❓ How do barcode scanners work on smartphones?
Answer
TL;DR: Camera-based barcode scanners, such as smartphones, combine modern cameras with advanced image pre-processing technology and barcode scanner software. As a result, they can read both 1D and 2D barcodes.
Long answer:
Developed as an alternative to laser scanners, camera-based scanners have been in use since the 1990s. Initially, these were dedicated devices. However, with the quality of phone cameras dramatically improving, mobile barcode scanners have become widespread.
Advances in image processing, and machine learning especially, have also done their part.
Camera-based barcode scanners work as follows: After the user initiates the scan, the device camera takes a digital photo of a barcode. Now, the barcode scanner software optimizes this image for scanning. The image pre-processing techniques applied here are the foundation of a mobile scanner’s superior performance.
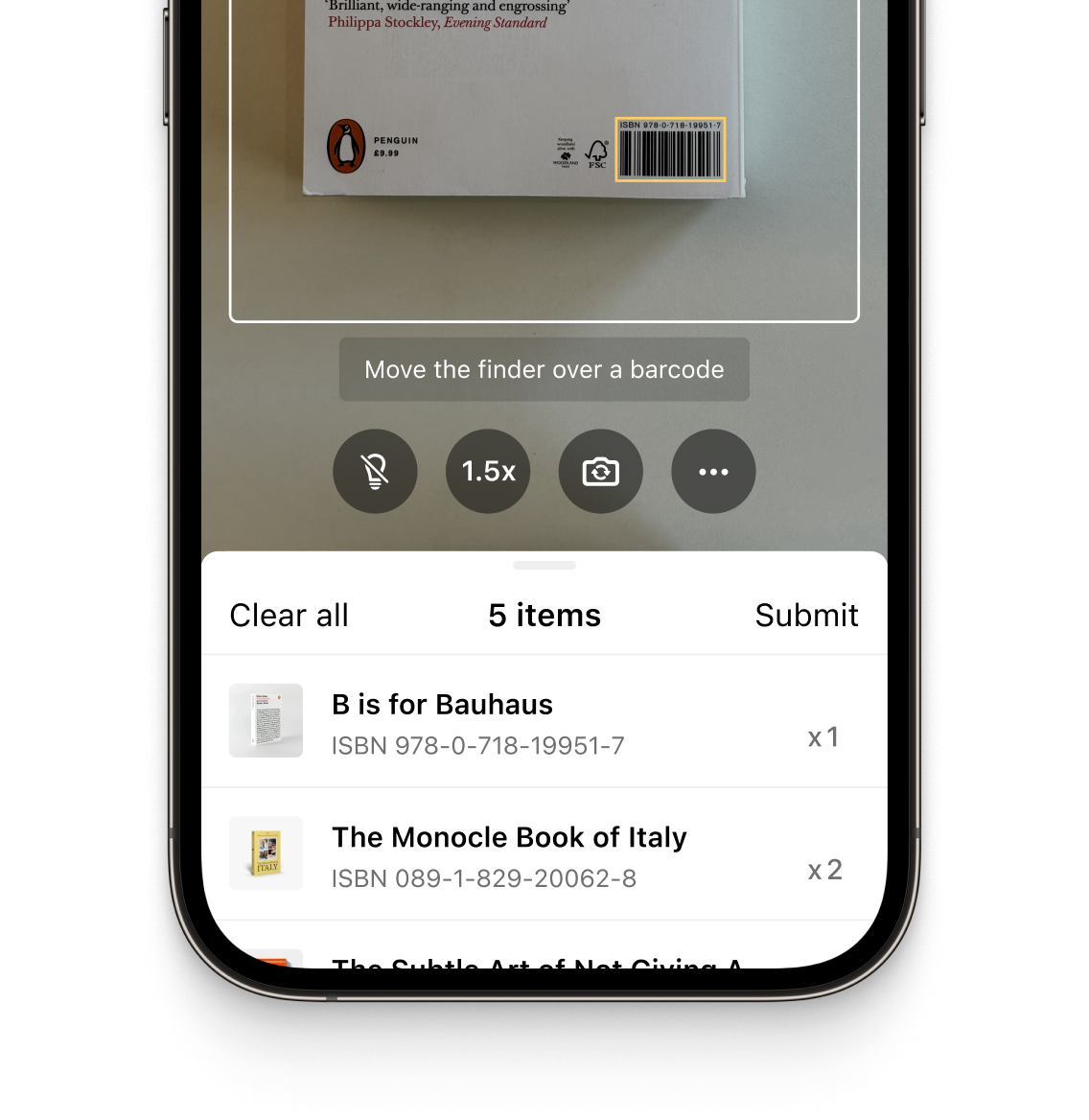
First, the image is converted to grayscale. Together with special filters, this reduces noise and enhances barcode edges. Afterward, binarization converts the image to black-and-white pixels.
Now, the software detects and identifies the barcode on the pre-processed image. Machine-learning algorithms analyze the barcode’s black-and-white pattern to interpret its information. This encoded data is then converted into readable text or numeric data.
Finally, the scanner software sends the decoded data to a connected device or database for further processing.
Camera-based barcode scanners vs. laser scanners
Camera-based barcode scanners are increasingly popular for several reasons. Most notably, they can read complex 2D barcodes – which laser scanners cannot.
Let’s take a step back to see why: A laser scanner’s scan line is a rapidly moving laser beam. When this line hits a barcode, its light is absorbed or reflected. In a black-and-white barcode, the black lines absorb more light and reflect less than the white lines. A light sensor converts these varying light intensities into an electrical signal, which is then processed by the scanner’s embedded electronics.
However large the barcode actually is, laser scanners only read a very thin, linear slice of it. This works well enough on 1D barcodes, but 2D barcodes are far more complex, two-dimensional patterns. They require full image capture for proper decoding.
This puts a limit on the applications for laser scanners. At the same time, the demand for 2D barcodes, such as QR codes, is growing in several industries.
Consequently, laser scanners are slowly being replaced by the more advanced camera-based barcode scanners. The latter are not only more versatile, but also more accurate, and perform reliably in challenging conditions. This is thanks to their advanced digital image pre-processing technology, which allows them to read damaged or blurry barcodes, even in low-light environments.
Modern software often comes with additional features that allow users to scan several barcodes simultaneously or consecutively. This streamlines scanning workflows, making them a perfect fit for demanding industries such as manufacturing or transportation.
Using mobile barcode scanners also has practical advantages. They run on standard smart devices – user-friendly, multi-purpose hardware with a wealth of functionalities. They are also easily scalable, as one barcode scanner app can be downloaded on as many devices as needed.
And finally: When paired with ruggedized devices, mobile barcode scanners excel even in harsh environments.
How to find suitable barcode scanner software
A quick Google search will throw up numerous barcode scanner libraries and SDKs that you can use to build an application.
Open-source solutions minimize the cost of the software proper, but they require deep knowledge of their library’s language. Just as importantly, they lack the fast support commercial solutions can offer. Though their communities’ work is commendable, their performance doesn’t compare.
Commercial barcode scanner SDKs with flat pricing are the most suitable for high-volume use cases. Thanks to constant development, these solutions deliver rapid bug fixes and regular updates that introduce new features and barcode symbologies.
With the Scanbot Barcode Scanner SDK, you can turn any smart device into a reliable barcode scanner. It scans all common 1D and 2D barcodes, even when they are blurry, damaged, or tiny, and performs reliably in less-than-ideal conditions, such as low lighting.See for yourself how it works in one of our free demo apps, or contact us at sdk@scanbot.io to learn more.

