Thanks to the Scanbot Web Barcode Scanner SDK‘s Ready-to-Use UI Components, you can add barcode scanning functionalities to your website or web app in a matter of minutes. This tutorial will demonstrate how to integrate the SDK using Vue.js and Vite.
Requirements
- Node.js (version 18 or higher)
Project setup
We’ll be using Vite to set up our project. Vite is a modern build tool optimized for speed and performance.
Open a terminal and create a new Vite project with the following command:
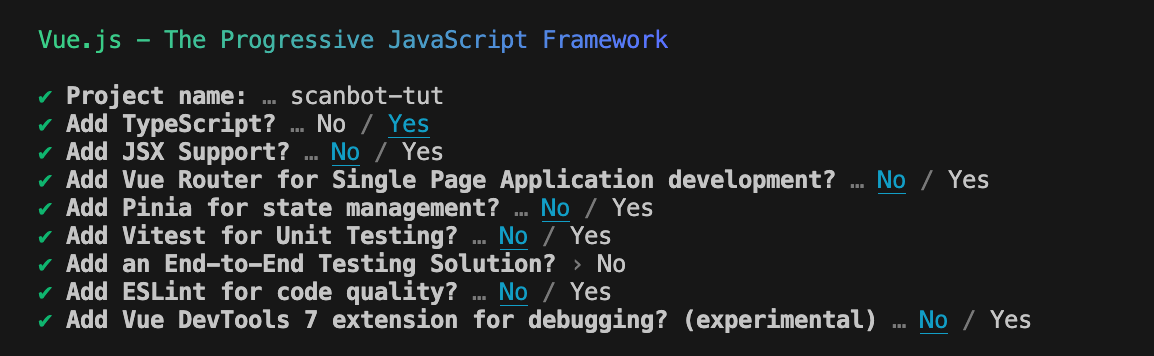
npm create vue@latestYou will be asked to name your project. For this tutorial, let’s go with “scanbot-tut”.
You will then be presented with prompts for several optional features. For this tutorial, we’ll use Typescript, but won’t need any of the other features, so feel free to answer No to them.
Now run:
cd scanbot-tut
npm install
npm run devOpen the App.vue file (located in the src directory) and replace the file’s contents with the following:
<script setup lang="ts">
</script>
<template>
<div>
</div>
</template>Initializing the SDK
Open another terminal, navigate to your project folder, and install the scanbot-web-sdk package with the following command:
npm i scanbot-web-sdkThe SDK contains WebAssembly binaries that should be hosted on your server. We ship these binaries with the npm package. Since Node.js doesn’t copy the binaries to the target automatically, you need to manually copy them to the desired destination (we recommend the public asset directory).
You can quickly copy them from node_modules to a folder called wasm in the public asset directory using the following command:
mkdir -p public/wasm && cp -r node_modules/scanbot-web-sdk/bundle/bin/barcode-scanner/* public/wasm💡 To ensure these files are always copied to the same directory for all users and updated when the SDK itself is updated, you can add the command as a post-installation script to your package.json:
"postinstall": "mkdir -p public/wasm && cp -r node_modules/scanbot-web-sdk/bundle/bin/barcode-scanner/* public/wasm"Back in in App.vue, add the code to import ScanbotSDK at the top of your script section:
<script setup lang="ts">
import ScanbotSDK from "scanbot-web-sdk/ui";
</script>We need to initialize ScanbotSDK within App.vue. You have the option of leaving the licenseKey empty to use a trial mode that works for 60 seconds per session or getting a free 7-day trial by submitting the trial license form on our website.
Your App.vue should now look like this:
<script setup lang="ts">
import { onBeforeMount } from "vue";
import ScanbotSDK from "scanbot-web-sdk/ui";
// Initialize the Scanbot SDK before the component mounts
onBeforeMount(async () => {
await ScanbotSDK.initialize({
licenseKey: "",
enginePath: "/wasm/"
});
});
</script>
<template>
<div>
</div>
</template>Creating our barcode scanner
First, we’ll need to create the configuration that we’ll use for the barcode scanner in App.vue.
To create the configuration, we can call a method that returns an instance of the configuration object, which can then modify as needed:
const config = new ScanbotSDK.UI.Config.BarcodeScannerScreenConfiguration();This config object will be what we use to make changes to the RTU UI. However, for now, let’s just use it to create our barcode scanner:
await ScanbotSDK.UI.createBarcodeScanner(config);Now, let’s assign the scanner to a variable and wrap it within an asynchronous function so we can easily assign it to a button within our App. This allows us to easily trigger the scanner with a button press in our application.
Let’s name the variable “result”, since it will store the outcome returned by createBarcodeScanner.
const startScanner = async () => {
const config = new ScanbotSDK.UI.Config.BarcodeScannerScreenConfiguration();
const result = await ScanbotSDK.UI.createBarcodeScanner(config);
return result;
};To trigger the scanner with a button press, we add a button to the template section and assign the startScanner function to its @click event:
<template>
<div>
<button @click="startScanner">Start</button>
</div>
</template>Next, let’s create a scanResult state.
We can then set the value of scanResult within our startScanner function when the scanning results are returned. Finally we can display those results below our button.
Our App.vue should now look like this:
<script setup lang="ts">
import { ref, onBeforeMount, type Ref } from "vue";
import ScanbotSDK from "scanbot-web-sdk/ui";
// Reactive variable to hold the scan result
const scanResult: Ref<string | null> = ref(null);
// Initialize the Scanbot SDK before the component mounts
onBeforeMount(async () => {
await ScanbotSDK.initialize({
licenseKey: "",
enginePath: "/wasm/"
});
});
const startScanner = async () => {
const config = new ScanbotSDK.UI.Config.BarcodeScannerScreenConfiguration();
const result = await ScanbotSDK.UI.createBarcodeScanner(config);
if (result && result.items.length > 0) {
scanResult.value = result.items[0].barcode.text;
}
return result;
};
</script>
<template>
<div>
<button @click="startScanner">Start</button>
<div v-if="scanResult">{{ scanResult }}</div>
</div>
</template>With this setup, we now have a fully functional barcode scanner!
If you haven’t already, go to the local server running your app and click the “Start Scanner” button to open the scanner and scan a barcode. After scanning a barcode, the scanner will automatically close and the result variable in the startScanner function will now contain the scan result, which will be displayed under the button.

Customizing our barcode scanner
The Scanbot SDK’s Ready-To-Use UI allows the user to customize several visual aspects of the RTU UI components, including its color palette, the user guidance, the top bar, and the action bar.
All the customization is done the same way: by changing values within the config object, within our startScanner function, before passing it to ScanbotSDK.UI.createBarcodeScanner(config).
Color palette
Let’s start by changing the primary and secondary colors of the scanner to give it a blue theme.
config.palette.sbColorPrimary = "#1E90FF";
config.palette.sbColorSecondary = "#87CEEB";User guidance
Next, we’ll change the text of the user guidance:
config.userGuidance.title.text = "Place the finder over the barcode";Top bar
Let’s also change the top bar’s visual mode. We have the options of 'SOLID', 'GRADIENT', or 'HIDDEN'. We’ll use 'GRADIENT' for our example.
config.topBar.mode = "GRADIENT";Action bar
Lastly, we have the option of changing the three action bar buttons that appear at the bottom of the screen: the Flash, Zoom and Flip Camera buttons. Let’s change the background color of our zoom button to match our blue theme.
config.actionBar.zoomButton.backgroundColor = "#1E90FF";After adding these customization options, our startScanner function should now look like this:
const startScanner = async () => {
const config = new ScanbotSDK.UI.Config.BarcodeScannerScreenConfiguration();
config.palette.sbColorPrimary = "#1E90FF";
config.palette.sbColorSecondary = "#87CEEB";
config.userGuidance.title.text = "Place the finder over the barcode";
config.topBar.mode = "GRADIENT";
config.actionBar.zoomButton.backgroundColor = "#1E90FF";
const result = await ScanbotSDK.UI.createBarcodeScanner(config);
if (result && result.items.length > 0) {
setScanResult(result.items[0].barcode.text);
}
return result;
};This only demonstrates a fraction of the available customization options for the RTU components. Please refer to our RTU UI documentation for more details and to the API documentation for a list of all available options.
Implementing more scanning modes
The Scanbot Web Barcode Scanner SDK’s RTU UI also lets us modify the behavior of the scanner itself. So, rather than immediately closing the scanner after scanning a barcode, we can visualize the results in a variety of ways.
Let’s try out multi-barcode scanning combined with an AR overlay.
Multi-barcode scanning
Let’s create our useCase object to pass to our config.
const useCase = new ScanbotSDK.UI.Config.MultipleScanningMode();
config.useCase = useCase;Now our scanner will have a collapsed list containing all scanned barcodes.
AR overlay
To enable the AR overlay, all we need to do is set the visibility to true within our use case configuration.
Let’s also disable the automatic selection, so we can manually select individual barcodes and add them to our list.
useCase.arOverlay.visible = true;
useCase.arOverlay.automaticSelectionEnabled = false;Running the app on your phone
To test your Vite project on your phone, you have a few options.
The simplest way is to run npm run build, zip the build folder within your project’s directory and upload it to static.app. After creating an account, you’ll be able to test your project with the URL provided on your mobile device.
Whilst using static.app is the simplest option, it does not allow you to access your development server and see changes as we make them.
One option for doing this is to use a tunnel service like ngrok, which allows you to access your development server securely over the internet.
Another option is to make your project accessible over the local network using https certificates.
Using a tunnel
The most flexible option for live development is to use ngrok.
Ngrok allows you to expose your local development server to the internet securely by enabling HTTPS access. Their Quick Start guide will help you get up and running quickly.
Over the local network
You can also choose to make your Vite project accessible over your local network. First, add the --host flag to the dev script in your package.json file. This will expose your development server to other devices on the same network.
"scripts": {
"dev": "vite --host",Start your development server by running npm run dev. You can then open a browser on your phone and enter your computer’s local IP address followed by the port number (which is usually 5173 for Vite projects, e.g. 192.168.1.100:5173).
However, when testing the barcode scanner on your phone via the network address, you may encounter an issue preventing the camera from opening. The reason is that most browsers require an HTTPS connection to allow camera access. To solve this, you can use the vite-plugin-mkcert, which enables you to use HTTPS during development by generating locally trusted certificates. This way, you can run your development server with HTTPS and ensure that your phone can access the camera without any issues.

Conclusion
🎉 Congratulations! You can now scan barcodes from your browser and adapt the scanner’s interface to suit your preferences.
These are just some of the customizations the Scanbot Web Barcode Scanner SDK has to offer. Check out the RTU UI Documentation for further details and the API Documentation for all available options.
Integration guides are also available for the following Web frameworks:
Should you have questions about this tutorial or run into any issues, we’re happy to help! Just shoot us an email via tutorial-support@scanbot.io.







