In this tutorial, we’ll use Android Studio and the Scanbot Credit Card Scanner SDK to create an app in Kotlin for extracting the card number, cardholder name, and expiry date from credit cards.
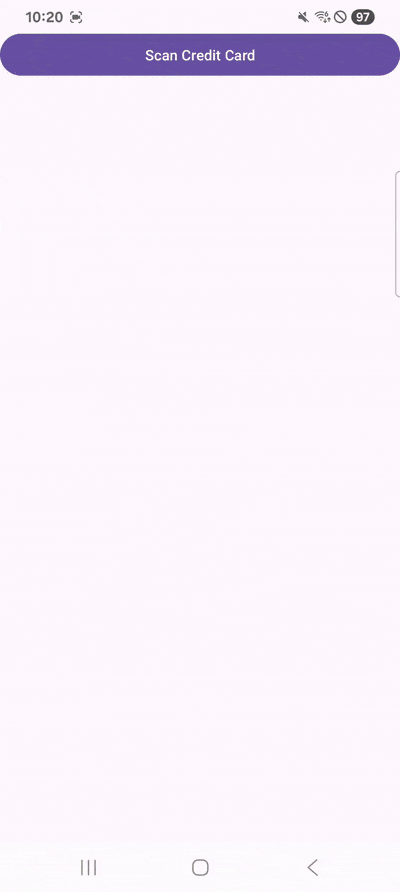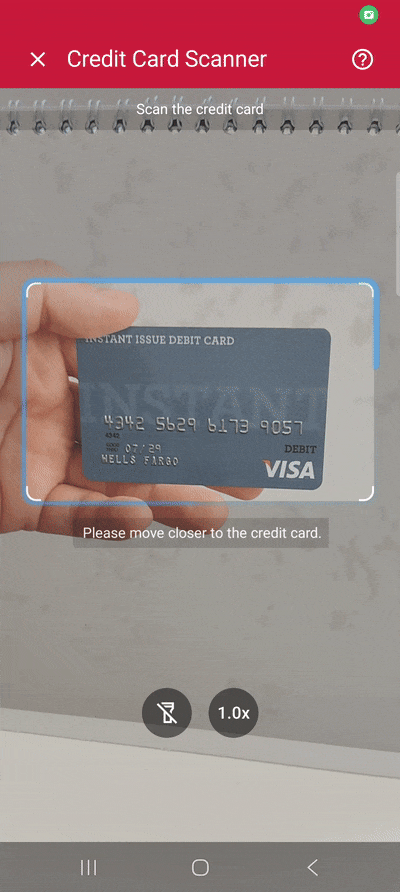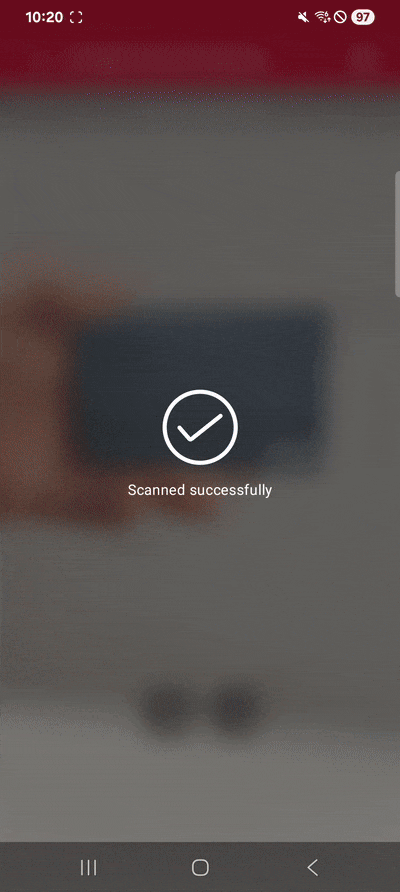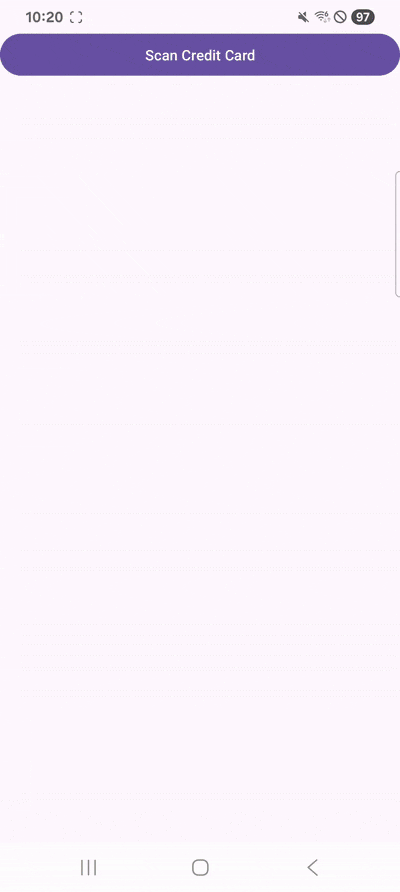
Extracting the card number, cardholder name, and expiry date with our Android Credit Card Scanner on a Samsung Galaxy XCover 7 Pro
We’ll achieve this by following these steps:
- Preparing the project
- Initializing the SDK
- Setting up the main screen
- Implementing the credit card scanning feature
All you need is the latest version of Android Studio and you’re good to go.
Want to see the final code right away? Click here.
MainActivity.kt:
package com.example.androidcreditcardscanner
import android.os.Bundle
import androidx.activity.enableEdgeToEdge
import androidx.appcompat.app.AppCompatActivity
import androidx.core.view.ViewCompat
import androidx.core.view.WindowInsetsCompat
import android.widget.Button
import android.widget.Toast
import androidx.activity.result.ActivityResultLauncher
import io.scanbot.sdk.creditcard.entity.CreditCard
import io.scanbot.sdk.ui_v2.creditcard.configuration.CreditCardScannerScreenConfiguration
import io.scanbot.sdk.ui_v2.creditcard.CreditCardScannerActivity
class MainActivity : AppCompatActivity() {
private val resultLauncher: ActivityResultLauncher<CreditCardScannerScreenConfiguration> =
registerForActivityResult(CreditCardScannerActivity.ResultContract()) { resultEntity: CreditCardScannerActivity.Result ->
if (resultEntity.resultOk) {
resultEntity.result?.creditCard?.let {
val creditCard = CreditCard(it)
val cardNumber: String = creditCard.cardNumber.value.text
val cardholderName: String = creditCard.cardholderName?.value?.text ?: ""
val expiryDate: String? = creditCard.expiryDate?.value?.text
Toast.makeText(
this,
"Card Number: $cardNumber, Cardholder Name: $cardholderName, Expiry Date: $expiryDate",
Toast.LENGTH_LONG
).show()
}
}
}
override fun onCreate(savedInstanceState: Bundle?) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState)
enableEdgeToEdge()
setContentView(R.layout.activity_main)
ViewCompat.setOnApplyWindowInsetsListener(findViewById(R.id.main)) { v, insets ->
val systemBars = insets.getInsets(WindowInsetsCompat.Type.systemBars())
v.setPadding(systemBars.left, systemBars.top, systemBars.right, systemBars.bottom)
insets
}
findViewById<Button>(R.id.btn_scan_creditcard).setOnClickListener {
val configuration = CreditCardScannerScreenConfiguration()
resultLauncher.launch(configuration)
}
}
}Step 1: Prepare the project
Create a new Empty Views Activity and name the project (e.g., “Android Credit Card Scanner”).
When your project is ready, go to settings.gradle.kts and add the Maven repositories for our SDK:
dependencyResolutionManagement {
repositoriesMode.set(RepositoriesMode.FAIL_ON_PROJECT_REPOS)
repositories {
google()
mavenCentral()
// Add the repositories here:
maven(url = "https://nexus.scanbot.io/nexus/content/repositories/releases/")
maven(url = "https://nexus.scanbot.io/nexus/content/repositories/snapshots/")
}
}Now go to app/build.gradle.kts and add the dependencies for the Scanbot SDK and the RTU UI:
dependencies {
implementation("io.scanbot:sdk-package-3:7.0.0")
implementation("io.scanbot:sdk-creditcard-assets:7.0.0")
implementation("io.scanbot:rtu-ui-v2-bundle:7.0.0")Sync the project.
💡 We use Scanbot SDK version 7.0.0 in this tutorial. You can find the latest version in the changelog.
We need to access the device camera to scan credit cards. Therefore, add the necessary permissions in AndroidManifest.xml:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<manifest xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
xmlns:tools="http://schemas.android.com/tools">
// Add the permissions here:
<uses-permission android:name="android.permission.CAMERA" />
<uses-feature android:name="android.hardware.camera" />
<application
<!-- ... -->Step 2: Initialize the SDK
Before we can use the Scanbot Credit Card Scanner SDK, we need to initialize it. The recommended approach is to do it in your Application implementation. This ensures the SDK is correctly initialized even when the app‘s process is restored after being terminated in the background.
First, we need to create an Application subclass by right-clicking on the folder app/kotlin+java/com.example.androidcreditcardscanner, selecting New > Kotlin Class/File, and naming it (e.g., “ExampleApplication”).
In the resulting ExampleApplication.kt, let’s first add the necessary imports.
import android.app.Application
import io.scanbot.sdk.ScanbotSDKInitializerThen we make ExampleApplication extend the Application class by adding : Application() and putting the code for initializing the SDK inside it.
class ExampleApplication : Application() {
override fun onCreate() {
super.onCreate()
ScanbotSDKInitializer()
// Optional: Uncomment the next line if you have a license key.
// .license(this, LICENSE_KEY)
.initialize(this)
}
}💡 Without a license key, our SDK only runs for 60 seconds per session. This is more than enough for the purposes of our tutorial, but if you like, you can generate a license key. Just make sure to change your applicationId in app/build.gradle.kts to io.scanbot.androiddocumentscanner and use that ID for generating the license.
Finally, we need to register the ExampleApplication class in AndroidManifest.xml.
<application
android:name=".ExampleApplication"
<!-- ... -->Step 3: Set up the main screen
We’re going to build a rudimentary UI so we can quickly start the Credit Card Scanner from the main screen.
For this tutorial, we’re going to go with a single-button layout, which you can copy and paste into app/res/layout/activity_main.xml:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<androidx.constraintlayout.widget.ConstraintLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
xmlns:app="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res-auto"
xmlns:tools="http://schemas.android.com/tools"
android:id="@+id/main"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
tools:context=".MainActivity">
<Button
android:id="@+id/btn_scan_creditcard"
android:layout_width="0dp"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:layout_marginBottom="20dp"
android:text="Scan Credit Card"
app:layout_constraintEnd_toEndOf="parent"
app:layout_constraintStart_toStartOf="parent"
app:layout_constraintTop_toTopOf="parent" />
</androidx.constraintlayout.widget.ConstraintLayout>Next, we’ll connect the button to our RTU UI’s credit card scanning screen.
Step 4: Implement the credit card scanning feature
Go to MainActivity.kt and add the necessary imports.
import android.widget.Button
import android.widget.Toast
import androidx.activity.result.ActivityResultLauncher
import io.scanbot.sdk.creditcard.entity.CreditCard
import io.scanbot.sdk.ui_v2.creditcard.configuration.CreditCardScannerScreenConfiguration
import io.scanbot.sdk.ui_v2.creditcard.CreditCardScannerActivityIn the MainActivity class, add a private property that we’ll use to launch the Credit Card Scanner. We’ll use the registerForActivityResult function, passing in a contract (CreditScannerActivity.ResultContract()) that describes how to start the Credit Card Scanner and how to interpret the result it returns.
Along with the contract, we provide a lambda function that processes the result when the Scanbot SDK detects credit card data and closes its screen. In this function, we create a strongly typed CreditCard object from the generic document data and extract the card number (also known as the primary account number or PAN), the name of the cardholder, and the card’s expiry date. These values are then displayed to the user as a toast notification.
class MainActivity : AppCompatActivity() {
// Add the private property here:
private val resultLauncher: ActivityResultLauncher<CreditCardScannerScreenConfiguration> =
registerForActivityResult(CreditCardScannerActivity.ResultContract()) { resultEntity: CreditCardScannerActivity.Result ->
if (resultEntity.resultOk) {
resultEntity.result?.creditCard?.let {
val creditCard = CreditCard(it)
val cardNumber: String = creditCard.cardNumber.value.text
val cardholderName: String = creditCard.cardholderName?.value?.text ?: ""
val expiryDate: String? = creditCard.expiryDate?.value?.text
Toast.makeText(
this,
"Card Number: $cardNumber, Cardholder Name: $cardholderName, Expiry Date: $expiryDate",
Toast.LENGTH_LONG
).show()
}
}
}
// ...Finally, in the onCreate() method, set up an OnClickListener for the Scan Credit Card button. When the button is clicked, it starts the resultLauncher using a configuration object.
// ... paste after the existing code in onCreate():
findViewById<Button>(R.id.btn_scan_creditcard).setOnClickListener {
val configuration = CreditCardScannerScreenConfiguration()
// Start the recognizer activity.
resultLauncher.launch(configuration)
}Your final MainActivity.kt will look like this:
package com.example.androidcreditcardscanner
import android.os.Bundle
import androidx.activity.enableEdgeToEdge
import androidx.appcompat.app.AppCompatActivity
import androidx.core.view.ViewCompat
import androidx.core.view.WindowInsetsCompat
import android.widget.Button
import android.widget.Toast
import androidx.activity.result.ActivityResultLauncher
import io.scanbot.sdk.creditcard.entity.CreditCard
import io.scanbot.sdk.ui_v2.creditcard.configuration.CreditCardScannerScreenConfiguration
import io.scanbot.sdk.ui_v2.creditcard.CreditCardScannerActivity
class MainActivity : AppCompatActivity() {
private val resultLauncher: ActivityResultLauncher<CreditCardScannerScreenConfiguration> =
registerForActivityResult(CreditCardScannerActivity.ResultContract()) { resultEntity: CreditCardScannerActivity.Result ->
if (resultEntity.resultOk) {
resultEntity.result?.creditCard?.let {
val creditCard = CreditCard(it)
val cardNumber: String = creditCard.cardNumber.value.text
val cardholderName: String = creditCard.cardholderName?.value?.text ?: ""
val expiryDate: String? = creditCard.expiryDate?.value?.text
Toast.makeText(
this,
"Card Number: $cardNumber, Cardholder Name: $cardholderName, Expiry Date: $expiryDate",
Toast.LENGTH_LONG
).show()
}
}
}
override fun onCreate(savedInstanceState: Bundle?) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState)
enableEdgeToEdge()
setContentView(R.layout.activity_main)
ViewCompat.setOnApplyWindowInsetsListener(findViewById(R.id.main)) { v, insets ->
val systemBars = insets.getInsets(WindowInsetsCompat.Type.systemBars())
v.setPadding(systemBars.left, systemBars.top, systemBars.right, systemBars.bottom)
insets
}
findViewById<Button>(R.id.btn_scan_creditcard).setOnClickListener {
val configuration = CreditCardScannerScreenConfiguration()
resultLauncher.launch(configuration)
}
}
}Now build and run the app and scan a credit card …

… to test your scanner!

Extracting the card number, cardholder name, and expiry date with our Android Credit Card Scanner on a Samsung Galaxy XCover 7 Pro
And that’s it! You’ve successfully integrated a fully functional Credit Card Scanner into your Android app 🎉
If you like, you can further customize the scanning interface to suit your preferences. Head over to the documentation to learn more.
Conclusion
If this tutorial has piqued your interest in integrating scanning functionalities into your Android app, make sure to take a look at the other neat features in the Data Capture SDK’s documentation – or run our example project for a more hands-on experience.
Should you have questions about this tutorial or run into any issues, we’re happy to help! Just shoot us an email via tutorial-support@scanbot.io.
Happy scanning! 🤳





