Aztec Code Reader
Add an Aztec code reader to your mobile application or website
Trusted by
400+
global
industry leaders
Turn smartphones into fast & reliable Aztec code scanners
The Scanbot Aztec Code Reader delivers exceptional performance even under challenging conditions – such as code damage, low contrast, or small symbol sizes. With a scanning speed of under 0.04 seconds, your users can read barcodes instantly for seamless workflows.
Key benefits include:
- Offline scanning: The Scanbot SDK works 100% on-device, ensuring both uninterrupted performance and data security.
- Enterprise support: Questions or requests? Contact our technical support team. We’re happy to assist you.
- Flat pricing model: Cost stays the same no matter how much your user base or scanning volume grows.

How this scanning tool works
Our free online Aztec code reader scans codes directly through your camera or on imported images. This barcode scanner works in any browser, no app download or signup needed. Enjoy real-time camera view scanning or decode barcodes on pictures in seconds – just point your mobile device at the Aztec code or import an image file to instantly access the encoded data.
This tool is powered by the Scanbot Barcode Scanner SDK!
(We don’t store any images or data you import. Everything stays on your device.)
Understanding Aztec codes
What is an Aztec code?
The Aztec code is a two-dimensional (2D) barcode named for its unique central pattern, which resembles an Aztec pyramid viewed from above. They were invented by Andrew Longacre Jr. and Robert Hussey in 1995, and are standardized in ISO/IEC 24778.
Aztec barcodes support any ASCII character and can have up to 32 data layers. They come in three different types:
| Type | Matrix size | Text capacity | Numeric capacity | Binary capacity |
| Aztec Rune | 11×11 | N/A | 3 digits (0-225) | 1 byte |
| Compact Aztec | 15×15 to 27×27 | 89 characters | 110 digits | 53 bytes |
| Full Aztec | 19×19 to 151×151 | 3,067 characters | 3,832 digits | 1,914 bytes |
Aztec codes do not require a quiet zone, making them more space-efficient than some other two-dimensional barcodes. Additionally, they can be read in any direction and even when mirrored, because of the orientation marks on the central target design.
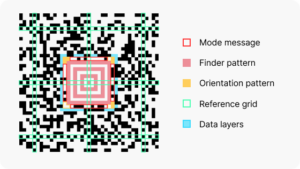
Structure and components
A full Aztec code consists of the following components:
- Finder pattern: A central bulls-eye pattern (9×9 or 13×13 modules) that helps locate the symbol
- Orientation pattern: Corner markers that determine the code’s orientation (even if rotated or mirrored).
- Mode message: This encodes information about the number of layers and data codewords. It is located in the same layer as the orientation pattern.
- Reference grid: This grid helps barcode readers maintain alignment over large symbols. It consists of alternating black and white pixels in every 16th row and column.
- Data layers: Up to 32 layers storing encoded information and check characters. They are read clockwise, starting next to the first orientation pattern.
Special symbols
Aztec barcodes support special symbols like FNC1 and ECI to enhance their functionality:
- FNC1 indicates an application identifier, like that used by GS1 barcode standards and commonly seen in product barcodes. It is encoded as “\f” in the data.
- ECI (Extended Channel Interpretation) specifies the character set to be used, such as UTF-8 or ISO 8859-1, and is encoded as “\e[number]”.
Error detection and correction
Aztec codes use Reed-Solomon error correction to generate check codewords. The number of check codewords depends on the symbol size and capacity as well as on the desired error correction level. This is highly customizable, ranging from 5% to 95%. Aztec barcode generators usually default to 23% error correction plus three additional check codewords.
The size of the Reed-Solomon codewords themselves varies from 6 to 12 bits, depending on the number of layers in the Aztec barcode.
Applications of Aztec codes
Transportation
Aztec barcodes are widely used in electronic ticketing in air and rail travel because of their accuracy and compactness. They are the International Union of Railways (UIC) standard for railway ticketing, and are used by companies such as Lufthansa and Deutsche Bahn.
Healthcare
In the healthcare sector, Aztec codes ensure accurate identification on patient wristbands and medical devices.
Supply chain and logistics
Switching from linear barcodes to Aztec codes streamlines inventory tracking and supply chain operations. Their scalability and reliability make them attractive to government agencies and private companies alike.
Digital identity
Aztec barcodes are increasingly used for secure digital identity verification due to their high capacity, advanced error correction, and small footprint on printed materials.
Advantages of Aztec codes
- Compact size: Store large amounts of information in little space. No quiet zone is required.
- High fault tolerance: Built-in error correction ensures readability even if the code is damaged or distorted.
- High density: Aztec code barcodes are approximately 30 times smaller than Code 39 symbols encoding the same information.
- Versatility: Encodes numeric, alphanumeric, and binary data, making it adaptable to diverse use cases.
- Ease of scanning: Scannable in any orientation – even mirrored – on various surfaces and materials.
Why choose the Scanbot SDK for Aztec code scanning?
The Scanbot Barcode Reader SDK is designed to handle the unique challenges of scanning Aztec barcodes in real-world conditions.
What sets us apart:
- Exceptional performance: Reliably decodes even damaged or dense Aztec codes and other matrix barcodes.
- High-speed scanning: Reads Aztec code barcodes in as little as 0.04 seconds.
- Cross-platform compatibility: Easily integrate with Android, iOS, cross-platform, web, Windows, and Linux platforms.
- Customizable UI: Customize the ready-to-use components to match your app or website design.
- Privacy-first: Operates offline for complete data security.
Whether your use case involves Aztec barcodes, QR codes, or any other barcode, the Scanbot SDK delivers the accuracy, speed, and reliability you need to succeed.
Related Barcode Types:
- Data Matrix Scanner
- QR Code Scanner
- PDF417 Scanner
- Code 128 Scanner
- Code 39 Scanner
- EAN Scanner
- UPC Scanner
- Micro QR Code Scanner
- GS1 DataBar Scanner
- GS1 DataMatrix Scanner
- GS1-128 Scanner
- MaxiCode Scanner
- ITF Scanner
- Codabar Scanner
- Intelligent Mail Barcode Scanner
- rMQR Code Scanner
- Royal Mail Scanner
- Micro PDF417 Scanner
Frequently Asked Questions
What is the Aztec code encoding?
Aztec code encoding converts data into a compact two-dimensional barcode using a series of square rings around a central bull's-eye pattern. It employs bit encoding, Reed-Solomon error correction, and a spiral arrangement of data.
What is the difference between a QR code and an Aztec code?
Aztec code barcodes feature a distinctive pattern, allowing them to occupy less space than QR codes. They don’t require quiet zones, which further contributes to their smaller size. While QR codes can store significantly more data—up to 7,089 numeric or 4,296 alphanumeric characters—Aztec codes remain efficient for applications where size is a priority.



