What is SaaS exactly?
Most people have heard of companies like Shopify, Dropbox, and Salesforce. All of these are so-called software-as-a-service (SaaS) providers. But what is the difference between conventional software and SaaS?
Unlike traditional software licensing, which requires users to set up a server, install the application and configure it, SaaS applications typically operate on a cloud network. Users access them remotely via a web interface or an API. Hence, instead of licensing the application, it can be virtually “rented” for a monthly or annual fee.
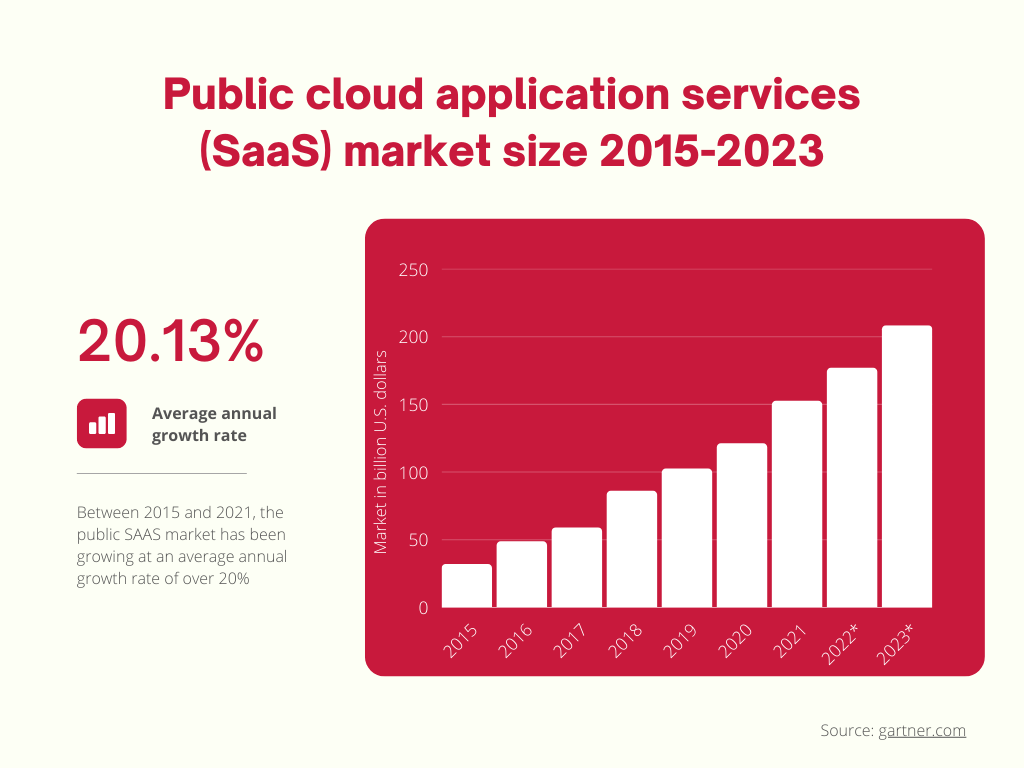
And the SaaS business model seems to be successful. The market has been expanding steadily at an average annual growth rate of over 20% (Gartner).
Let’s now explore the advantages that drive the success of SaaS — and its downsides.
What are the benefits of SaaS?
Lower cost
SaaS providers charge a monthly or yearly fee for their software service. There is no upfront purchasing cost or any maintenance cost, neither for the software itself nor the related servers. This pricing model is attractive for startups and small businesses because it is cheaper than a traditional in-house or licensing solution. SaaS providers can offer their software at a lower price because they can spread out development and maintenance costs over time.
Fast deployment
In the traditional software installation model, setting up new software is not only cost-intensive but also requires time. In the case of SaaS, the software is (almost) fully configured. SaaS customers can set up the application within hours or a few days. SaaS applications generally come with detailed best practices, facilitating initial usage and preventing problems.
Try before you buy
SaaS providers typically offer free trial periods or demo versions. These allow users to test software capabilities or new release features in advance without risk. Even large enterprises can test software extensively before signing a contract.
Scalability
SaaS solutions are cloud-based, meaning that the SaaS provider handles the server hardware. Hence, SaaS utilization can be flexibly scaled up or down. For the same reason, customers can begin using additional features quickly and without extra server costs.
What are the downsides of SaaS?
Data security
Data security is a core concern for companies opting for a SaaS application model. If any data is processed on an external server, providers must first satisfy all questions about the security of the data on this server.
Lack of control
As always with externally developed applications, control over features lies with a third party. Despite their downsides, in-house software applications can give organizations more control than hosted solutions. For instance, upgrades or feature changes typically cannot be deferred in SaaS — everyone must use the latest version.
An internet connection is required
Under the SaaS model, applications generally require an internet connection. If this connection is unstable or unavailable, working with these apps becomes challenging.
In sum, SaaS applications can add value to any business, large or small. Companies benefit from lower costs, short setup times, and the possibility to test software extensively before signing a contract. On the other hand, these applications usually depend on a stable internet connection, offer limited customization, and raise data security concerns.
These drawbacks can be addressed, however.
With the Scanbot SDK, data security and internet access are no problem. The Scanbot SDK is a SaaS product that enables companies to integrate Barcode Scanner SDK, Document scanner SDK, and data extraction into their mobile applications or websites. The Scanbot SDK works 100% offline, so the features are not dependent on a stable internet connection, and data security is assured.
If you would like to integrate this technology into your app, feel free to contact our solution experts. We are looking forward to help you find the perfect application for your use case.







