In this tutorial, you’ll learn how to use Flutter and Dart to build an app for scanning documents and exporting them as PDFs.
For the document scanner functionalities, we’ll use the flutter_doc_scanner package, a wrapper around Google’s ML Kit and Apple’s VisionKit that streamlines their integration into Flutter projects.
To achieve this, we’ll follow these steps:
- Preparing the project
- Setting the camera permissions
- Implementing the document scanning feature
- Implementing the PDF export feature
Prerequisites
- Flutter SDK: Ensure you have the latest version installed.
- Development tools:
- For Android: Android Studio with the Android SDK.
- For iOS: macOS with the latest Xcode and CocoaPods installed.
- Optional: Visual Studio Code with the Flutter and Dart extensions.
Step 1: Prepare the project
Open your terminal and execute:
flutter create flutter_document_scanner_app
cd flutter_document_scanner_appOpen pubspec.yaml and add the flutter_doc_scanner dependency.
dependencies:
flutter:
sdk: flutter
flutter_doc_scanner: ^0.0.16Then fetch the package.
flutter pub getStep 2: Set the camera permissions
We need to access the device camera to scan documents.
For Androidm, open android/app/src/main/AndroidManifest.xml and add the necessary permissions:
<uses-permission android:name="android.permission.CAMERA" />
<uses-feature android:name="android.hardware.camera" />For iOS, open ios/Runner/Info.plist and add:
<key>NSCameraUsageDescription</key>
<string>Grant camera access to scan documents.</string>Step 3: Implement the document scanning feature
Now we can integrate the document scanner package into our app.
Open lib/main.dart and replace the code with the following:
import 'dart:io';
import 'package:flutter/material.dart';
import 'package:flutter/services.dart';
import 'package:flutter_doc_scanner/flutter_doc_scanner.dart';
void main() {
runApp(MaterialApp(home: MyApp()));
}
class MyApp extends StatefulWidget {
MyApp({Key? key}) : super(key: key);
@override
State<MyApp> createState() => _MyAppState();
}
class _MyAppState extends State<MyApp> {
dynamic _scannedDocuments;
Future<void> scanDocument() async {
dynamic scannedDocuments;
try {
scannedDocuments =
await FlutterDocScanner().getScannedDocumentAsPdf(page: 4) ??
'Unknown platform documents';
} on PlatformException {
scannedDocuments = 'Failed to get scanned documents.';
}
if (!mounted) return;
setState(() {
_scannedDocuments = scannedDocuments;
});
}
@override
Widget build(BuildContext context) {
return MaterialApp(
title: 'Flutter Document Scanner',
home: Scaffold(
appBar: AppBar(title: const Text('Flutter Document Scanner')),
body: Center(
child: SingleChildScrollView(
child: Column(
mainAxisAlignment: MainAxisAlignment.center,
children: [
_scannedDocuments != null
? Text(_scannedDocuments.toString())
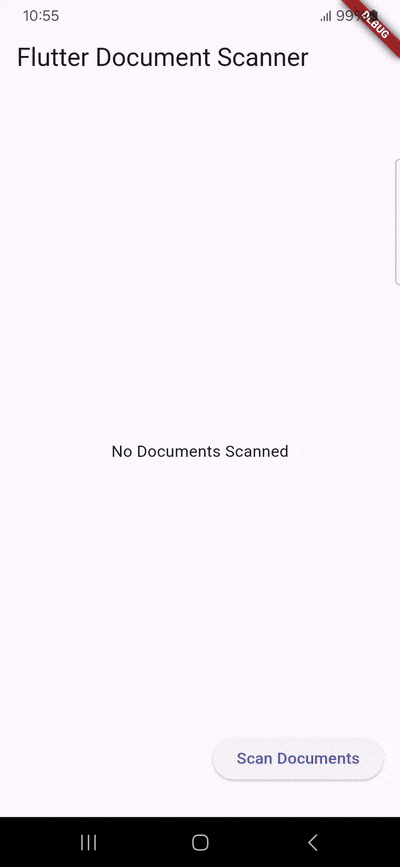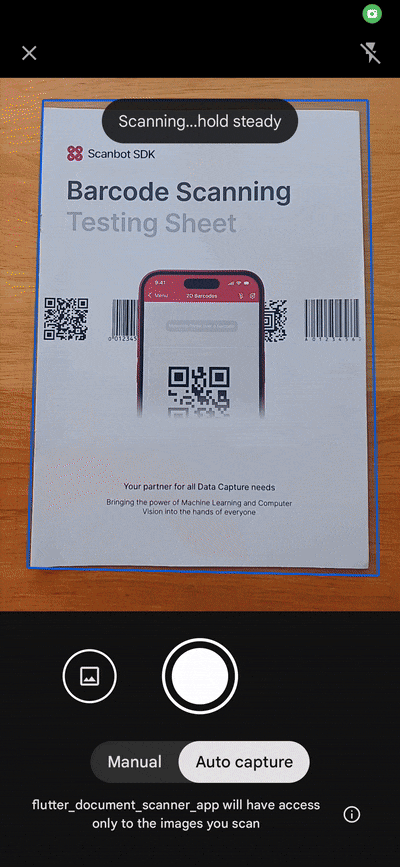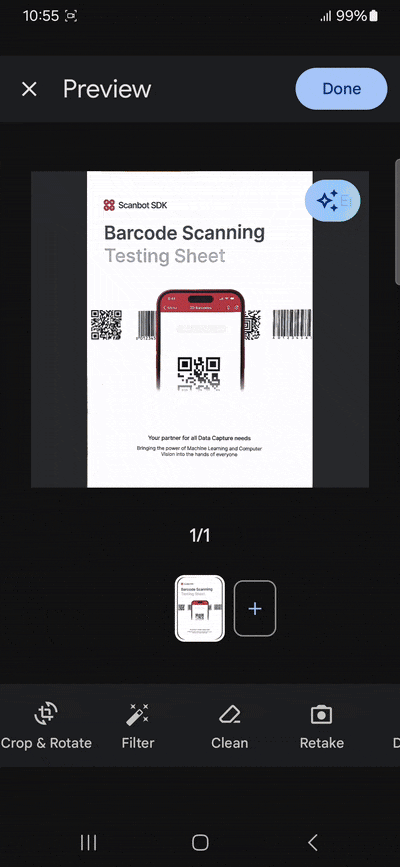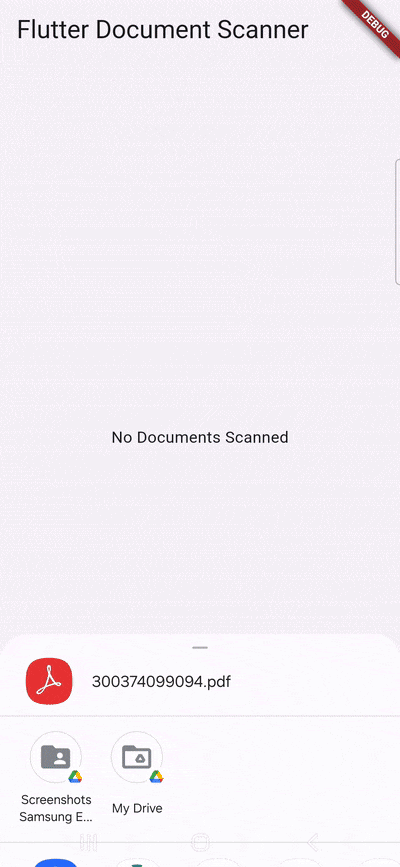
: const Text("No Documents Scanned"),
],
),
),
),
floatingActionButton: Padding(
padding: const EdgeInsets.only(bottom: 16.0),
child: ElevatedButton(
onPressed: () {
scanDocument();
},
child: const Text("Scan Documents"),
),
),
),
);
}
}When the user taps on the “Scan Documents” button, the scanDocument() method is called. It uses the FlutterDocScanner().getScannedDocumentAsPdf() method to open the device’s camera and initiate the scanning process with a four-page limit (which you can change to suit your needs). The scanned documents are then processed into a PDF and stored in the _scannedDocuments variable. The file’s URI is presented to the user.
Step 4: Implement the PDF export feature
As it is now, the app only prints the PDF file’s URI to the screen. To automatically show a sharing dialog after the PDF has been created, we’ll use the share_plus package.
First, add the share_plus dependency to pubspec.yaml and run flutter pub get once more.
dependencies:
flutter:
sdk: flutter
scanbot_sdk: ^6.1.2
share_plus: ^11.1.0In main.dart, import the package.
import 'package:share_plus/share_plus.dart';Then add the following function:
Future<void> _sharePdf(String pdfURI) async {
if (pdfURI.isEmpty) return;
final file = File(pdfURI);
if (!file.existsSync()) {
ScaffoldMessenger.of(
context,
).showSnackBar(SnackBar(content: Text("PDF file not found")));
return;
}
final box = context.findRenderObject() as RenderBox?;
await Share.shareXFiles(
[XFile(pdfURI)],
text: "Share PDF file!",
sharePositionOrigin: box!.localToGlobal(Offset.zero) & box.size,
);
}This function takes a file path as a string (pdfURI) and uses the share_plus package to open the device’s native sharing dialog.
Call this function inside scanDocument() while making sure the URI has the correct format.
Future<void> scanDocument() async {
dynamic scannedDocuments;
try {
scannedDocuments =
await FlutterDocScanner().getScannedDocumentAsPdf(page: 4) ??
'Unknown platform documents';
} on PlatformException {
scannedDocuments = 'Failed to get scanned documents.';
}
// Prepare the URI and call the share function
final pdfUri = scannedDocuments['pdfUri'].replaceFirst("file://", "");
await _sharePdf(pdfUri);
if (!mounted) return;
setState(() {
_scannedDocuments = scannedDocuments;
});
}Your final main.dart will look like this:
import 'dart:io';
import 'package:flutter/material.dart';
import 'package:flutter/services.dart';
import 'package:flutter_doc_scanner/flutter_doc_scanner.dart';
import 'package:share_plus/share_plus.dart';
void main() {
runApp(MaterialApp(home: MyApp()));
}
class MyApp extends StatefulWidget {
MyApp({Key? key}) : super(key: key);
@override
State<MyApp> createState() => _MyAppState();
}
class _MyAppState extends State<MyApp> {
dynamic _scannedDocuments;
Future<void> scanDocument() async {
dynamic scannedDocuments;
try {
scannedDocuments =
await FlutterDocScanner().getScannedDocumentAsPdf(page: 4) ??
'Unknown platform documents';
} on PlatformException {
scannedDocuments = 'Failed to get scanned documents.';
}
final pdfUri = scannedDocuments['pdfUri'].replaceFirst("file://", "");
await _sharePdf(pdfUri);
if (!mounted) return;
setState(() {
_scannedDocuments = scannedDocuments;
});
}
Future<void> _sharePdf(String pdfURI) async {
if (pdfURI.isEmpty) return;
final file = File(pdfURI);
if (!file.existsSync()) {
ScaffoldMessenger.of(
context,
).showSnackBar(SnackBar(content: Text("PDF file not found")));
return;
}
final box = context.findRenderObject() as RenderBox?;
await Share.shareXFiles(
[XFile(pdfURI)],
text: "Share PDF file!",
sharePositionOrigin: box!.localToGlobal(Offset.zero) & box.size,
);
}
@override
Widget build(BuildContext context) {
return MaterialApp(
title: 'Flutter Document Scanner',
home: Scaffold(
appBar: AppBar(title: const Text('Flutter Document Scanner')),
body: Center(
child: SingleChildScrollView(
child: Column(
mainAxisAlignment: MainAxisAlignment.center,
children: [
_scannedDocuments != null
? Text(_scannedDocuments.toString())
: const Text("No Documents Scanned"),
],
),
),
),
floatingActionButton: Padding(
padding: const EdgeInsets.only(bottom: 16.0),
child: ElevatedButton(
onPressed: () {
scanDocument();
},
child: const Text("Scan Documents"),
),
),
),
);
}
}Now use the flutter run command to test your app!

Conclusion
This concludes our tutorial on how to set up a document scanning app in Flutter using flutter_doc_scanner.
Free solutions like this one can be great for prototyping and personal projects. However, they have their drawbacks.
Since flutter_doc_scanner is a wrapper for Google’s ML Kit and Apple’s VisionKit, its functionality depends entirely on these two libraries. This also means document scanning will look and behave differently on Android and iOS devices.
For companies looking to integrate a document scanning solution into their mobile apps, there’s an additional challenge: Neither Google nor Apple offer dedicated support for their ML Kit and Vision Kit libraries. This means you cannot submit feature requests nor count on help when things don’t work as expected.
We developed the Scanbot Document Scanner SDK to help companies overcome these hurdles. Our goal was to provide a developer-friendly solution for a wide range of platforms that consistently delivers high-quality results, even in challenging circumstances – enterprise-grade support included.
In the following tutorial, we’ll show you how to set up a document scanning app using the Scanbot Flutter Document Scanner SDK.
Building a Flutter document scanner app with the Scanbot SDK
To set up our app, we’ll follow these steps:
- Preparing the project
- Initializing the SDK
- Implementing the scanning feature
- Implementing the PDF export feature
Thanks to the SDK’s Ready-to-Use UI Components, we’ll have an intuitive user interface out of the box.

Let’s get started!
Step 1: Prepare the project
After you’ve created a new Flutter project, add the scanbot_sdk dependency to pubspec.yaml.
dependencies:
flutter:
sdk: flutter
scanbot_sdk: ^7.0.1Then fetch the package.
flutter pub get💡 We use Document Scanner SDK version 7.0.1 in this tutorial. You can find the latest version in the changelog.
Now set the necessary camera permissions in android/app/src/main/AndroidManifest.xml …
<uses-permission android:name="android.permission.CAMERA" />
<uses-feature android:name="android.hardware.camera" />… and ios/Runner/Info.plist.
<key>NSCameraUsageDescription</key>
<string>Grant camera access to scan documents.</string>Step 2: Initialize the SDK
Before we can use the Document Scanner SDK, we need to initialize it. Make sure to call the initialization after entering the main widget creation. This ensures the SDK is correctly initialized.
In lib/main.dart, import the Scanbot SDK package:
import 'package:scanbot_sdk/scanbot_sdk.dart';
import 'package:scanbot_sdk/scanbot_sdk_ui_v2.dart';Within your main widget, initialize the Scanbot SDK. This is typically done in the initState method of your main widget’s state class:
class _MyHomePageState extends State<MyHomePage> {
@override
void initState() {
super.initState();
_initScanbotSdk();
}
Future<void> _initScanbotSdk() async {
var config = ScanbotSdkConfig(
licenseKey: "",
loggingEnabled: true,
);
try {
await ScanbotSdk.initScanbotSdk(config);
print('Scanbot SDK initialized successfully');
} catch (e) {
print('Error initializing Scanbot SDK: $e');
}
}
//...💡 Without a license key, our SDK only runs for 60 seconds per session. This is more than enough for the purposes of our tutorial, but if you like, you can generate a license key using your app identifier.
Step 3: Implement the scanning feature
Now we’ll create a simple user interface that includes a button to initiate the document scanning process.
Still in lib/main.dart, and in your main widget’s state class, define a widget with a button labeled “Scan Document”:
class _MyHomePageState extends State<MyHomePage> {
// ... (existing code)
@override
Widget build(BuildContext context) {
return Scaffold(
appBar: AppBar(
title: Text('Document Scanner'),
),
body: Center(
child: ElevatedButton(
onPressed: _startDocumentScanner,
child: Text('Scan Document'),
),
),
);
}
Future<void> _startDocumentScanner() async {
// To be implemented in the next step
}
}Next, let’s connect the button with our RTU UI’s scanning screen.
Within the _startDocumentScanner method, configure and launch the Document Scanner UI. This involves creating a DocumentScanningFlow configuration and starting the scanner:
Future<void> _startDocumentScanner() async {
// Launch the Scanbot Document Scanner UI
var configuration = multiPageScanningFlow();
var documentResult = await ScanbotSdkUiV2.startDocumentScanner(configuration);
// Check if the scanning operation was successful
if(documentResult.status == OperationStatus.OK) {
}
}
DocumentScanningFlow multiPageScanningFlow() {
// Create the default configuration object.
var configuration = DocumentScanningFlow();
// Customize text resources, behavior and UI:
// ...
return configuration;
}
}In this tutorial, we use a default configuration object. It will start the Document Scanner UI with the default settings: in multi-page scanning mode with an acknowledge screen after scanning each page. You can customize the UI and behavior of the Document Scanner by modifying the configuration object. For more information on how to customize the Document Scanner UI, please refer to the RTU UI documentation.
If you want, you can now run the app to try out the scanner without the PDF export feature.

Step 4: Implement the PDF export feature
Once again, we’ll use the share_plus package to implement the share dialog. Add the dependency to pubspec.yaml and run flutter pub get once more.
dependencies:
flutter:
sdk: flutter
scanbot_sdk: ^7.0.1
share_plus: ^11.1.0Back in main.dart, import the package.
import 'package:share_plus/share_plus.dart';To enable users to scan documents, generate a PDF, and share it, we need to modify the _startDocumentScanner method. This method will first launch the document scanner, then process the scanned document to generate a PDF, and finally provide an option to share it.
Future<void> _startDocumentScanner() async {
var configuration = multiPageScanningFlow();
var documentResult = await ScanbotSdkUiV2.startDocumentScanner(
configuration,
);
if (documentResult.status == OperationStatus.OK) {
// Convert the scanned document into a PDF file
var result = await ScanbotSdk.document.createPDFForDocument(
PDFFromDocumentParams(
documentID: documentResult.data!.uuid,
pdfConfiguration: PdfConfiguration(
pageSize: PageSize.A4,
pageDirection: PageDirection.PORTRAIT
)
)
);
// Extract the PDF file URI and trigger the sharing process
final pdfURI = result.pdfFileUri.replaceFirst("file://", "");
await _sharePdf(pdfURI);
}
}
// Method to share the generated PDF file
Future<void> _sharePdf(String pdfURI) async {
if (pdfURI.isEmpty) return;
final file = File(pdfURI);
if (!file.existsSync()) {
ScaffoldMessenger.of(
context,
).showSnackBar(SnackBar(content: Text("PDF file not found")));
return;
}
// Locate the UI box to ensure proper sharing dialog positioning
final box = context.findRenderObject() as RenderBox?;
await Share.shareXFiles(
[XFile(pdfURI)],
text: "Share PDF file!",
sharePositionOrigin: box!.localToGlobal(Offset.zero) & box.size,
);
}
DocumentScanningFlow multiPageScanningFlow() {
var configuration = DocumentScanningFlow();
return configuration;
}Now you can share a scanned document as a PDF file and use it. For example, you can send it via email or save it to a cloud storage.

Conclusion
And that’s it! You’ve successfully integrated a fully functional document scanner into your app 🎉
If this tutorial has piqued your interest in integrating document scanning functionalities into your Flutter app, make sure to take a look at the other neat features in the Flutter Document Scanner SDK’s documentation – or run our example project for a more hands-on experience.
Should you have questions about this tutorial or run into any issues, we’re happy to help! Just shoot us an email via tutorial-support@scanbot.io.
Happy scanning! 🤳






