By streamlining their operations, companies can reduce expenses and improve their goods or services. This blog post will show you how to consistently improve your operations and why process optimization is crucial for every business.
What is process optimization?
Process optimization describes a methodical examination, assessment, and improvement of an organization’s current operating procedures in order to increase productivity, reduce expenses, and enhance quality.
It can be applied to both manual and automated workflows. Effective business process optimization requires the active involvement of employees in order to leverage on their practical experience.
The goals of process optimization
Naturally, the exact aims of a process optimization depend on the particular organization. There are, however, some common general objectives:
- Cost reduction: More efficient procedures typically result in lower costs. By removing inefficiencies in process chains, businesses can cut expenses for labor, materials, or other operating resources, and optimize the utilization of office space or other assets.
- Quality improvement: Improved processes lead to better service or product quality, which results in high customer loyalty and a good reputation.
- Security: Business process optimization can also strengthen safety and security. This ranges from avoiding potential hazards in production facilities to improving internal data protection measures.
- Working conditions: The redesign of process steps directly affects employees. They can eliminate health risks and render repetitive tasks obsolete. This increases employee satisfaction – and often also productivity.
- Agility and adaptability: Optimized, agile workflows enable companies to rapidly adapt to changing market conditions.
Steps to successful business process optimization
Process optimization requires a systematic, methodical approach by the respective company. Additionally, employees’ mindset is crucial: They must accept that processes are subject to permanent change, which means they must be prepared to flexibly adapt to process improvements.
There are three vital prerequisites for process optimization to work at all:
- All processes are known and documented.
- Each process can be assigned to one or more responsible parties.
- The procedures for process optimization are clearly defined.
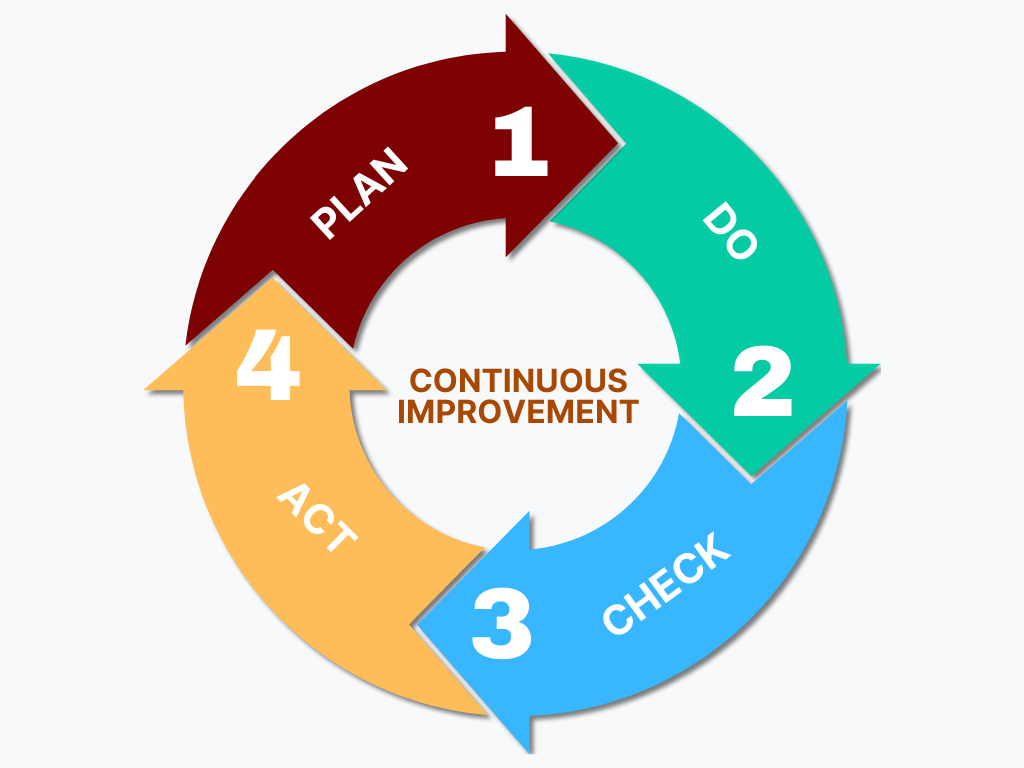
The so-called PDCA cycle describes the latter. It is part of almost all models for business process optimization. Each letter of the acronym refers to one of the four steps:
Plan (plan, analyze): First, the current state and the set goals are analyzed to find potential for improvement. Based on this, optimization methods are planned and developed.
Do: The planned measures are now implemented step by step.
Check: Following the process change, the organization measures whether – and to what extent – the planned goal is achieved.
Act (act, improve): If the targets were achieved or exceeded, the new process becomes the standard. If not, a new PDCA cycle must be carried out to find more effective alternatives.
A practical example using the Scanbot SDK
Let’s look at a practical example from the insurance industry that demonstrates how the PDCA workflow was used to successfully improve a key process: Receipt submission for insurance claims.
Plan (analyze)
A private insurer allows customers to submit claim receipts as photos using a mobile app or email.
An analysis of this process reveals the following weaknesses:
- Photo submission quality is often insufficient for automated processing. Only around 50% of the applications can be processed fully automatically.
- As a result, employees must manually enter the required data into the system.
- This often results in mistakes that require subsequent correction.
- Often, photo quality is so poor that employees must request them again in higher quality. This causes substantial delays.
- It can, therefore, take up to a week to process a claim.
The process optimization goals are thus defined as follows:
- The mobile app should assist users with creating high-quality digital copies.
- Users should receive immediate feedback on the quality of the photos and, if necessary, the app should prompt them to retake them.
- Manual intervention by employees should be reduced to a minimum so that 95% of claims can be processed automatically.
Do (implement)
To achieve these goals, the IT department chooses the Scanbot Document Scanner SDK, which can be integrated into the insurance company’s mobile app quickly.
With the help of the document scanner, users can create high-quality scans of their receipts in seconds. First, the detailed user guidance leads the policyholder into the optimum scanning position. Poor light, unfavorable angles, or crumpled paper are automatically compensated by image-enhancing filters.
Visual feedback then informs the user whether the quality of the scans is sufficient. If not, they are prompted to try again. Only documents suitable for automated processing are finally transferred to the backend.
Check (review)
Following the introduction of this new workflow, it is determined whether the desired improvements can be achieved. The insurer was, in fact, able to automate a large part of the claim submissions. However, the team notes that the quality check of the scanned documents still needs to be optimized to achieve the automated processing target
Act (improve)
The process is improved once again in line with the findings. Ultimately, the option to submit photos of receipts is discontinued entirely. Instead, only scans optimized by the Scanbot Document Scanner SDK are accepted.
Conclusion
Digitalization opens up a wide range of opportunities for companies to optimize their business processes. Companies that actively drive this transition can position themselves as technologically advanced and achieve sustainable competitive advantages in an increasingly digitized business world.
Would you like to see how the Scanbot SDK could streamline your processes? We offer a free 7-day trial license so you can test the Scanbot SDK in your mobile app or website. You can also contact our solution experts, who look forward to helping you find the best approach for your individual use case.



