Data Matrix Code Scanner
Add Data Matrix scanning to your mobile application or website
Trusted by
400+
global
industry leaders
Turn smartphones into fast & reliable Data Matrix scanners
The Scanbot Data Matrix Scanner delivers exceptional performance even under challenging conditions – such as code damage or when scanning the very small codes commonly found in industrial environments. With a scanning speed of under 0.04 seconds, your users get instant reads for seamless workflows.
Key benefits include:
- Offline scanning: The Scanbot SDK works 100% on-device, ensuring both uninterrupted performance and data security.
- Enterprise support: Questions or requests? Contact our technical support team. We’re happy to assist you.
- Flat pricing model: Cost stays the same no matter how much your user base or scanning volume grows.
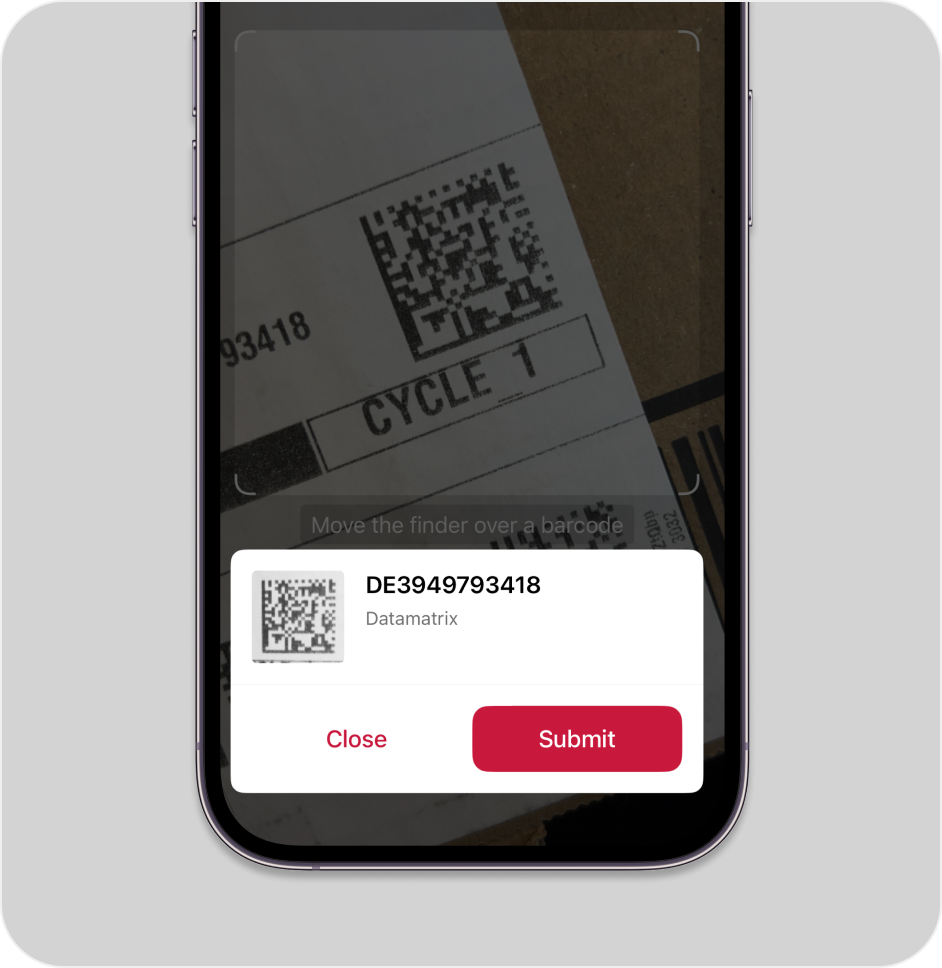

How this scanning tool works
Our free online Data Matrix code reader scans codes directly through your camera or on imported images. This barcode scanner works in any browser, no app download or signup needed. Enjoy real-time camera view scanning or decode barcodes on pictures in seconds – just point your camera at the Data Matrix code or import an image file to instantly access the encoded data.
This tool is powered by the Scanbot Barcode Scanner SDK!
(We don’t store any images or data you import. Everything stays on your device.)
Understanding Data Matrix codes
What is a Data Matrix code?
A Data Matrix code is a 2D barcode made up of black and white cells arranged in a square or rectangular pattern. The symbols can encode up to 3,116 numeric, 2,335 alphanumeric, or 1,556 binary characters, making them ideal for storing a lot of data in a small space. Standardized in ISO/IEC 16022, Data Matrix is widely used in industrial applications. One major use case is direct part marking (DPM) on components where durability and traceability are critical.
Industry applications
Because the symbols can be made microscopically small, they are ideal for products with limited space, such as electronic parts, medical devices, or surgical instruments. Data Matrix is often used together with GS1 standards to encode product identifiers along with key details like batch numbers, expiry dates, or serial numbers. This enables reliable tracking and tracing across global supply chains.
Error correction
All modern Data Matrix codes use the ECC 200 version, which applies Reed–Solomon error correction. This system can recover the full data even if up to 30% of the code is damaged or obscured.
How to scan Data Matrix barcodes
Traditional laser scanners are designed for 1D barcodes, so specialized 2D barcode scanners are required to read Data Matrix codes. While many smartphones will natively scan QR codes, they usually cannot read Data Matrix codes without additional software.
Barcode scanning software is the solution. Software Development Kits (SDKs) enable developers to quickly integrate reliable Data Matrix scanning into their web and mobile applications.
The Scanbot Barcode Scanner SDK supports a wide range of 1D, 2D, and postal barcodes, including Data Matrix and GS1 DataMatrix.
The SDK’s key capabilities include:
- Omnidirectional scanning: Scan from any angle.
- Multi-scanning: Capture multiple Data Matrix codes in one scan.
- Robust performance: Optimized for damaged, poorly printed, tiny, or low-contrast barcodes.
- Advanced parsing: Supports GS1, HIBC barcodes, and Data Matrix on German medication plans.
- DPM and reflective surfaces: Handles direct part marking and challenging materials.
The SDK is available for Android, iOS, web, Windows, Linux, React Native, Flutter, .NET MAUI, Capacitor, Cordova, Xamarin, and Compose Multiplatform.
How KROHNE Group switched from open source to Scanbot SDK
KROHNE Group, a global leader in process instrumentation, uses Data Matrix codes printed on product nameplates to give customers quick access to manuals, data sheets, and spare parts lists.
Previously, the team used the open-source ZXing.Net.Maui library in its PICK app. However, the software did not reliably detect the nameplate Data Matrix codes. Scanning was slow and often failed altogether, forcing users to manually type in long serial numbers.
To solve this issue, KROHNE switched to the Scanbot Barcode Scanner SDK. The team chose the SDK because it delivers fast, accurate decoding, even on small, low-contrast, or slightly damaged symbols. It is also fully offline, enabling uninterrupted workflows even in remote locations. Thanks to its cross-platform .NET MAUI support and comprehensive documentation, KROHNE easily integrated it into their app – within hours.
Ever since the Scanbot SDK was rolled out, customers have enjoyed seamless access to product information through quick, reliable Data Matrix scans. As Process Improvement Officer Benedikt Niermann puts it:
“Switching to Scanbot SDK significantly improved our ability to scan Data Matrix codes. We evaluated several solutions, and the Scanbot SDK provided the perfect blend of performance and value.”
How to build a Data Matrix Code Scanner in JavaScript
Creating a browser-based Data Matrix Code Scanner is straightforward. In the following example, we’ll implement it in a single stand-alone HTML file.
To achieve this, we’ll use plain JavaScript and the Scanbot Web Barcode Scanner SDK.
First, create an index.html with some boilerplate code.
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8" />
<meta
name="viewport"
content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0, maximum-scale=1.0, user-scalable=0"
/>
<title>Data Matrix Code Scanner</title>
</head>
<body>
</body>
</html>
To set up our scanner, we’ll have to do the following:
- Create a button that calls up the scanning interface when clicked.
- Include a
<p>element on the page for displaying the scanning result. - Import the Scanbot Web SDK using a CDN.
- Process the scan result before displaying it on the page.
⚠️ In this example, we’re importing the SDK via jsDelivr. However, you should only do this for quick prototyping. In your production environment, please download the Web SDK directly (or install it via npm) and include its files in your project.
The result should look something like this:
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8" />
<meta
name="viewport"
content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0, maximum-scale=1.0, user-scalable=0"
/>
<title>Data Matrix Code Scanner</title>
</head>
<body style="margin: 0">
<button id="start-scanning">Start scanning</button>
<p id="result"></p>
<script type="module">
import "https://cdn.jsdelivr.net/npm/scanbot-web-sdk@7.0.0/bundle/ScanbotSDK.ui2.min.js";
const sdk = await ScanbotSDK.initialize({
enginePath:
"https://cdn.jsdelivr.net/npm/scanbot-web-sdk@7.0.0/bundle/bin/barcode-scanner/",
});
document
.getElementById("start-scanning")
.addEventListener("click", async () => {
const config =
new ScanbotSDK.UI.Config.BarcodeScannerScreenConfiguration();
const scanResult = await ScanbotSDK.UI.createBarcodeScanner(config);
if (scanResult?.items?.length > 0) {
document.getElementById("result").innerText = scanResult.items[0].barcode.text;
} else {
document.getElementById("result").innerText = "Scanning aborted by the user";
}
});
</script>
</body>
</html>
💡 We use Web Barcode Scanner SDK version 7.0.0 in this tutorial. You can find the latest version in the changelog.
This already provides us with a fully functional barcode scanner that will read any barcode type. Restricting it to scanning only Data Matrix Codes prevents unintended scans and improves the scanner’s performance, as it doesn’t need to check each supported symbology.
So let’s restrict scanning to the Data Matrix symbology by modifying the BarcodeScannerScreenConfiguration we assigned to the config constant in the previous step.
config.scannerConfiguration.barcodeFormats = ["DATA_MATRIX"];
Your final index.html will look like this:
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8" />
<meta
name="viewport"
content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0, maximum-scale=1.0, user-scalable=0"
/>
<title>Data Matrix Code Scanner</title>
</head>
<body style="margin: 0">
<button id="start-scanning">Start scanning</button>
<p id="result"></p>
<script type="module">
import "https://cdn.jsdelivr.net/npm/scanbot-web-sdk@7.0.0/bundle/ScanbotSDK.ui2.min.js";
const sdk = await ScanbotSDK.initialize({
enginePath:
"https://cdn.jsdelivr.net/npm/scanbot-web-sdk@7.0.0/bundle/bin/barcode-scanner/",
});
document
.getElementById("start-scanning")
.addEventListener("click", async () => {
const config =
new ScanbotSDK.UI.Config.BarcodeScannerScreenConfiguration();
config.scannerConfiguration.barcodeFormats = ["DATA_MATRIX"];
const scanResult = await ScanbotSDK.UI.createBarcodeScanner(config);
if (scanResult?.items?.length > 0) {
document.getElementById("result").innerText = scanResult.items[0].barcode.text;
} else {
document.getElementById("result").innerText = "Scanning aborted by the user";
}
});
</script>
</body>
</html>
Now run the app and scan a Data Matrix Code to test your scanner!

💡 You can run the Scanbot SDK for 60 seconds per session without a license. For more in-depth testing, we recommend you generate a free trial license.
For more information on how to customize your scanner, head over to the documentation.
Related Barcode Types:
- QR Code Scanner
- PDF417 Scanner
- Aztec Code Scanner
- Code 128 Scanner
- Code 39 Scanner
- EAN Scanner
- UPC Scanner
- Micro QR Code Scanner
- GS1 DataBar Scanner
- GS1 DataMatrix Scanner
- GS1-128 Scanner
- MaxiCode Scanner
- ITF Scanner
- Codabar Scanner
- Intelligent Mail Barcode Scanner
- rMQR Code Scanner
- Royal Mail Scanner
- Micro PDF417 Scanner
Frequently Asked Questions
How do you create a Data Matrix barcode?
To create a Data Matrix barcode, start with the essentials. Decide exactly what you will encode, then let an encoder select the smallest symbol that fits—sizes run from 10×10 up to 144×144. Choose a practical module size for print (about 0.25–0.40 mm per square) and keep a quiet zone around the symbol that is at least one module wide.
Generation is straightforward. Enter your data into a Data Matrix generator and ensure it uses ECC 200. Export the result, print it dark on light without distortion, and verify it with a phone or handheld scanner.
What are variations in Data Matrix?
Data Matrix codes come in different versions. The current one is ECC 200, which provides robust error correction and supports two main shapes:
Square Data Matrix: Stores up to 3,116 numeric, 2,335 alphanumeric, or 1,556 binary characters. Sizes range from 10×10 to 144×144 modules. Larger symbols are automatically divided into smaller 24×24 blocks to avoid distortion.
Rectangular Data Matrix (DMRE): Stores up to 98 numeric, 72 alphanumeric, or 47 binary characters, with sizes from 8×18 to 16×48 modules. Larger symbols are divided into blocks as well.
Earlier versions, known as ECC 000–140, are largely obsolete.
How were Data Matrix codes invented?
The Data Matrix code was created in 1987 by International Data Matrix, Inc.
It quickly attracted attention in industries such as aerospace and electronics. Data Matrix codes can store up to 50 characters in an area as small as 2–3 mm² and remain readable even with low contrast, making them ideal for small parts and direct marking.
Its adoption accelerated after 2000, when the code was standardized as ISO/IEC 16022. Around the same time, the US Department of Defense (DoD) mandated its use for part identification through the IUID program, making Data Matrix an essential technology for defense supply chains.
In 2006, the ECC 200 version introduced Reed–Solomon error correction, which ensured codes could still be read even when partially damaged. The following years saw increasing use in healthcare and logistics, where tracking and traceability became regulatory priorities. This included the introduction of Unique Device Identification (UDI) for medical devices.
A major milestone came in 2008, when GS1 formally adopted Data Matrix for global supply chain applications. This allowed the encoding of product identifiers, expiration dates, and batch or serial numbers in a standardized way, and paved the way for regulatory mandates. The US DSCSA(2013) and the EU Falsified Medicines Directive (2019) both require 2D barcodes – GS1 DataMatrix – on prescription medicines.
Today, the code is a cornerstone of healthcare, aerospace, and industrial traceability. With the GS1 Sunrise initiative for 2D barcodes, it is now moving toward wider adoption at retail checkout systems worldwide by 2027.
How are Data Matrix codes structured?
The key components include:
- Finder pattern: This consists of two solid adjacent borders forming an “L” shape along the left and bottom edges, helping scanners locate and determine the orientation of the symbol.
- Timing pattern: The timing pattern, located along the top and right edges, allows scanners to determine the exact number of rows and columns.
- Data regions: These contain arrays of modules. Each black or white module represents a binary digit (1 or 0) to encode text, numbers, or other data.
- Quiet zone: Also known as the margin, the quiet zone surrounds the entire symbol, creating a buffer that helps scanners distinguish the code from background elements.
- Alignment pattern: For larger Data Matrix codes, the alignment pattern divides the symbol into multiple, individual blocks. This minimizes distortion risk and ensures accurate scanning.
What are the advantages of Data Matrix codes?
- Compact size: They can store large amounts of data in minimal space (up to 3,116 numeric characters) – as small as 2–3 mm² for 50 characters.
- Error correction: Reed-Solomon error correction maintains readability even when the code is partially damaged or has low contrast (down to 20% contrast). They have an error rate of less than 1 in 10 million characters scanned.
- Scalability: Data Matrix codes are available in multiple sizes from 10×10 to 144×144 modules for square formats, with automatic block division for larger sizes to prevent distortion. Rectangular formats also exist for specific applications.
- Omnidirectional: Finder patterns ensure seamless decoding from any angle.
What are the disadvantages of Data Matrix codes?
While they are slightly less compact, QR codes are often more practical for encoding long strings like URLs.
Traditional scanners typically cannot read Data Matrix codes, so often specialized 2D barcode scanners are required. They are also not natively supported by most smartphones’ default camera apps.
Data Matrix codes excel in industrial use cases, but QR codes are more suitable for consumer-facing applications.
What is Reed-Solomon error correction?
Reed–Solomon error correction is a mathematical algorithm used to ensure reliable data recovery. It works by adding extra “check” information to the data so that, if part of it is lost or damaged, the original message can still be reconstructed.
This technology is widely used in barcodes like Data Matrix (version ECC 200). In fact, Reed–Solomon can reconstruct complete data strings even when up to 30% of the symbol is damaged, as long as the scanner can still find the matrix position.
Unlike earlier versions or other 2D codes, ECC 200’s error correction level is fixed at a high level. It cannot be manually adjusted, ensuring consistent reliability across all implementations. This standardization helps maintain data integrity across different scanning environments and applications.
What is the difference between QR and Data Matrix?
They are two different 2D barcode types. Though QR codes are more popular in consumer applications, Data Matrix dominates in industrial applications requiring high data density and small sizes.
What is direct part marking?
Common direct part marking methods are lasering, dot peen marking, or etching. All these change the actual surface, making them more durable than print or labels. Data Matrix barcodes are preferred as they remain readable even when damaged, and so are used for permanent product identification in industries like manufacturing, automotive, and aerospace.



