols in black-and-white lines or squares.
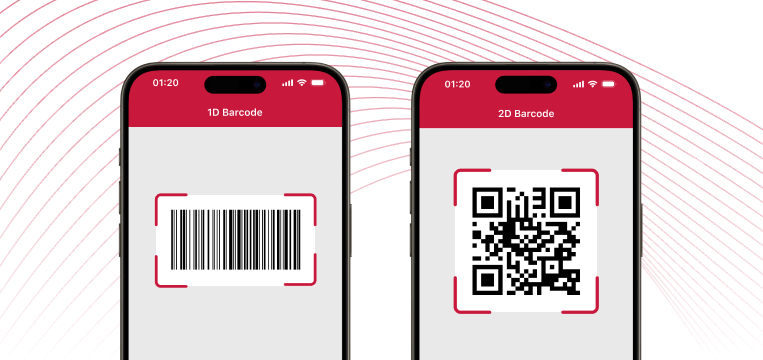
There are two types of barcodes: one-dimensional (1D) and two-dimensional (2D) symbologies. One-dimensional barcodes consist of lines and are designed to be scanned horizontally with laser scanners.
Two-dimensional codes use vertical and horizontal space, enabling them to encode more information. However, they can only be scanned with devices that have a camera, like imager scanners or smartphones.
What are the benefits of utilizing barcodes for your inventory management system?
Manual inventory management is prone to human error, resulting in faulty stock level data and slow operations. Technology such as RFID tags can lead to faster and more accurate inventory tracking, but it is expensive.
Barcodes, however, are already used for countless applications across industries because they address the issues of speed, accuracy, and cost – besides offering a range of other benefits.
Let’s go over the main advantages of a barcode inventory management system.
- Efficiency and speed: Scanning barcodes is much faster than manual data entry. This significantly reduces transaction times, shortens waiting lines, and makes inventory management more efficient.
- Accuracy: Barcodes eliminate human error. Manual data entry is not only slower, but also produces significantly more errors than barcode scanning.
- Cost-effectiveness: Barcode labels are relatively cheap to design and print. Barcode systems also require next to no training to use and can save money by reducing the time spent on correcting data entry errors.
- Inventory control: Barcodes offer very efficient and immediate inventory tracking. As counts are updated with every scan, barcode inventory systems provide real-time stock level data and efficiently track inventory.
- Data availability: Since barcodes, especially 2D codes, can hold a lot of data in a small space, they allow for the storage of detailed product information.
- Scalability: Barcode systems are easy to implement and can handle surges in inventory volume without compromising accuracy or speed, ideal for industries to track inventory during seasonal demand fluctuations.
- Automation capabilities: In combination with inventory software, barcode scanning helps businesses automate processes such as low-stock alerts. This reduces the need for manual interventions and improves stock management efficiency.
But how can you make use of these advantages in your inventory management system?
How to use barcodes for inventory management
A barcode-based inventory system monitors stock using barcode labels affixed to items. Consequently, inventory operations only require a swift scan with a reader or smartphone. Combined with an inventory management system, this approach delivers real-time insights into the whereabouts and quantity of any item in your warehouse or store.
When an item is scanned, the barcode data is transmitted to the inventory management backend for processing and monitoring. This direct access to precise product data enhances decision-making concerning stock levels, purchasing patterns, and other relevant factors.
Furthermore, the data provided by a barcode inventory system streamlines report generation on performance metrics, including sales figures and item popularity.
Industries that benefit from barcode inventory systems
Because of their ability to update stocks in real-time – while being accurate, cost-effective, and easily scalable – barcode inventory systems are widespread in several industries.
E-commerce
An ever-growing industry, retail e-commerce sales are expected to exceed 4.3 trillion U.S. dollars worldwide in 2025. The global distribution operations typical for the industry require efficient inventory tracking across multiple warehouses. Barcodes deliver accurate product availability information and enable timely restocking.
Retail
Both online and brick-and-mortar stores need to keep up with a diverse product range and handle seasonal fluctuations. Introducing automated replenishment systems based on barcode scanning ensures that products are available when needed. This reduces stockouts, improving the customer experience.
Food retailers need to pay special attention to precise inventory management due to the perishable nature of their products. Barcode scanning software can be combined with software to track levels and expiration dates, reducing spoilage and loss.
Manufacturing
Operators in the manufacturing industry must balance raw materials stocking with the storage of finished goods.
The real-time inventory updates that barcode systems enable help prevent supply chain interruptions and ensure continuous production.
Healthcare
Patient care is the number one priority in the healthcare industry. This includes the efficient management of medical supplies and equipment. Barcodes require very little space, which makes them ideal for medical product labeling.
The same barcode system can be used for positive patient identification (PPID) and medication administration.
Which barcode scanner to use for inventory management
Barcode technology is deeply established in a range of industries. Over the last decades, different types of barcode scanners have been developed. They all have their advantages and disadvantages and are thus suitable for different use cases. Let’s take a look at four common types of barcode scanning devices.
- CCD (charge-coupled device) barcode scanners: CCD barcode scanners are the standard in point-of-sale environments. They work in distances from a few centimeters to about half a meter, depending on LED strength, optics (depth of field), barcode size, and ambient light. They are limited to 1D codes.
- Laser scanner: Due to their fast and reliable detection, even in bad lighting conditions and at considerable distances, laser scanners are well-suited for industrial and transport use cases. They, too, are limited to linear barcodes.
- Imager barcode scanner: Imager barcode scanners function more like cameras than the traditional scanner types described above. Thus, they are suitable for 2D barcode scanning and are used in healthcare, ticketing, and industrial production.
- Smartphones: The right software enables even inexpensive smartphones to quickly and reliably scan all common barcodes, no costly extra hardware needed. Enterprises can take advantage of this by creating mobile apps or web applications to enable digital workflows based on barcode scanning. A Barcode Scanner SDK simplifies the development of such apps significantly.
Although all types of barcode scanners will do the job, the dedicated devices we listed are single-purpose and often costly. Smartphones, on the other hand, offer a whole range of other functionalities. Barcode scanner software can be integrated into an inventory management application, allowing the same device to provide and access crucial information.
How to set up a barcode inventory system in 7 steps
1. Define your inventory structure
Categorize products logically and determine the organization of your inventory.
2. Choose a barcode system
Select a barcode symbology based on the required data density, industry standards, and your specific needs.
1D barcodes are fairly simple: A specific sequence of bars of varying widths corresponds to exactly one character. This also makes 1D barcodes easy to create. 1D barcodes are commonly used for storing information such as product identification.
Thanks to their structure, 2D codes have a higher data capacity than 1D codes. They can even store URLs and text files. Scanning from an angle, in poor lighting conditions, or with a low-resolution camera presents much less of a problem than with 1D barcodes.
3. Generate and print barcode labels
Use barcode generation tools or software to create barcodes for each item – ideally, unique ones. For internal uses, you can simply choose free online barcode generator software. For global operations, you will have to opt for GS1-standardized barcodes.
The printer choice depends on the barcode symbology used for the inventory management system. Wet-ink printing works for 1D barcodes, while the more intricate 2D barcodes require the precision of digital printers.
4. Choose a barcode scanner
Decide on a reliable hardware- or software-based barcode scanner that supports your chosen symbology. Mobile barcode scanners, like smartphones, are capable of scanning both 1D and 2D barcodes, making them a versatile choice for inventory management purposes.
5. Configure your inventory management software
Ensure seamless communication between the barcode scanning system and your inventory database. Offline scanning functionality ensures continuity even if network connectivity is not guaranteed: Data can still be captured and synced later.
6. Train your team
Educate your team on barcode scanner usage and how scanning will be integrated into daily operations. The required training time depends on the choice of barcode scanner. For instance, employees are usually used to handling smartphones, which makes introducing mobile barcode scanners more seamless.
7. Schedule regular maintenance and updates
Routine maintenance for hardware and software components keeps them at peak performance. It also pays to stay informed about barcode technology advancements. All this is crucial for preventing security breaches and bugs, ensuring safe, seamless operations.
The future of barcode inventory systems
Barcode inventory systems can do more than enable real-time inventory tracking and the automation based on it. Advanced technologies are opening up a whole range of new possibilities.
Let’s take a look at the most promising advances.
GS1 Digital Link
The GS1 Digital Link will connect physical products with digital information in a never-before-seen way. The key advantage: A single 2D barcode containing a Digital Link URL will lead to different sources of information depending on who scans it. This means that the same barcode that is scanned at the point-of-sale can be used for a range of inventory tasks – from updating inventory levels in real time over find-and-pick operations to perishable goods management.
If you are interested in how it works, we have already covered the technology behind the GS1 Digital Link in a previous article.
Drones in inventory management
Equipped with barcode scanner software, drones can be used in warehouses to perform full inventory counts, effortlessly reaching spaces that might be dangerous for employees. Like smartphones, they scan barcodes with their cameras, ensuring accurate and fast scans of both 1D and 2D codes.
Augmented Reality (AR) overlays
AR overlays are digital displays of information in the live camera view of a device, such as a smartphone.
In barcode inventory management, AR overlays can be used to display information about an item’s inventory level, its location in the warehouse, and guidance to said location.
Integrating barcode scanner software into your inventory management workflows
Integrating barcode scanning into your inventory management operations can significantly streamline and improve them. Apart from higher efficiency, you also benefit from greater accuracy.
By implementing barcode scanner software into your existing mobile or web app, you empower your team to scan barcodes effortlessly using a smartphone or tablet. This eliminates the need for manual data entry, reduces the risk of errors, and ensures fast inventory updates.
Introducing the Scanbot Barcode Scanner SDK
The Scanbot Barcode Scanner SDK offers several features that streamline inventory management operations, such as Batch Scanning and Multi Scanning modes. Scanning can be enhanced further with Augmented Reality (AR) Overlays to highlight barcodes or give additional information about scanned items.
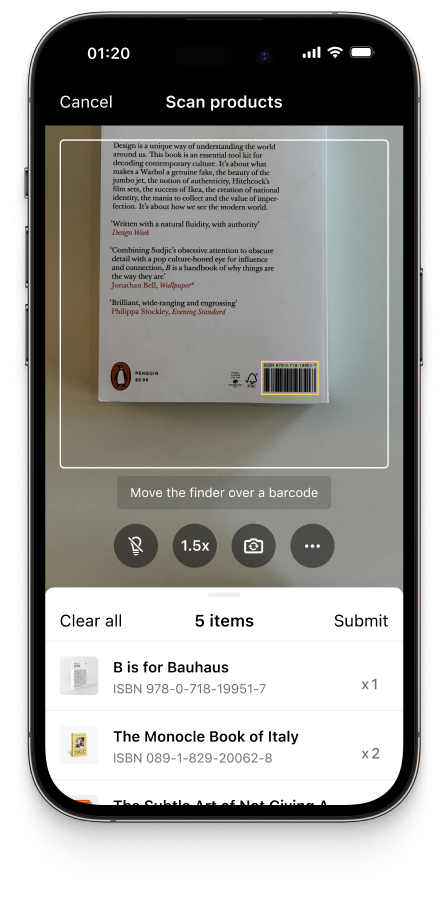

With its ability to reliably scan even tiny or damaged barcodes in low-light environments, the SDK is a perfect fit for fast-paced environments that require real-time data capture.
Our Barcode Scanner SDK can be integrated into the inventory management software in any mobile or web app for seamless communication with your inventory system.
Our flat-fee pricing allows your business to grow without additional costs. The SDK operates entirely offline, with no usage tracking. This also ensures complete data security, and uninterrupted performance regardless of network connectivity, including in offline environments.
Experience for yourself how the SDK performs in our free web or mobile demo app. If you are ready to try out the SDK for your project, get a free 7-day trial license, or contact sdk@scanbot.io.
How the Scanbot SDK transforms real-life inventory management operations: BarTrack
BarTrack, a Dutch provider of digital inventory management and restocking solutions, sought to enable automated order management processes and real-time inventory visibility in their B2B customers’ applications.
With the Scanbot Barcode Scanner SDK, they got a reliable barcode scanner – integrated in only a single day. Now, BarTrack’s mobile applications allow users to scan barcodes on an item to directly re-order it from their preferred supplier.
What is the function of a barcode system?
A barcode system functions as a tool for tracking and managing inventory efficiently by encoding product information into machine-readable barcodes.
What are the common challenges when implementing a barcode inventory system, and how can I overcome them?
Extreme temperatures, low lighting, and damaged or poorly printed barcode labels can affect barcode readability. The Scanbot Barcode Scanner SDK was made for real-world conditions and overcomes even these challenges.
What is the best barcode for inventory management?
Depending on the industry and operational requirements, you can choose between 1D and 2D barcodes. UPC and EAN are widely used in retail, while Code 39 and Code 128 are suitable for manufacturing and shipping. QR codes and Data Matrix are suitable for encoding large amounts of detailed information, such as expiration dates or batch numbers.
What is the difference between SKU and barcode?
Like barcodes, stock-keeping units (SKUs) are unique identifiers used in inventory management, often represented as barcodes or QR codes. However, while barcodes provide a standardized, universal method for product identification and tracking, SKUs are customized by each business and are mainly for internal use.