Barcodes have been around for more than 50 years now and have since become essential tools for data storage. They first gained traction with the use of UPC and EAN codes on products, making supermarket checkouts much faster. Since then, a lot of different barcode types have emerged, with around 30 of the most important variants being used all around the world.
The different barcode types can be categorized as one-dimensional (1D) and two-dimensional (2D). While one-dimensional barcodes consist only of lines and are usually scanned horizontally with laser scanners, two-dimensional codes make use of vertical space as well and can only be scanned with devices that contain a camera, such as imager scanners or smartphones. In this article, you will discover the most popular barcode types and their characteristics.
If you would like to generate your own barcodes, try our barcode generator!
One-dimensional (1D) barcodes / linear barcodes
One-dimensional barcodes can only hold a very limited amount of data encoded by lines of varying widths and the spaces between them (hence they are also called linear barcodes). Since 1D barcodes can be detected by optical laser scanners, which are less costly than imager scanners, they are widely used in different industries. Of course, if your device is capable of scanning two-dimensional codes like QR, it can scan 1D barcodes as well. Your smartphone camera might actually have this functionality built in already. For commercial use, a powerful barcode scanning software is the key to efficient workflows in many different areas, be it retail, logistics, insurance, or healthcare.
Code 39

- Type: Lines with two different widths
- Max. amount of characters: Variable
- Common usage: Industrial
- ISO/IEC certification: ISO/IEC 16388
Learn more about Code 39
One of the earliest examples of linear barcodes, Code 39 can only encode digits, upper-case alphabetical characters, and some special characters. It takes up quite a bit of space, which makes it unsuitable for smaller objects. This was rectified with the introduction of Code 128.
VIN Barcode
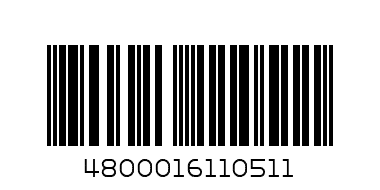
- Type: Lines with different widths
- Max. amount of characters: 17
- Common usage: Automotive
- ISO/IEC certification: ISO/IEC 16388 (Code 39)
VIN (Vehicle Identification Number) barcodes use the Code 39 symbology with a very distinct set of specifications. They are used exclusively to distinguish individual motor vehicles and consist of 17 alphanumeric characters, sometimes preceded by an “I”, which stands for “import”. VINs come with or without the corresponding barcodes, but scanning a VIN barcode instead of manually recording the long series of characters reduces error rates significantly.
Code 93

- Type: Lines with different widths
- Max. amount of characters: Variable
- Common usage: Industrial
Learn more about Code 93
As a more compact version of Code 39, Code 93 encodes the full ASCII character set while taking up less space. It is variable in length and requires two checksums.
Code 128
- Type: Lines with different widths
- Max. amount of characters: Variable
- Common usage: Commonly used in all industries
- ISO/IEC certification: ISO/IEC 15417
Learn more about Code 128
A big improvement over its predecessors, Code 128 can encode the entire ASCII character set and always includes a check digit. It comprises more data while taking up less space and is widely used in the transportation of goods.
GS1–128

Learn more about GS1-128
The GS1 barcode is a substandard of Code 128 and was heavily adopted by the industry, since it connects the data structure (GS1) with a data carrier (Code 128), encoding things like order numbers, weights, manufacturing dates, expiration dates, and storage location numbers.
EAN (European Article Number)

- Type: Lines with different widths
- Max. amount of characters: 8 or 12 digits
- Common usage: Retail
- ISO/IEC certification: ISO/IEC 15420
Learn more about EAN
A barcode familiar to European readers, EAN is widely used in the retail sector. It can encode up to 12 digits and is used for the International Standard Book Number (ISBN). The UPC (Universal Product Code) can be thought of as an equivalent primarily used North America. Both EAN and UPC are defined as GS1 standards.
UPC

- Type: Lines with different widths
- Max. amount of characters: 12
- Common usage: Retail, warehousing, distribution
- ISO/IEC certification: ISO/IEC 15420
UPC, short for Universal Product Code, encodes 12 numeric characters constituting a Global Trade Item Number (GTIN). Its European equivalent is the EAN code. The retail sector uses it in combination with databases to connect products with prices or quantities.
Codabar

- Type: Lines with different widths
- Max. amount of characters: 16
- Common usage: Libraries, laboratories, blood banks
Learn more about Codabar
The main advantage of the Codabar code is that it is very easy to print accurately, even with inexpensive printers. It encodes up to 16 characters (the numbers 0 to 9 and some special symbols) plus 4 start and stop characters (A, B, C, D). Codabar is self-checking, which means that a failed scan will not result in inaccurate information, but in error.
ITF

- Type: Lines with different widths
- Max. amount of characters: Variable
- Common usage: Industrial, distribution
Learn more about ITF
ITF, or Interleaved 2 of 5 (also Standard Distribution Code), encodes numbers in pairs and uses both the black lines and the white space in between for higher information density. Its length is variable, but the number of numeric characters must be even due to the pairing feature.
Industrial 2 of 5

- Type: Lines with different widths
- Max. amount of characters: Variable
- Common usage: Distribution, air travel
Industrial 2 of 5 is similar to the ITF barcode in that out of the five black bars used to encode a digit, two are wide. A difference of the Industrial 2 of 5 symbology is that the spaces in-between the bars have a fixed width.
Standard 2 of 5 (IATA)

- Type: Lines with different widths
- Max. amount of characters: Variable
- Common usage: Air travel
As a subtype of Industrial 2 of 5, the Standard 2 of 5 barcode is used by the International Air Transport Association to encode information for processing airline cargo and is therefore also called IATA 2 of 5. It encodes only an even number of digits and includes a check digit.
MSI Plessey

- Type: Lines with different widths
- Max. amount of characters: 255
- Common usage: Warehousing, groceries, libraries
Learn more about MSI Plessey
This simple symbology only encodes the numerals 0 to 9, with no fixed length. MSI Plessey is a variant of the Plessey code. Others include Anker Plessey and Telxon Plessey, but MSI Plessey is more widely used today, especially in the US.
4-State Customer Codes
Intelligent Mail barcode (IMb)

- Type: Lines with different heights
- Max. amount of characters: 31
- Common usage: Postal services
Learn more about IMb
Developed by the United States Postal Service as a successor to the POSTNET and PLANET barcodes, the Intelligent Mail barcode is used to sort and track letters, cards, and flats. It comprises 65 bars in one of four different states, which together encode up to 31 digits. In contrast to other 1D barcodes, it is not the width but the height of the bars that encodes information.
Royal Mail 4-State Customer Code (RM4SCC)
- Type: Lines with different heights
- Max. amount of characters: 36
- Common usage: Postal services
Learn more about RM4SCC
Created by the Royal Mail in the 1990s, the RM4SCC was the first 4-state customer code symbology to be introduced for streamlining the routing and tracking of mail. It inspired the barcode’s use by other postal services around the world.
Klant Index Barcode (KIX)
- Type: Lines with different heights
- Max. amount of characters: 12
- Common usage: Postal services
Learn more about KIX
A slightly altered version of the RM4SCC used by the Dutch PostNL. It lacks start and stop characters as well as the checksum.
Australia Post 4-State Customer Code

- Type: Lines with different heights
- Max. amount of characters: 14
- Common usage: Postal services
Learn more about AP4SCC
A variation of the RM4SCC used by the Australian postal service. It comes in three different formats (Standard Customer Barcode, Customer Barcode 2, and Customer Barcode 3) and features Reed-Solomon error correction.
Japan Post 4-State Customer Code
- Type: Lines with different heights
- Max. amount of characters: 24
- Common usage: Postal services
Learn more about JP4SCC
Also know as the Kasutama Barcode (with “Kasutama” being the Katakana version of the English word “customer”), this barcode was created for the Japanese postal system to encode addresses on mail for faster automatic processing.
Learn more about how your company can save time and money with a Barcode Scanner SDK
Download the bookletTwo-dimensional (2D) barcodes / matrix codes
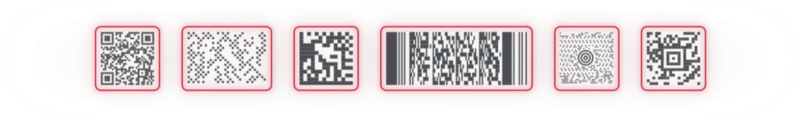
Two-dimensional barcodes consist of a grid of pixels that can have either an on (black) or off (white) state. These pixels usually have a fixed width and height. A visual anchor, called a marker or symbology, makes it easier for the reading devices to detect the code. An example of this are the corners of a QR code. Other types of markers include the central squares of the Aztec code or the black lines of the Data Matrix code.
Since 2D codes are scanned horizontally and vertically (hence two-dimensional), they can store more data while using less space and have a high fault tolerance. This means that they provide accurate data, even in less than ideal lighting conditions or if the code itself is damaged. Unfortunately, 2D codes cannot be read by the laser scanners used for 1D barcodes, so an imager scanner is required instead.
PDF417

- Type: Stacked lines with different widths
- Max. amount of characters: Variable
- Common usage: Transportation, ticketing, driver’s licenses, visas, ID cards
- ISO/IEC certification: ISO/IEC 15438
Learn more about PDF417
Unlike most 2D barcodes, PDF417 codes are actually multiple linear barcodes stacked on top of each other. They are used by the United States Postal Service for postage and by the Department of Homeland Security for driver’s licenses and identification cards.
PDF417 codes consist of a start pattern (left) and end pattern (right), with the information itself encoded in the middle section. The dimensions of the barcode are variable, making it very versatile.
Data Matrix

- Type: Pixel matrix with an L-shaped border as a marker
- Max. amount of characters: 3116
- Common usage: Aerospace, automotive, electronics
- ISO/IEC certification: ISO/IEC 16022
Learn more about Data Matrix
A two-dimensional code consisting of black (on) and white (off) cells that comprise the eponymous matrix. The dark, L-shaped border defines the code’s orientation, while the alternating patterns on the opposite sides enumerate the rows and columns. Depending on its size, it can store more than 3000 characters, which means that a relatively large amount of data can be stored on a very small area. Applied through permanent marking, the code can help to identify spare parts throughout their whole lifespan.
NTIN
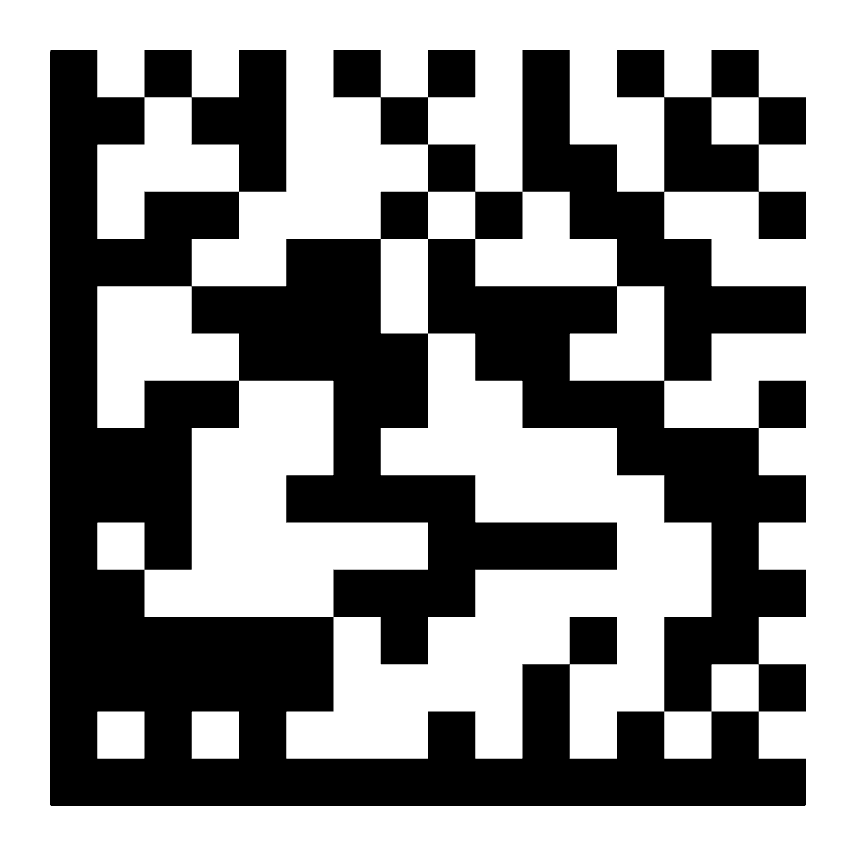

- Type: Pixel matrix with an L-shaped border as a marker
- Max. amount of characters: 3116
- Common usage: Pharmaceutical industry
- ISO/IEC certification: ISO/IEC 16022 (Data Matrix)
Learn more about NTIN codes
These Data Matrix codes are printed on medicine packages to prevent drug counterfeiting. They combine 8-digit national product registration numbers with a global, 4-digit GTIN prefix. Before selling any medicine, pharmacists scan the NTIN (National Trade Item Number) barcode to ensure that the product is authentic and has not been tampered with.
PPN

- Type: Pixel matrix with an L-shaped border as a marker
- Max. amount of characters: 3116
- Common usage: Pharmaceutical industry
- ISO/IEC certification: ISO/IEC 16022 (Data Matrix)
Learn more about PPN codes
The PPN (Pharmacy Product Number) was created to make medicine packages identifiable worldwide and to prevent drug counterfeiting. As with the NTIN (National Trade Item Number), it is encoded by a Data Matrix code and encompasses the Product Registration Agency Code, the national registration number, and two check digits.
Royal Mail Mailmark
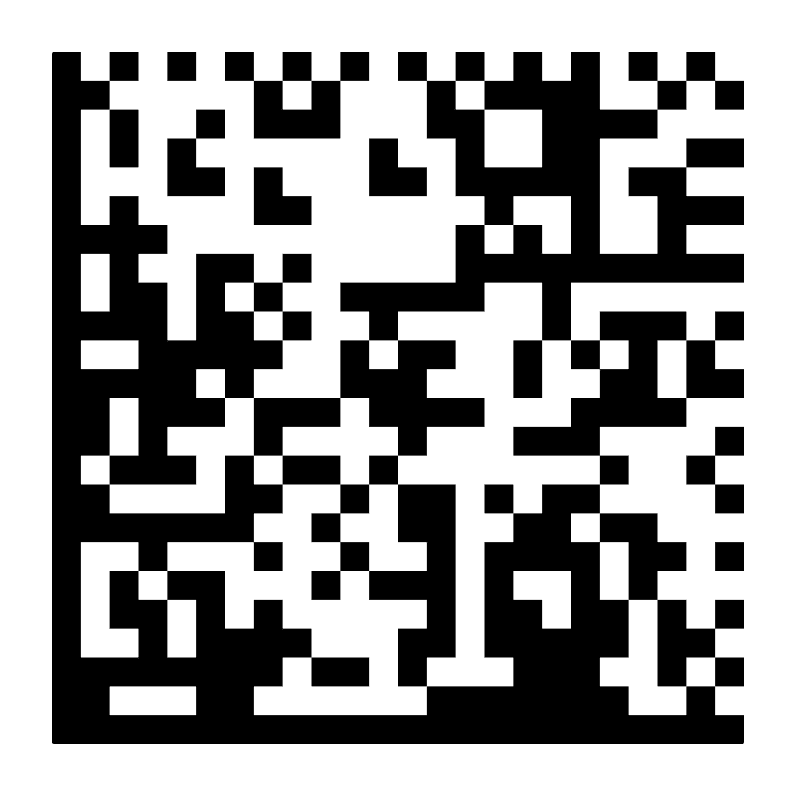

- Type: Pixel matrix with an L-shaped border as a marker
- Max. amount of characters: 3116
- Common usage: Postal system
- ISO/IEC certification: ISO/IEC 16022 (Data Matrix)
Learn more about Royal Mail Mailmark
A barcode exclusively used in the UK that functions as postage but also gives companies various insights into their mail data. They are available only via Royal Mail franking machines.
Aztec Code

- Type: Pixel matrix with a marker in the center
- Max. amount of characters: 3832
- Common usage: Transportation, healthcare
- ISO/IEC certification: ISO/IEC 24778
Learn more about Aztec Code
The Aztec Code derives its name from the square located in the middle, resembling an Aztec pyramid. It eliminates the need for a so-called “quiet zone” around the edges, saving space. Aztec code is read in a spiral pattern starting from the center, making use of the same error-checking procedure as QR codes. It is widely used in public transport, e.g., on the digital train tickets issued by the Deutsche Bahn.
QR Code

- Type: Pixel matrix with markers in the corners
- Max. amount of characters: 7089
- Common usage: Marketing, public transport, package delivery
- ISO/IEC certification: ISO/IEC 18004
This barcode has become increasingly widespread with the rising popularity of smartphones and is easily recognizable by its three squares communicating the position to the scanning device. With just one scan, users can quickly open a website or connect to a wireless network. Recently, QR codes have also been used to encode information on Covid-19 vaccination certificates. Thanks to Reed-Solomon error correction, QR codes scan correctly even if a significant part of the matrix is missing, making them a reliable choice for ticketing and similar use cases.
GiroCode
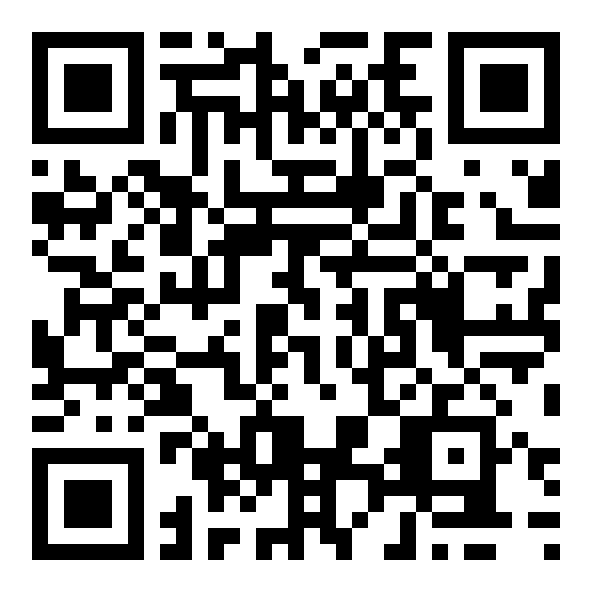

- Type: Pixel matrix with markers in the corner
- Max. amount of characters: 7089
- Common usage: Financial transactions
- ISO/IEC certification: ISO/IEC 18004 (QR Code)
Learn more about GiroCodes
Financial transactions within the EU can be rapidly processed via GiroCodes (also called EPC QR Codes). They are standardized by the European Payments Council and contain all data required for SEPA credit transfers. Scanning these barcodes eliminates the need to manually enter long IBANs, which can be error-prone.
Swiss QR Code
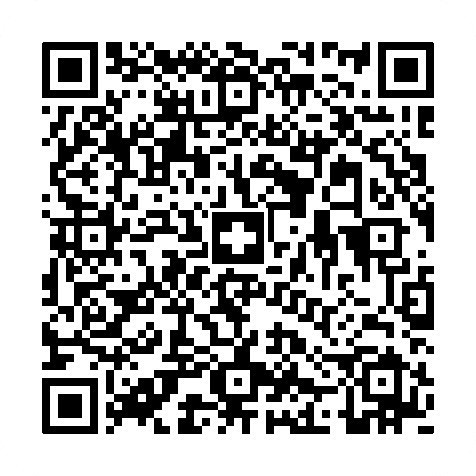

- Type: Pixel matrix with markers in the corner
- Max. amount of characters: 997
- Common usage: Financial transactions
- ISO/IEC certification: ISO/IEC 18004 (QR Code)
Learn more about Swiss QR Codes
As part of QR invoices in Switzerland, Swiss QR Codes allow for quick and easy payments using a machine-readable format. The contents of the code are as follows: Currency, amount, IBAN, account owner, payer details, reference, and a free text field for additional information.
FAQs
How many types of barcodes are there?
There are several types of barcodes, including UPC (Universal Product Code), EAN (European Article Number), Code 39, Code 128, QR Code, and Data Matrix. The total number of symbologies is unclear, as some are open formats that can be adapted to individual use cases.
What are most common barcode types?
The most common 1D barcodes are UPC and EAN, which are widely used in retail for product identification and inventory management. In terms of 2D barcodes, the QR Code and Data Matrix Code are among the most widely used.
What barcode types are 12-digit?
UPC-A, a variant of the UPC barcode, is a 12-digit barcode commonly used in North America.
What is the difference between EAN-8 and EAN-13?
The main difference between EAN-8 and EAN-13 barcodes is their length. EAN-8 consists of 8 digits, while EAN-13 has 13 digits. Both types are used for product identification but serve different purposes based on the required number of digits.

