In this tutorial, you’ll build an iOS app for scanning documents and exporting them as PDFs using SwiftUI and VNDocumentCameraViewController, a view controller from the VisionKit framework that provides a pre-built UI for document scanning.

To build your app, you’ll follow these steps:
- Creating a new SwiftUI project
- Configuring camera permissions
- Implementing the VNDocumentCameraViewController
- Implementing the PDF export feature (optional)
Prerequisites
- A Mac with Xcode 14 or later
- A physical iOS device (since the iOS simulator lacks camera access)
Step 1: Create a new SwiftUI project
First, open Xcode and create a new iOS app project.
Enter a name (e.g., “VisionKit Document Scanner”) and select the following:
- Interface: SwiftUI
- Language: Swift
For simplicity’s sake, you can set Testing System and Storage to “None”.
Step 2: Configure camera permissions
You’ll need to ensure the app can access the device camera so users can scan documents.
To do that, select your project in the project navigator, select the target once more in the project and targets list, and open the Info tab. Add a new key “Privacy – Camera Usage Description” and provide a value, e.g., “Grant camera access to scan documents”.
Alternatively, you can directly edit the project’s Info.plist file.
<key>NSCameraUsageDescription</key>
<string>Grant camera access to scan documents</string>Step 3: Implement the VNDocumentCameraViewController
Next, open ContentView.swift.
Delete its content and import the required frameworks:
import SwiftUI
import VisionKitYou’ll now set up the document scanner UI and functionality.
To jump to the final code, click here.
1. Create the main view structure
Start by creating the main ContentView with state variables.
struct ContentView: View {
@State private var scannedImage: UIImage?
@State private var isShowingScanner = false
var body: some View {
// We'll fill this in next
}
}@State private var scannedImageholds the scanned document image (nil if nothing scanned yet).@State private var isShowingScannertracks whether the scanner is showing or not.
2. Build the UI layout
Inside the body: some View {, add:
VStack(spacing: 20) {
if let image = scannedImage {
Image(uiImage: image)
.resizable()
.scaledToFit()
.frame(maxHeight: 400)
} else {
Text("No document scanned yet")
.foregroundColor(.gray)
}
Button("Scan Document") {
isShowingScanner = true
}
.buttonStyle(.borderedProminent)
}
.padding()VStack(spacing: 20)arranges items vertically with 20 points between them.if let image = scannedImagechecks if there’s a scanned image.- If yes, the image is displayed.
- If not, placeholder text is shown.
Button("Scan Document"), when tapped, setsisShowingScannerto true..padding()adds space around the edges.
3. Add the sheet modifier
Right after .padding(), add:
.sheet(isPresented: $isShowingScanner) {
DocumentScannerView(scannedImage: $scannedImage)
}.sheet()presents a modal sheet (pop-up screen).isPresented: $isShowingScannershows when this is true.DocumentScannerView(scannedImage: $scannedImage)shows the scanner (which you’ll create next).- The
$passes a binding so the scanner can update the image.
4. Create the scanner wrapper
Below the ContentView (after its closing brace), start a new struct:
struct DocumentScannerView: UIViewControllerRepresentable {
@Binding var scannedImage: UIImage?
@Environment(\.dismiss) var dismissUIViewControllerRepresentablelets you use UIKit’s VNDocumentCameraViewController in SwiftUI.@Binding var scannedImagereceives a reference to the parent’s image variable.@Environment(\.dismiss)gives you a way to close the scanner.
5. Create the scanner
Add these three functions inside DocumentScannerView:
func makeUIViewController(context: Context) -> VNDocumentCameraViewController {
let scanner = VNDocumentCameraViewController()
scanner.delegate = context.coordinator
return scanner
}
func updateUIViewController(_ uiViewController: VNDocumentCameraViewController, context: Context) {}
func makeCoordinator() -> Coordinator {
Coordinator(scannedImage: $scannedImage, dismiss: dismiss)
}makeUIViewControllercreates Apple’s document scanner and sets its delegate.updateUIViewControlleris required but empty (no updates needed).makeCoordinatorcreates your coordinator (handles scanner events).
6. Create the coordinator class
Still inside DocumentScannerView add the Coordinator class:
class Coordinator: NSObject, VNDocumentCameraViewControllerDelegate {
@Binding var scannedImage: UIImage?
var dismiss: DismissAction
init(scannedImage: Binding<UIImage?>, dismiss: DismissAction) {
self._scannedImage = scannedImage
self.dismiss = dismiss
}- Creates a coordinator to handle scanner callbacks.
- Stores references to the image binding and dismiss action.
- The
initinitializes these when the coordinator is created.
7. Handle successful scans
Inside the Coordinator class, add:
func documentCameraViewController(_ controller: VNDocumentCameraViewController, didFinishWith scan: VNDocumentCameraScan) {
if scan.pageCount > 0 {
scannedImage = scan.imageOfPage(at: 0)
}
dismiss()
}- Called when the user taps “Save” in the scanner.
if scan.pageCount > 0checks if any pages were scanned.scannedImage = scan.imageOfPage(at: 0)gets the first scanned page.dismiss()closes the scanner.
8. Handle canceled scans
Still inside the Coordinator class, add:
func documentCameraViewControllerDidCancel(_ controller: VNDocumentCameraViewController) {
dismiss()
}- Called when the user taps “Cancel”.
- Simply closes the scanner without saving.
9. Handle scan errors
Finally in Coordinator, add:
func documentCameraViewController(_ controller: VNDocumentCameraViewController, didFailWithError error: Error) {
print("Scan failed: \(error.localizedDescription)")
dismiss()
}
}
}- Called if scanning fails.
- Prints errors to the console for debugging.
- Closes the scanner.
10. Check your code for completeness
Following the steps above will leave you with the following ContentView.swift file:
import SwiftUI
import VisionKit
struct ContentView: View {
@State private var scannedImage: UIImage?
@State private var isShowingScanner = false
var body: some View {
VStack(spacing: 20) {
if let image = scannedImage {
Image(uiImage: image)
.resizable()
.scaledToFit()
.frame(maxHeight: 400)
} else {
Text("No document scanned yet")
.foregroundColor(.gray)
}
Button("Scan Document") {
isShowingScanner = true
}
.buttonStyle(.borderedProminent)
}
.padding()
.sheet(isPresented: $isShowingScanner) {
DocumentScannerView(scannedImage: $scannedImage)
}
}
}
struct DocumentScannerView: UIViewControllerRepresentable {
@Binding var scannedImage: UIImage?
@Environment(\.dismiss) var dismiss
func makeUIViewController(context: Context) -> VNDocumentCameraViewController {
let scanner = VNDocumentCameraViewController()
scanner.delegate = context.coordinator
return scanner
}
func updateUIViewController(_ uiViewController: VNDocumentCameraViewController, context: Context) {}
func makeCoordinator() -> Coordinator {
Coordinator(scannedImage: $scannedImage, dismiss: dismiss)
}
class Coordinator: NSObject, VNDocumentCameraViewControllerDelegate {
@Binding var scannedImage: UIImage?
var dismiss: DismissAction
init(scannedImage: Binding<UIImage?>, dismiss: DismissAction) {
self._scannedImage = scannedImage
self.dismiss = dismiss
}
func documentCameraViewController(_ controller: VNDocumentCameraViewController, didFinishWith scan: VNDocumentCameraScan) {
if scan.pageCount > 0 {
scannedImage = scan.imageOfPage(at: 0)
}
dismiss()
}
func documentCameraViewControllerDidCancel(_ controller: VNDocumentCameraViewController) {
dismiss()
}
func documentCameraViewController(_ controller: VNDocumentCameraViewController, didFailWithError error: Error) {
print("Scan failed: \(error.localizedDescription)")
dismiss()
}
}
}Feel free to build and run the app to test its functionalities. If you don’t need a PDF export feature, your app is now complete.
Step 4: Implementing the PDF export feature (optional)
If you want to export all scanned pages as a PDF file, you can extend your ContentView.swift by doing the following.
To jump to the final code, click here.
1. Import the PDFKit framework
Apple’s PDFKit provides tools to create and work with PDF documents. Add the import at the top of the file.
import SwiftUI
import VisionKit
import PDFKit2. Update the state variables
Inside ContentView, change the state variables to support multiple pages.
@State private var scannedImages: [UIImage] = [] // Changed to array
@State private var isShowingScanner = false
@State private var isShowingShareSheet = false // New
@State private var pdfURL: URL? // NewscannedImagesis now an array to hold multiple pages.isShowingShareSheettracks if the share sheet is visible.pdfURLstores the PDF file location for sharing.
3. Update the UI display
In the body of ContentView, replace the VStack content with the following:
VStack(spacing: 20) {
if !scannedImages.isEmpty {
ScrollView {
VStack(spacing: 10) {
ForEach(scannedImages.indices, id: \.self) { index in
VStack {
Text("Page \(index + 1)")
.font(.caption)
.foregroundColor(.gray)
Image(uiImage: scannedImages[index])
.resizable()
.scaledToFit()
.frame(maxHeight: 300)
.border(Color.gray, width: 1)
}
}
}
.padding()
}
HStack(spacing: 15) {
Button("Scan More") {
isShowingScanner = true
}
.buttonStyle(.bordered)
Button("Export as PDF") {
createAndSharePDF()
}
.buttonStyle(.borderedProminent)
Button("Clear All") {
scannedImages.removeAll()
}
.buttonStyle(.bordered)
.foregroundColor(.red)
}
} else {
Text("No documents scanned yet")
.foregroundColor(.gray)
Button("Scan Document") {
isShowingScanner = true
}
.buttonStyle(.borderedProminent)
}
}
.padding()- Shows all scanned pages in a scrollable view.
- Adds a “Scan More” button to add more pages.
- Adds an “Export as PDF” button (you’ll create this function in step 5).
- Adds a “Clear All” button to start over.
- If there are no scans, shows the original simple view.
4. Update the sheet modifier
Replace the .sheet() modifier with this updated version:
.sheet(isPresented: $isShowingScanner) {
DocumentScannerView(scannedImages: $scannedImages)
}
.sheet(isPresented: $isShowingShareSheet) {
if let url = pdfURL {
ShareSheet(items: [url])
}
}- Updates the scanner to use a
scannedImagesarray. - Adds a second sheet for sharing the PDF.
5. Create the PDF generation function
Add this function inside ContentView (after the body and before the closing brace):
func createAndSharePDF() {
let pdfDocument = PDFDocument()
for (index, image) in scannedImages.enumerated() {
if let pdfPage = PDFPage(image: image) {
pdfDocument.insert(pdfPage, at: index)
}
}
let tempURL = FileManager.default.temporaryDirectory
.appendingPathComponent("ScannedDocument.pdf")
pdfDocument.write(to: tempURL)
pdfURL = tempURL
isShowingShareSheet = true
}- Creates a new PDF document.
- Loops through all scanned images and adds each as a page.
- Saves PDF to a temporary location.
- Opens the share sheet to let the user export and save the PDF.
6. Update DocumentScannerView
Replace the entire DocumentScannerView struct with this updated version:
struct DocumentScannerView: UIViewControllerRepresentable {
@Binding var scannedImages: [UIImage] // Changed from scannedImage
@Environment(\.dismiss) var dismiss
func makeUIViewController(context: Context) -> VNDocumentCameraViewController {
let scanner = VNDocumentCameraViewController()
scanner.delegate = context.coordinator
return scanner
}
func updateUIViewController(_ uiViewController: VNDocumentCameraViewController, context: Context) {}
func makeCoordinator() -> Coordinator {
Coordinator(scannedImages: $scannedImages, dismiss: dismiss)
}
class Coordinator: NSObject, VNDocumentCameraViewControllerDelegate {
@Binding var scannedImages: [UIImage] // Changed
var dismiss: DismissAction
init(scannedImages: Binding<[UIImage]>, dismiss: DismissAction) { // Changed
self._scannedImages = scannedImages
self.dismiss = dismiss
}
func documentCameraViewController(_ controller: VNDocumentCameraViewController, didFinishWith scan: VNDocumentCameraScan) {
// Get ALL scanned pages (changed from just first page)
for i in 0..<scan.pageCount {
let image = scan.imageOfPage(at: i)
scannedImages.append(image)
}
dismiss()
}
func documentCameraViewControllerDidCancel(_ controller: VNDocumentCameraViewController) {
dismiss()
}
func documentCameraViewController(_ controller: VNDocumentCameraViewController, didFailWithError error: Error) {
print("Scan failed: \(error.localizedDescription)")
dismiss()
}
}
}- The single
scannedImageis now an arrayscannedImages. - Now captures all pages from the scan (not just the first page).
- Appends new scans to existing images (so that “Scan More” works).
7. Create the share sheet
Add this new struct at the bottom of the file (after DocumentScannerView):
struct ShareSheet: UIViewControllerRepresentable {
let items: [Any]
func makeUIViewController(context: Context) -> UIActivityViewController {
let controller = UIActivityViewController(
activityItems: items,
applicationActivities: nil
)
return controller
}
func updateUIViewController(_ uiViewController: UIActivityViewController, context: Context) {}
}- Wraps iOS’s native share sheet
- Lets users save the PDF to Files as well as share it via Messages, email, etc.
- The system handles all the sharing options automatically.
8. Check the final code
After you’ve followed the steps above, your final ContentView.swift will look like this:
import SwiftUI
import VisionKit
import PDFKit
struct ContentView: View {
@State private var scannedImages: [UIImage] = []
@State private var isShowingScanner = false
@State private var isShowingShareSheet = false
@State private var pdfURL: URL?
var body: some View {
VStack(spacing: 20) {
if !scannedImages.isEmpty {
ScrollView {
VStack(spacing: 10) {
ForEach(scannedImages.indices, id: \.self) { index in
VStack {
Text("Page \(index + 1)")
.font(.caption)
.foregroundColor(.gray)
Image(uiImage: scannedImages[index])
.resizable()
.scaledToFit()
.frame(maxHeight: 300)
.border(Color.gray, width: 1)
}
}
}
.padding()
}
HStack(spacing: 15) {
Button("Scan More") {
isShowingScanner = true
}
.buttonStyle(.bordered)
Button("Export as PDF") {
createAndSharePDF()
}
.buttonStyle(.borderedProminent)
Button("Clear All") {
scannedImages.removeAll()
}
.buttonStyle(.bordered)
.foregroundColor(.red)
}
} else {
Text("No documents scanned yet")
.foregroundColor(.gray)
Button("Scan Document") {
isShowingScanner = true
}
.buttonStyle(.borderedProminent)
}
}
.padding()
.sheet(isPresented: $isShowingScanner) {
DocumentScannerView(scannedImages: $scannedImages)
}
.sheet(isPresented: $isShowingShareSheet) {
if let url = pdfURL {
ShareSheet(items: [url])
}
}
}
func createAndSharePDF() {
let pdfDocument = PDFDocument()
for (index, image) in scannedImages.enumerated() {
if let pdfPage = PDFPage(image: image) {
pdfDocument.insert(pdfPage, at: index)
}
}
let tempURL = FileManager.default.temporaryDirectory
.appendingPathComponent("ScannedDocument.pdf")
pdfDocument.write(to: tempURL)
pdfURL = tempURL
isShowingShareSheet = true
}
}
struct DocumentScannerView: UIViewControllerRepresentable {
@Binding var scannedImages: [UIImage]
@Environment(\.dismiss) var dismiss
func makeUIViewController(context: Context) -> VNDocumentCameraViewController {
let scanner = VNDocumentCameraViewController()
scanner.delegate = context.coordinator
return scanner
}
func updateUIViewController(_ uiViewController: VNDocumentCameraViewController, context: Context) {}
func makeCoordinator() -> Coordinator {
Coordinator(scannedImages: $scannedImages, dismiss: dismiss)
}
class Coordinator: NSObject, VNDocumentCameraViewControllerDelegate {
@Binding var scannedImages: [UIImage]
var dismiss: DismissAction
init(scannedImages: Binding<[UIImage]>, dismiss: DismissAction) {
self._scannedImages = scannedImages
self.dismiss = dismiss
}
func documentCameraViewController(_ controller: VNDocumentCameraViewController, didFinishWith scan: VNDocumentCameraScan) {
for i in 0..<scan.pageCount {
let image = scan.imageOfPage(at: i)
scannedImages.append(image)
}
dismiss()
}
func documentCameraViewControllerDidCancel(_ controller: VNDocumentCameraViewController) {
dismiss()
}
func documentCameraViewController(_ controller: VNDocumentCameraViewController, didFailWithError error: Error) {
print("Scan failed: \(error.localizedDescription)")
dismiss()
}
}
}
struct ShareSheet: UIViewControllerRepresentable {
let items: [Any]
func makeUIViewController(context: Context) -> UIActivityViewController {
let controller = UIActivityViewController(
activityItems: items,
applicationActivities: nil
)
return controller
}
func updateUIViewController(_ uiViewController: UIActivityViewController, context: Context) {}
}Now build and run your app to test your document scanner!

Conclusion
This concludes our tutorial on how to use VisionKit’s VNDocumentCameraViewController to build a document scanner app for iOS.
Free solutions like this one can be great for prototyping and personal projects. However, VisionKit’s customization options are limited, making this a convenient yet constrained approach. Setting a maximum page number, cropping, rotating, or reordering scanned pages, and customizing UI strings are not possible when using VNDocumentCameraViewController.
Furthermore, Apple doesn’t offer enterprise support for VisionKit, so companies relying on it for their scanning needs won’t be able to submit feature requests nor count on help when things don’t work as expected.
We developed the Scanbot Document Scanner SDK to help companies overcome these hurdles. Our goal was to provide a developer-friendly solution for a wide range of platforms that consistently delivers high-quality results, even in challenging circumstances – enterprise-grade support included.
In the following tutorial, we’ll show you how to set up a document scanning app using the Scanbot iOS Document Scanner SDK.
Building an iOS document scanner app with the Scanbot SDK
To set up our app, we’ll follow these steps:
- Preparing the project
- Setting up the main screen
- Implementing the scanning feature
- Implementing the PDF export feature
Thanks to the SDK’s Ready-to-Use UI Components, we’ll have an intuitive user interface out of the box.

All you need is a Mac with the latest version of Xcode and a test device, since we’ll need to use the camera.
Step 1: Prepare the project
Open Xcode and create a new iOS App project. Name the project (e.g., “iOS Document Scanner”), choose Storyboard as the interface, and Swift as the language.
After opening your project, go to File > Add Package Dependencies… and add the Scanbot SDK package for the Swift Package Manager.
Open your Main App Target’s Info tab and add a Privacy – Camera Usage Description key with a value such as “Grant camera access to scan documents”.
In AppDelegate.swift, add a line for setting the license key to the application(_:didFinishLaunchingWithOptions:) method. We don’t need one for this tutorial, but if you have a license key you’d like to use, uncomment the code below and replace <YOUR_LICENSE_KEY> with your actual key.
func application(_ application: UIApplication, didFinishLaunchingWithOptions launchOptions: [UIApplication.LaunchOptionsKey: Any]?) -> Bool {
// Uncomment the following line and replace <YOUR_LICENSE_KEY> with your actual key
// Scanbot.setLicense("<YOUR_LICENSE_KEY>")
return true
}Without a license key, the SDK will run in trial mode for 60 seconds per session. If you need more than that, you can generate a free trial license.
Step 2: Set up the main screen
We’ll now create a simple UI for starting our document scanner.
First, open Main.storyboard and add a UIButton with a meaningful label (e.g., “Scan Document”) to the main view.
After that, create an IBAction for the button in ViewController.swift and implement the button action to present the scanner view controller.
@IBAction func scanDocumentButtonTapped(_ sender: UIButton) {
// Code to present the scanner view controller will go here
}We’ll also need to add the following import to ViewController.swift:
import ScanbotSDKStep 3: Implement the scanning feature
This step involves presenting the Document Scanner view controller. The Scanbot SDK provides a pre-built UI for the scanning process. You’ll need to instantiate the scanner, present it modally, and handle the scanned document. Note that we’ll implement the share(url:) function in the next step.
Inside scanDocumentButtonTapped() in ViewController.swift, add the following code:
let configuration = SBSDKUI2DocumentScanningFlow()
SBSDKUI2DocumentScannerController.present(on: self,
configuration: configuration) { documentResult in
guard let documentResult = documentResult else { return }
let configuration = SBSDKPDFConfiguration()
let generator = SBSDKPDFGenerator(configuration: configuration)
Task {
guard let url = try? await generator.generate(from: documentResult) else { return }
self.share(url: url)
}
}Step 4: Implement the PDF export feature
In its current state, our app can scan documents, but there’s no way to export them. Let’s implement the following function in ViewController.swift so that after a user has scanned a document and taps the “Submit” button, a PDF will automatically be generated, ready to be shared.
func share(url: URL) {
let activityViewController = UIActivityViewController(activityItems: [url],
applicationActivities: nil)
if let popoverPresentationController = activityViewController.popoverPresentationController {
popoverPresentationController.sourceView = view
}
present(activityViewController, animated: true)
}Your final ViewController.swift will look like this:
import UIKit
import ScanbotSDK
class ViewController: UIViewController {
override func viewDidLoad() {
super.viewDidLoad()
// Do any additional setup after loading the view.
}
@IBAction func scanDocumentButtonTapped(_ sender: Any) {
let configuration = SBSDKUI2DocumentScanningFlow()
SBSDKUI2DocumentScannerController.present(on: self,
configuration: configuration) { documentResult in
guard let documentResult = documentResult else { return }
let configuration = SBSDKPDFConfiguration()
let generator = SBSDKPDFGenerator(configuration: configuration)
Task {
guard let url = try? await generator.generate(from: documentResult) else { return }
self.share(url: url)
}
}
}
func share(url: URL) {
let activityViewController = UIActivityViewController(activityItems: [url],
applicationActivities: nil)
if let popoverPresentationController = activityViewController.popoverPresentationController {
popoverPresentationController.sourceView = view
}
present(activityViewController, animated: true)
}
}Now our iOS Document Scanner app is ready. Build and run the app and give it a try!

Conclusion
This completes the basic implementation of an iOS Document Scanner using the Scanbot SDK. We used the SDK’s Ready-to-Use UI Components with their default values for this tutorial, but you can customize each screen in the document scanning workflow to fit your needs.
The available screens are:
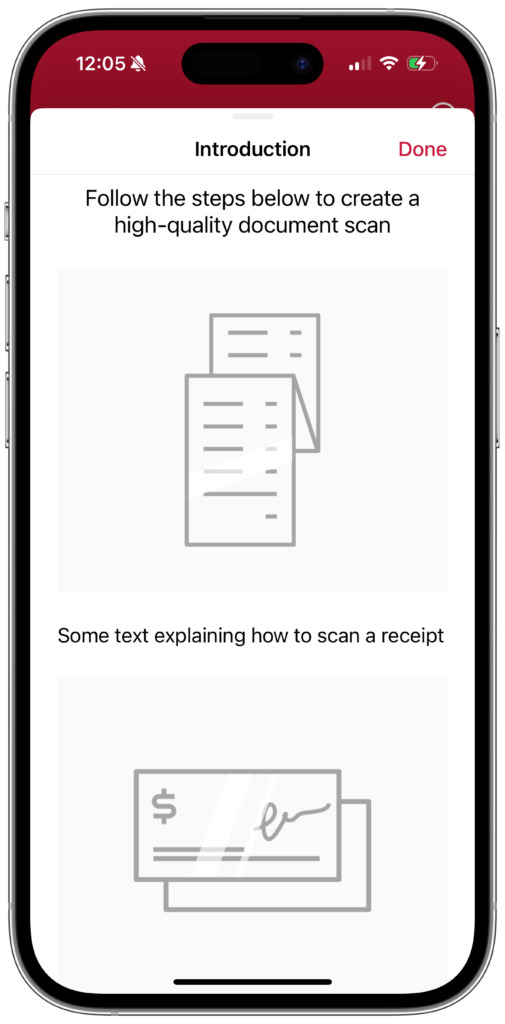
The Introduction Screen gives users a step-by-step guide for how to use the scanner effectively. You can configure each step with your custom text.
The introduction can be used to highlight key features and outline the specific scanning workflow of your use case.

The Scanning Screen provides a seamless and efficient document capture experience. Here are some key features:
- Import from gallery: Users can import images from their device’s gallery. This lets you use existing photos in your document scanning workflow.
- Page limit configuration: You can limit the number of pages that can be scanned in a single session. This helps manage document size and user expectations.
- Capture feedback animation: Choose between a checkmark animation or the document genie/funnel animation to enhance user interaction and provide visual confirmation of successful captures.
- User guidance: Overlay dynamic text instructions to guide the user through the scanning process. This guidance adapts to the current state, such as suggesting adjustments if the document is at a poor angle or if the lighting is insufficient. You can set custom text for each state.

The Acknowledge Screen helps ensure the quality of the scanned documents. To determine suitability, the captured image is thoroughly analyzed. You can set the minimum quality required using the following enums:
noDocumentveryPoorpoorreasonablegoodexcellent
You can also configure whether the Acknowledge Screen itself is shown by using the following modes:
badQuality: The screen is shown only if the minimum quality is not met.always: The screen is shown after every capture, regardless of image quality.none: The screen is never shown, even if the quality threshold is not met.

The Review Screen allows users to manage and review their scanned documents before finalizing them. This screen provides several tools to ensure that all pages are in the correct order and meet the requirements:
- Rotate: For changing a page’s orientation
- Crop: Takes users to the Crop Screen (see below)
- Reorder: Takes users to the Reorder Screen (see below)
- Retake: For scanning a page once more
- Add Page: For adding pages at any position within a multi-page document
- Delete: For deleting one or more pages
- Zoom: For zooming in on the document
- Submit: For completing the scanning flow

The Crop Screen enables a cropping tool for precise adjustments to document images. It can also be initialized as a standalone screen.

The Reorder Screen allows users to easily change the order of the scanned pages in an intuitive drag-and-drop interface.
At the end of the scanning workflow, users can export the document file, as shown in this tutorial. In addition to PDF, the SDK also supports TIFF, JPEG, and PNG.
For more information on how to configure and implement each screen in your app, head over to our RTU UI documentation.
Should you have questions or run into any issues, we’re happy to help! Just shoot us an email via tutorial-support@scanbot.io.
Happy scanning! 🤳





