Serial Number Scanner SDK
Empower your mobile and web applications to capture serial numbers with speed and precision, offline and on-device, eliminating manual data entry errors.
Trusted by
400+
global
industry leaders
Fast and accurate Serial Number Scanner
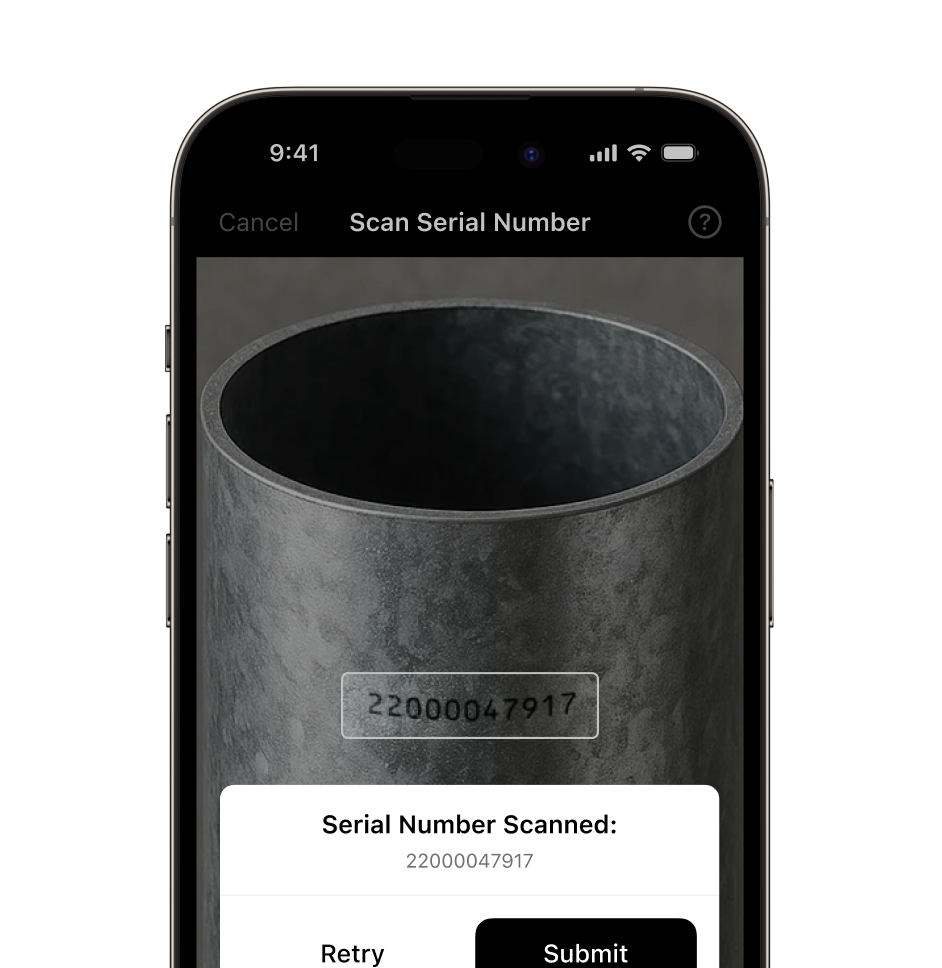
Quickly and reliably capture serial numbers directly through your mobile or web application. The Scanbot Serial Number Scanner SDK replaces slow, error-prone manual input with efficient, automatic data extraction – even from challenging surfaces or in low-light conditions. Its advanced OCR and pattern recognition technology ensures high accuracy for a wide variety of serial number formats.
The Scanbot Serial Number Scanner SDK works entirely offline, keeping all data on the user’s device. This ensures dependable scanning performance anywhere and robust data security.
What is a serial number?
A serial number is a unique identifier, typically a sequence of letters and numbers, assigned to one particular item. The core idea is simple: this gives the individual product a unique mark to differentiate it from all other units, even if they are visually identical or from the same batch.
You’ll find these codes vary quite a bit in how they are structured, with different lengths and character sets used by different makers. The reason for often including letters, not just numbers, is practical: it vastly increases the number of distinct codes that can be created, so every different item gets a unique one.
The practical use of these distinct codes boils down to enabling item-specific tracking. Businesses use this to maintain individual records for their products, which can tell them, for instance, an item’s point of origin, its time spent in inventory, or when it should be considered for replacement.
Types of serial numbers
No single blueprint fits all serial numbers; their look and makeup shift to handle specific identification jobs. We generally see these key forms in action:
Standard alphanumeric serial numbers
For many everyday goods – think consumer electronics, various machinery, or items on retail shelves – a flexible yet straightforward tag is essential. Mixing letters with numbers gives these products their unique ID, a system that offers a vast number of distinct codes while still being relatively easy for people to read and use.
USNR (United States Serial Numbers Registry) codes
When an item is connected to U.S. military and defense operations, its serial code often follows a very specific, federally mandated playbook: the USNR system. This isn’t just any identifier; it’s a structured approach designed to guarantee highly reliable tracking and full compliance with stringent government regulations for critical assets.
Custom manufacturer serial codes
Often, a company’s internal workings and specific product details demand a more personalized identification method. In these cases, businesses will engineer their own custom manufacturer serial codes. These unique-to-the-company tags can cleverly pack in vital internal data – such as batch origins, exact production dates, or line numbers – acting almost like a shorthand for their specific operational and tracking logic.
Encoded serial numbers
Manually entering serial numbers can be slow and error-prone, especially with many items. The practical fix is to use encoded serial numbers. The idea is simple: any type of existing serial number can be transformed into a visual, machine-friendly format, like the stripes of a barcode or the squares of a QR code. Scanners then read these in an instant, making data input both quick and much more accurate.
Applications of serial number scanning
Manufacturing & industrial sector
In factories, thousands of parts go into making products, and each can have its own unique serial number. If workers have to manually read and type these numbers, it’s incredibly slow. Worse, it’s easy to make typos or misread a number. This can lead to big problems, like using the wrong component in an assembly or having incorrect records for quality control and traceability.
Instead of manual entry, workers can use a device with a scanning app. They just point it at the serial number on a part – whether it’s a barcode, QR code, or even plain text numbers on a label. The app reads the serial number instantly. Even if a part is a bit greasy or the lighting isn’t perfect, good scanning technology can often still capture the number correctly. The app can then immediately check if it’s the right part for that stage of production and automatically log it.
Logistics & warehousing sector
Warehouses are constantly buzzing with items coming in and going out – things like computers, tools, electronics, you name it. Each of these items often has a serial number, sometimes on tiny labels or directly on the product, and these labels can get worn or be hard to reach. Keeping track of all these serial numbers correctly is essential to avoid losing items and to know exactly what’s in stock. Trying to do this by hand, especially when dealing with large volumes, is very difficult and prone to mistakes.
Warehouse staff can use mobile apps on phones or dedicated scanners to quickly read these serial numbers. Whether an item is being received, moved, counted during a stocktake, or shipped out, a quick scan captures its serial number. Modern scanning can often read numbers even from slightly damaged labels or when there are many items close together. Some systems even work offline, so a poor internet connection in the warehouse doesn’t stop the work.
Electronics & telecommunications sector
Repair technicians working in the field often need to identify specific equipment, like internet routers, servers, or other electronic devices, by their serial numbers. These numbers are frequently printed very small, might be on curved surfaces, or could be faded or dirty, making them hard to read clearly and type correctly into a service app or database, especially when the technician is on-site, possibly in an awkward location. This can slow down the repair process considerably. With a service app on their smartphone or tablet that includes good scanning capabilities, technicians can use the device’s camera to quickly capture the serial number. Even if the label is worn or the number is tiny, the app can often decipher it. Once scanned, the app can instantly pull up the equipment’s details, repair history, customer information, or warranty status.
Frequently Asked Questions
What types of serial numbers can the Scanbot SDK read?
The Scanbot SDK reads printed alphanumeric serial numbers (a mix of letters and numbers). It's built to handle these across many surfaces and materials, adapting to different fonts, sizes, and layouts. Its capability extends to challenging situations, such as curved surfaces, worn labels, or low-contrast print.
Does the Scanbot Serial Number Scanner SDK work offline?
Yes, the Scanbot SDK operates fully offline. All scanning and data processing are performed directly on the user's device, meaning no internet connection is necessary. This design ensures functionality in remote locations and supports secure environments where data privacy is critical.
Is the Scanbot SDK GDPR compliant?
Yes, the Scanbot SDK is fully GDPR – compliant. Its on-device data processing model, where no data leaves the user's device, inherently supports privacy-first application development and aligns with the strictest data protection regulations like GDPR.



