This tutorial shows how to create a simple barcode scanning app in Flutter using the flutter_barcode_scanner package. While this library hasn’t been updated in years, it’s still widely used for both Android and iOS apps.
This guide covers installation, configuration, basic usage, and solutions to common problems. For this tutorial, we’ll focus on testing with an Android application.
Setting up the project
Before diving into the code, let’s set up the Flutter project and install the necessary dependencies.
Step 1: Create a new Flutter project
To create the Flutter project, open your terminal and run the following commands:
flutter create barcode_scanner_app
cd barcode_scanner_appStep 2: Add dependencies to pubspec.yaml
Now add the flutter_barcode_scanner package to barcode_scanner_app/pubspec.yaml.
You can either use the original package …
dependencies:
flutter:
sdk: flutter
flutter_barcode_scanner: ^2.0.0… or a fork that includes fixes for Android:
dependencies:
flutter:
sdk: flutter
flutter_barcode_scanner:
git:
url: https://github.com/decodevM/flutter_barcode_scanner.git
ref: masterTo install the dependencies, run the following command in your terminal:
flutter pub getWe’ll need to access the device camera to scan barcodes. Therefore, open android/app/src/main/AndroidManifest.xml and add the necessary permissions:
<uses-permission android:name="android.permission.CAMERA" />
<uses-feature android:name="android.hardware.camera" />Step 3: Fixes for Android building
To ensure compatibility with newer Android versions and resolve common build issues, apply the following fixes to your application.
1. Update minSdkVersion
Open android/app/build.gradle and set the minSdkVersion to at least 21:
defaultConfig {
minSdkVersion 21
targetSdkVersion 33
}2. Set the correct NDK version
This package requires a specific Android NDK version (27.0.12077973). First, check your installed NDK versions by running:
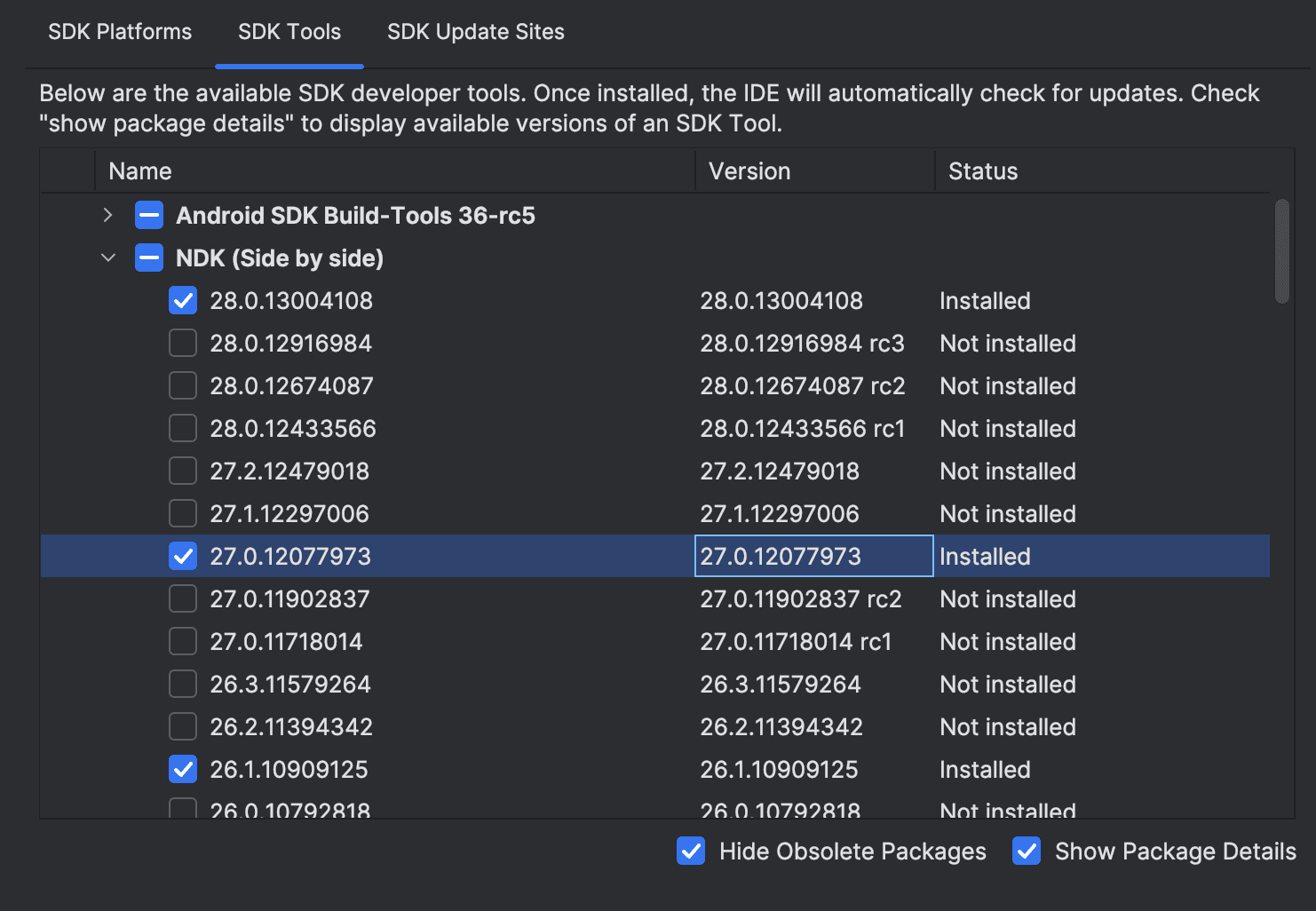
sdkmanager --list | grep ndk💡 You can also check the installed NDK versions in Android Studio:
- Go to Tools > SDK Manager.
- Open the SDK Tools tab.
- Check the Show Package Details box and look for NDK (Side by side). The installed versions will be listed there.
If the required version is missing, install it using the following command or via Android Studio’s SDK Manager:
sdkmanager "ndk;27.0.12077973"Then update android/app/build.gradle:
android {
ndkVersion "27.0.12077973"
}3. Fix namespace issue for Android Gradle Plugin (AGP 7.0+)
If you encounter a “Namespace not specified” error, manually add a namespace in the package directory. Navigate to the package location …
cd ~/.pub-cache/hosted/pub.dev/flutter_barcode_scanner-2.0.0/android… then add the following to the build.gradle file located there:
android {
namespace 'com.amolg.flutterbarcodescanner'
}Basic implementation
Now we’ll implement a minimal barcode scanning feature. To start, open lib/main.dart and import the required packages.
import 'package:flutter/material.dart';
import 'package:flutter/services.dart';
import 'package:flutter_barcode_scanner/flutter_barcode_scanner.dart';Next, define the main application:
void main() {
runApp(const MyApp());
}
class MyApp extends StatelessWidget {
const MyApp({super.key});
@override
Widget build(BuildContext context) {
return MaterialApp(
title: 'Barcode Scanner Demo',
theme: ThemeData(
colorScheme: ColorScheme.fromSeed(seedColor: Colors.deepPurple),
),
home: const MyHomePage(title: 'Barcode Scanner Demo'),
);
}
}We need to initialize the scanBarcode method (declared inside a try except block to handle errors) with four parameters:
class MyHomePage extends StatefulWidget {
const MyHomePage({super.key, required this.title});
final String title;
@override
State<MyHomePage> createState() => _MyHomePageState();
}
class _MyHomePageState extends State<MyHomePage> {
String _scanResult = "";
Future<void> scanCode() async {
String barcodeScanRes;
try {
barcodeScanRes = await FlutterBarcodeScanner.scanBarcode(
"#ff6666", // Red scanning line
"Cancel",
true, // Show flash toggle
ScanMode.BARCODE,
);
} on PlatformException {
barcodeScanRes = "Failed to scan";
}
setState(() {
_scanResult = barcodeScanRes;
});
}
@override
Widget build(BuildContext context) {
return Scaffold(
appBar: AppBar(
backgroundColor: Theme.of(context).colorScheme.inversePrimary,
title: Text(widget.title),
),
body: Center(
child: Column(
mainAxisAlignment: MainAxisAlignment.center,
children: <Widget>[
const Text('Scan Result:', style: TextStyle(fontSize: 16)),
const SizedBox(height: 8),
Text(
_scanResult.isEmpty ? 'No scan yet' : _scanResult,
style: const TextStyle(
fontSize: 20,
fontWeight: FontWeight.bold,
color: Colors.blue,
),
),
],
),
),
floatingActionButton: FloatingActionButton(
onPressed: scanCode,
tooltip: 'Scan Barcode',
child: const Icon(Icons.qr_code_scanner),
),
);
}
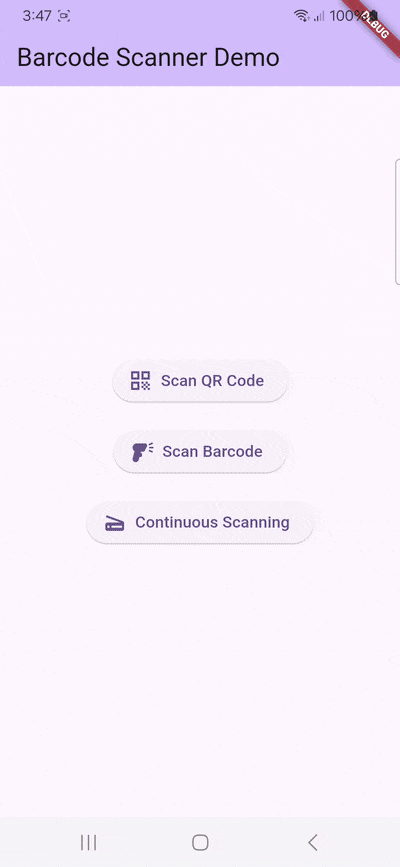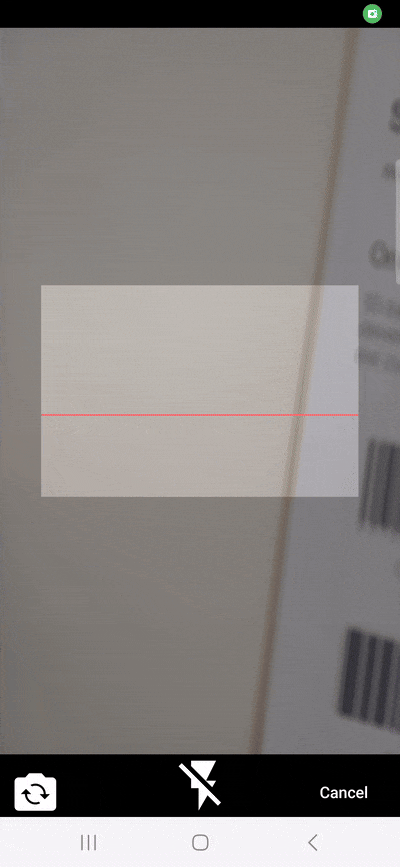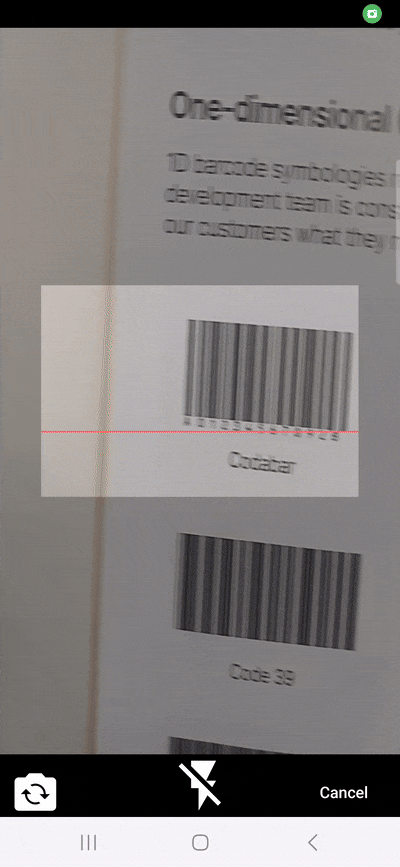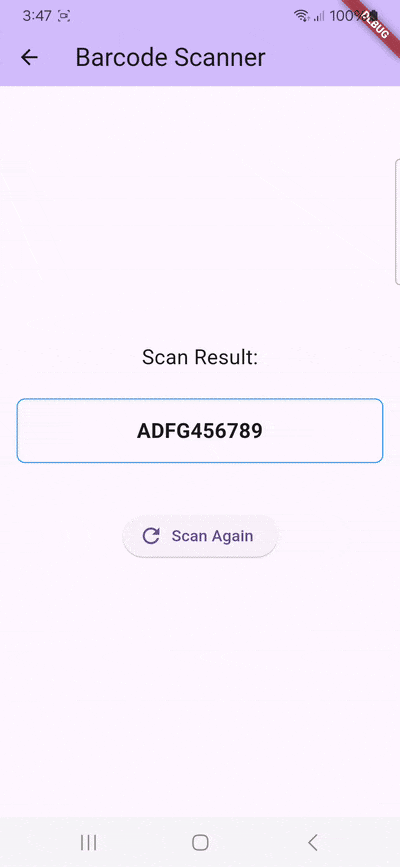
}With this, we’ve built a basic barcode scanning app. Try it out if you like:
flutter run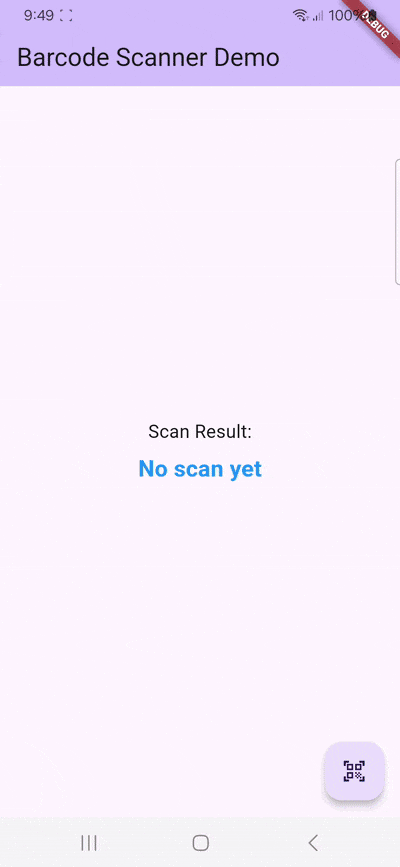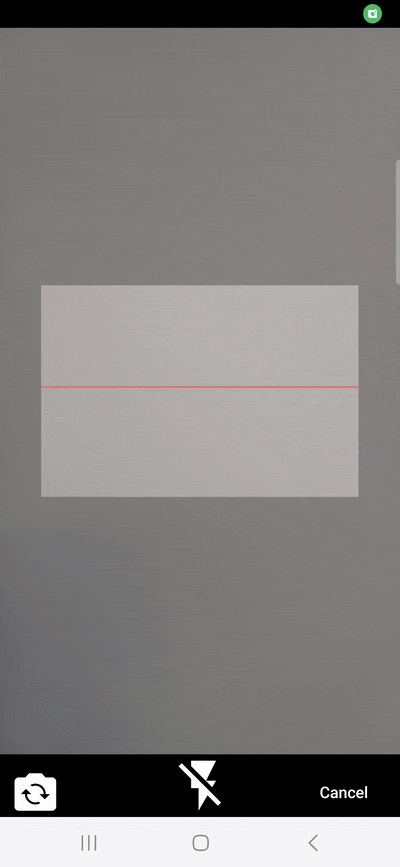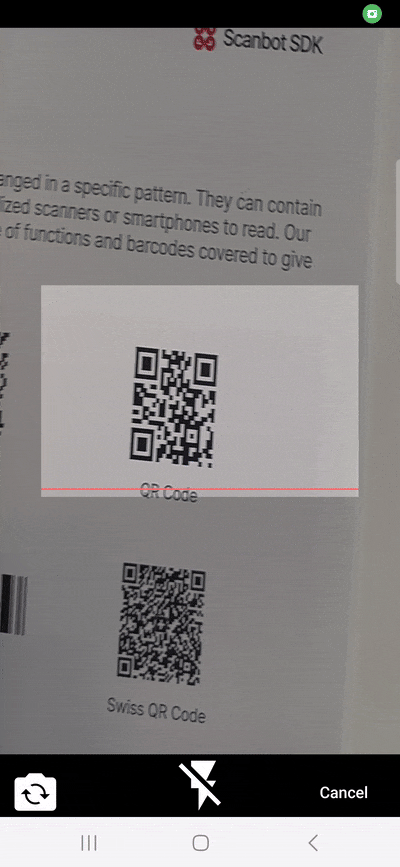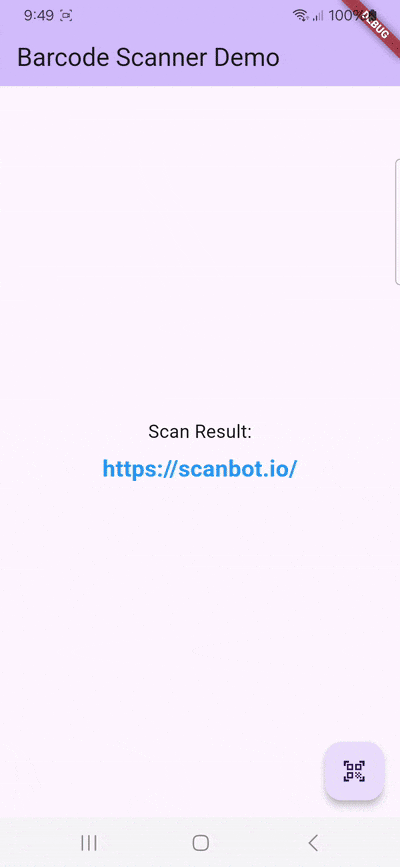
You might notice that the camera stream’s aspect ratio is wrong. Unfortunately, this is a common issue with the flutter_barcode_scanner package. More on this further down.
Advanced features
The flutter_barcode_scanner library provides additional capabilities to add to your barcode scanner app.
1. Different scanning modes
The flutter_barcode_scanner supports three scan modes:
| Scan Mode | Description |
|---|---|
ScanMode.BARCODE | Restricts scanning to 1D barcodes. |
ScanMode.QR | Restricts scanning to 2D barcodes. |
ScanMode.DEFAULT | Scans both 1D and 2D barcodes. |
Restricting scanning to certain barcode types prevents accidental scans and improves the scanner’s performance, as it doesn’t need to check for each supported symbology.
2. Customizing the scanner’s appearance
You can change the scanner’s appearance by modifying the following parameters:
| Parameter | Example Value | Description |
|---|---|---|
COLOR_CODE | "#ff6666" | HEX color for the scanning line. |
CANCEL_BUTTON_TEXT | "Cancel" | Custom text for the cancel button. |
isShowFlashIcon | true | Whether to show the flash toggle button. |
The following code snippet shows an example of how to define the appearance configurations:
Future<void> scanWithCustomAppearance() async {
String barcodeScanRes;
try {
barcodeScanRes = await FlutterBarcodeScanner.scanBarcode(
"#4CAF50", // Green scanning line
"Close", // Custom cancel button text
true, // Enable flash toggle
ScanMode.DEFAULT,
);
} on PlatformException {
barcodeScanRes = "Failed to scan";
}
setState(() {
_scanResult = barcodeScanRes;
});
}3. Continuous barcode scanning
By default, the scanner stops after detecting a barcode. To enable continuous scanning, you need to use a stream listener (listen), as shown in the following code snippet:
void startContinuousScanning() {
FlutterBarcodeScanner.getBarcodeStreamReceiver(
"#ff6666",
"Cancel",
true,
ScanMode.DEFAULT,
)?.listen((barcode) {
if (barcode != '-1') {
setState(() {
_scanResult = barcode;
});
}
});
}In the above code example, the scanner listens for barcodes (barcode). If the scan result is not -1, meaning it wasn’t canceled, it updates the _scanResult state to ensure all barcode results are available after the scanning stops.
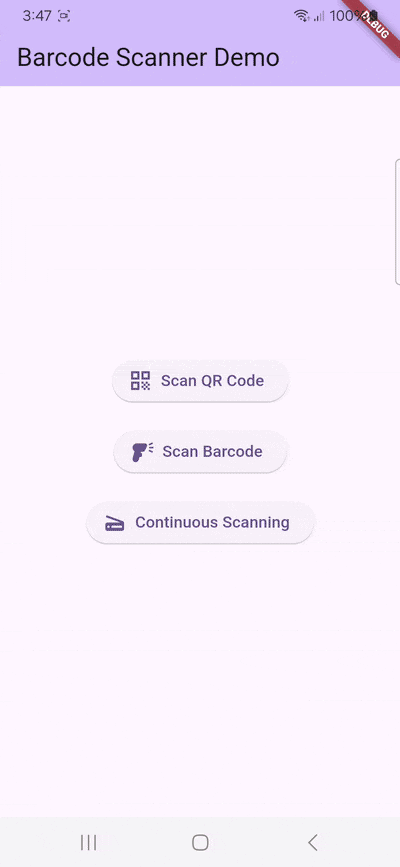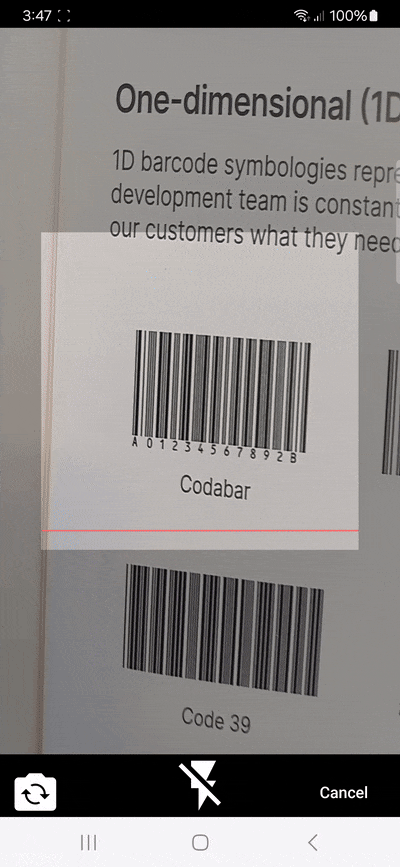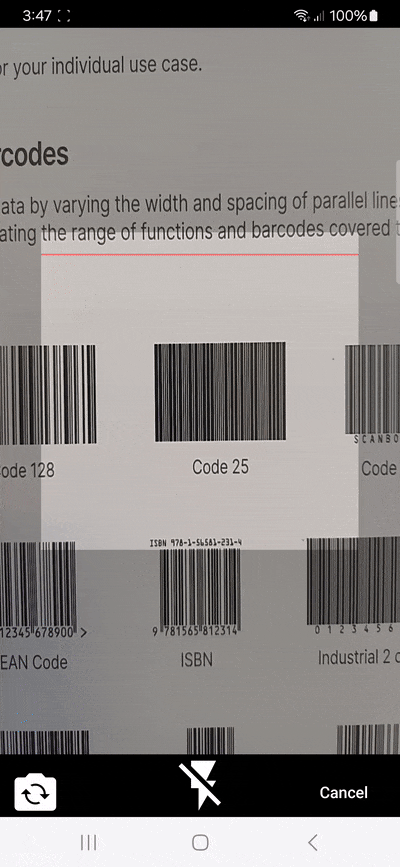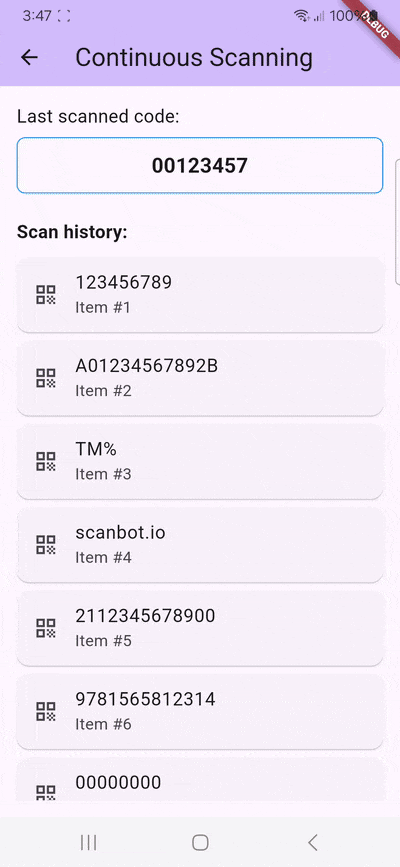
Unfortunately, the continuous scanning mode lacks an indication of which barcodes have been successfully scanned. Worse still, barcodes outside the viewfinder are also picked up, leading to unexpected entries in the results list. When using the flutter_barcode_scanner package in your project, you might want to remedy this with your own code.
Disadvantages of using the flutter_barcode_scanner package to scan barcodes
While the flutter_barcode_scanner package can be useful for quickly prototyping a Flutter app with barcode scanning functionalities, its lack of maintenance results in compatibility issues with modern Flutter, Android, and iOS environments. Issues users have faced when integrating the package into their Flutter apps include:
- Wrong aspect ratio of the camera stream
- Problems compiling with newer Flutter versions
- Incompatibility with older devices
- Black screen when trying to scan a barcode
- Crashes on startup
For companies that heavily rely on barcode scanning in their business processes, we recommend using an enterprise-grade solution instead.
Building a Flutter Barcode Scanner with the Scanbot SDK
We developed the Scanbot Barcode Scanner SDK to help enterprises overcome the hurdles presented by free barcode scanning software. Our goal was to have a developer-friendly solution available for a wide range of platforms that consistently delivers high-quality results – even in challenging circumstances.
With the SDK’s Ready-to-Use UI Components, you can even use an AR overlay to display multiple barcodes’ contents directly in the viewfinder, enhancing the scanning experience.


Setting up a Flutter app to scan 1D or 2D barcodes is straightforward. We’re going to follow these steps:
- Prepare the project.
- Install the SDK.
- Initialize the SDK.
- Implement the scanning modules.
- Start scanning barcodes!
Requirements
To develop Flutter applications for Android and iOS, ensure you have the following:
- Flutter SDK: Download the latest version for your OS.
- Dart SDK: No separate installation needed, since it’s integrated with Flutter.
- The right IDEs for your target platforms:
- Android Studio to develop for Android. It includes the Android SDK and AVD Manager.
- Xcode for iOS development on macOS.
- You can also use Visual Studio Code, which supports Flutter plugins.
⚠️ A note to Windows users: A Mac is necessary to build and test iOS apps. Consider using a remote Mac service or a physical Mac as a build server.
1. Preparing the project
First, create a new directory for your project and navigate into it:
mkdir test-flutter
cd test-flutter
Create a new Flutter project:
flutter create test_barcode_scanner
cd test_barcode_scanner
Since we need access to the device camera to scan barcodes, let’s add the necessary camera permissions for Android and iOS.
Add camera permissions to android/app/src/main/AndroidManifest.xml:
<uses-permission android:name="android.permission.CAMERA"/>
<uses-feature android:name="android.hardware.camera" />
And in ios/Runner/Info.plist:
<key>NSCameraUsageDescription</key>
<string>We need camera access to scan barcodes.</string>
2. Installing the SDK
Add the Scanbot Flutter Barcode Scanner package to your pubspec.yaml:
dependencies:
flutter:
sdk: flutter
barcode_scanner: ^5.1.0
Run the following commnand to install the packages:
flutter pub get
💡 Please refer to our changelog for the latest version of the Barcode Scanner SDK.
Now that the project is set up, we can integrate the barcode scanning functionalities.
3. Initializing the SDK
Initialize the SDK in main.dart:
import 'package:flutter/material.dart';
import 'package:barcode_scanner/scanbot_barcode_sdk_v2.dart';
const BARCODE_SDK_LICENSE_KEY = "";
void main() {
runApp(const MyApp());
}
class MyApp extends StatelessWidget {
const MyApp({super.key});
@override
Widget build(BuildContext context) {
return const MaterialApp(
home: MyHomePage(),
);
}
}
class MyHomePage extends StatefulWidget {
const MyHomePage({super.key});
@override
State<MyHomePage> createState() => _MyHomePageState();
}
class _MyHomePageState extends State<MyHomePage> {
@override
void initState() {
super.initState();
_initScanbotSdk();
}
Future<void> _initScanbotSdk() async {
var config = ScanbotSdkConfig(
licenseKey: BARCODE_SDK_LICENSE_KEY,
loggingEnabled: true,
);
try {
await ScanbotBarcodeSdk.initScanbotSdk(config);
print('Scanbot SDK initialized successfully');
} catch (e) {
print('Error initializing Scanbot SDK: $e');
}
}
@override
Widget build(BuildContext context) {
...
}
💡 Without a license key, our SDK only runs for 60 seconds per session. This is more than enough for the purposes of our tutorial, but if you like, you can generate a license key using your applicationId.
4. Implementing the scanning modes
The SDK’s RTU UI components make it easy to deploy our Flutter Barcode Scanner package’s different scanning modes in your app. Let’s start with the simplest use case: single-barcode scanning.
Implement the barcode scanning functionality:
void _startBarcodeScanning() async {
try {
// Create the default configuration object.
var configuration = BarcodeScannerConfiguration();
// Initialize the use case for single scanning.
var scanningMode = SingleScanningMode();
// Enable and configure the confirmation sheet.
scanningMode.confirmationSheetEnabled = true;
scanningMode.sheetColor = ScanbotColor("#FFFFFF");
// Hide/unhide the barcode image.
scanningMode.barcodeImageVisible = true;
// Configure the barcode title of the confirmation sheet.
scanningMode.barcodeTitle.visible = true;
scanningMode.barcodeTitle.color = ScanbotColor("#000000");
// Configure the barcode subtitle of the confirmation sheet.
scanningMode.barcodeSubtitle.visible = true;
scanningMode.barcodeSubtitle.color = ScanbotColor("#000000");
// Configure the cancel button of the confirmation sheet.
scanningMode.cancelButton.text = "Close";
scanningMode.cancelButton.foreground.color = ScanbotColor("#C8193C");
scanningMode.cancelButton.background.fillColor = ScanbotColor("#00000000");
// Configure the submit button of the confirmation sheet.
scanningMode.submitButton.text = "Submit";
scanningMode.submitButton.foreground.color = ScanbotColor("#FFFFFF");
scanningMode.submitButton.background.fillColor = ScanbotColor("#C8193C");
// Configure other parameters, pertaining to single-scanning mode as needed.
configuration.useCase = scanningMode;
// Set an array of accepted barcode types.
// configuration.recognizerConfiguration.barcodeFormats = [
// scanbotV2.BarcodeFormat.AZTEC,
// scanbotV2.BarcodeFormat.PDF_417,
// scanbotV2.BarcodeFormat.QR_CODE,
// scanbotV2.BarcodeFormat.MICRO_QR_CODE,
// scanbotV2.BarcodeFormat.MICRO_PDF_417,
// scanbotV2.BarcodeFormat.ROYAL_MAIL,
/// .....
// ];
// Configure other parameters as needed.
var result = await ScanbotBarcodeSdk.startBarcodeScanner(configuration);
if(result.operationResult == OperationResult.SUCCESS)
{
// TODO: present barcode result as needed
print(result.value?.items.first.type?.name);
}
} catch (e) {
print('Error: $e');
}
}
Now let’s go to the build method and add the button on the start screen so it calls our _startBarcodeScanning method when clicked:
@override
Widget build(BuildContext context) {
return Scaffold(
appBar: AppBar(
title: const Text('Barcode Scanner'),
),
body: Center(
child: ElevatedButton(
onPressed: _startBarcodeScanning,
style: ElevatedButton.styleFrom(
padding: const EdgeInsets.symmetric(vertical: 20, horizontal: 40),
textStyle: const TextStyle(fontSize: 18),
),
child: const Text("Start single-barcode scanning"),
),
),
);
}
If you like, you can build and run the app to see if everything is working correctly so far:
flutter run
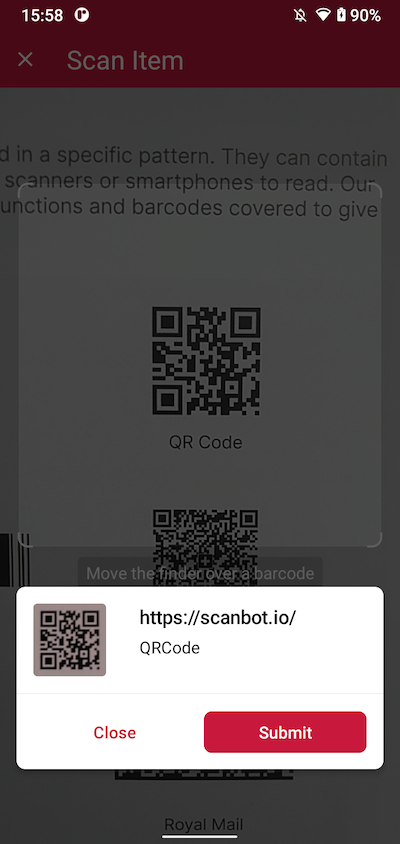
In the next step, we’re going to insert both the multi-barcode scanning and the AR overlay modules.
Let’s create two more methods, _startBarcodeMultiScanning and _startAROverlay:
void _startBarcodeMultiScanning() async {
try {
// Create the default configuration object.
var configuration = BarcodeScannerConfiguration();
// Initialize the use case for multiple scanning.
var scanningMode = MultipleScanningMode();
// Set the counting mode.
scanningMode.mode = MultipleBarcodesScanningMode.COUNTING;
// Set the sheet mode for the barcodes preview.
scanningMode.sheet.mode = SheetMode.COLLAPSED_SHEET;
// Set the height for the collapsed sheet.
scanningMode.sheet.collapsedVisibleHeight = CollapsedVisibleHeight.LARGE;
// Enable manual count change.
scanningMode.sheetContent.manualCountChangeEnabled = true;
// Set the delay before same barcode counting repeat.
scanningMode.countingRepeatDelay = 1000;
// Configure the submit button.
scanningMode.sheetContent.submitButton.text = "Submit";
scanningMode.sheetContent.submitButton.foreground.color =
ScanbotColor("#000000");
// Configure other parameters, pertaining to multiple-scanning mode as needed.
configuration.useCase = scanningMode;
// Set an array of accepted barcode types.
// configuration.recognizerConfiguration.barcodeFormats = [
// BarcodeFormat.AZTEC,
// BarcodeFormat.PDF_417,
// BarcodeFormat.QR_CODE,
// BarcodeFormat.MICRO_QR_CODE,
// BarcodeFormat.MICRO_PDF_417,
// BarcodeFormat.ROYAL_MAIL,
/// .....
// ];
// Configure other parameters as needed.
var result = await ScanbotBarcodeSdk.startBarcodeScanner(configuration);
if(result.operationResult == OperationResult.SUCCESS)
{
// TODO: present barcode result as needed
print(result.value?.items.first.type?.name);
}
} catch (e) {
print('Error: $e');
}
}
void _startAROverlay() async {
try {
// Create the default configuration object.
var configuration = new BarcodeScannerConfiguration();
// Configure the usecase.
var usecase = new MultipleScanningMode();
usecase.mode = MultipleBarcodesScanningMode.UNIQUE;
usecase.sheet.mode = SheetMode.COLLAPSED_SHEET;
usecase.sheet.collapsedVisibleHeight = CollapsedVisibleHeight.SMALL;
// Configure AR Overlay.
usecase.arOverlay.visible = true;
usecase.arOverlay.automaticSelectionEnabled = false;
// Set the configured usecase.
configuration.useCase = usecase;
// Set an array of accepted barcode types.
// configuration.recognizerConfiguration.barcodeFormats = [
// BarcodeFormat.AZTEC,
// BarcodeFormat.PDF_417,
// BarcodeFormat.QR_CODE,
// BarcodeFormat.MICRO_QR_CODE,
// BarcodeFormat.MICRO_PDF_417,
// BarcodeFormat.ROYAL_MAIL,
/// .....
// ];
var result = await ScanbotBarcodeSdk.startBarcodeScanner(configuration);
if (result.operationResult == OperationResult.SUCCESS) {
// TODO: present barcode result as needed
print(result.value?.items.first.type?.name);
}
} catch (e) {
print('Error: $e');
}
}
And let’s not forget to insert the buttons:
@override
Widget build(BuildContext context) {
return Scaffold(
appBar: AppBar(
title: const Text('Barcode Scanner'),
),
body: Center(
child: Column(
mainAxisAlignment: MainAxisAlignment.center,
children: [
ElevatedButton(
onPressed: _startBarcodeScanning,
style: ElevatedButton.styleFrom(
padding: const EdgeInsets.symmetric(vertical: 20, horizontal: 40),
textStyle: const TextStyle(fontSize: 18),
),
child: const Text("Start single-barcode scanning"),
),
const SizedBox(height: 20),
ElevatedButton(
onPressed: _startBarcodeMultiScanning,
style: ElevatedButton.styleFrom(
padding: const EdgeInsets.symmetric(vertical: 20, horizontal: 40),
textStyle: const TextStyle(fontSize: 18),
),
child: const Text("Start multi-barcode scanning"),
),
const SizedBox(height: 20),
ElevatedButton(
onPressed: _startAROverlay,
style: ElevatedButton.styleFrom(
padding: const EdgeInsets.symmetric(vertical: 20, horizontal: 40),
textStyle: const TextStyle(fontSize: 18),
),
child: const Text("Start the AR overlay"),
),
],
),
),
);
}
Your final main.dart should look something like this:
import 'package:flutter/material.dart';
import 'package:barcode_scanner/scanbot_barcode_sdk_v2.dart';
const BARCODE_SDK_LICENSE_KEY = "";
void main() {
runApp(const MyApp());
}
class MyApp extends StatelessWidget {
const MyApp({super.key});
@override
Widget build(BuildContext context) {
return const MaterialApp(
home: MyHomePage(),
);
}
}
class MyHomePage extends StatefulWidget {
const MyHomePage({super.key});
@override
State<MyHomePage> createState() => _MyHomePageState();
}
class _MyHomePageState extends State<MyHomePage> {
@override
void initState() {
super.initState();
_initScanbotSdk();
}
Future<void> _initScanbotSdk() async {
var config = ScanbotSdkConfig(
licenseKey: BARCODE_SDK_LICENSE_KEY,
loggingEnabled: true,
);
try {
await ScanbotBarcodeSdk.initScanbotSdk(config);
print('Scanbot SDK initialized successfully');
} catch (e) {
print('Error initializing Scanbot SDK: $e');
}
}
@override
Widget build(BuildContext context) {
return Scaffold(
appBar: AppBar(
title: const Text('Barcode Scanner'),
),
body: Center(
child: Column(
mainAxisAlignment: MainAxisAlignment.center,
children: [
ElevatedButton(
onPressed: _startBarcodeScanning,
style: ElevatedButton.styleFrom(
padding: const EdgeInsets.symmetric(vertical: 20, horizontal: 40),
textStyle: const TextStyle(fontSize: 18),
),
child: const Text("Start single-barcode scanning"),
),
const SizedBox(height: 20),
ElevatedButton(
onPressed: _startBarcodeMultiScanning,
style: ElevatedButton.styleFrom(
padding: const EdgeInsets.symmetric(vertical: 20, horizontal: 40),
textStyle: const TextStyle(fontSize: 18),
),
child: const Text("Start multi-barcode scanning"),
),
const SizedBox(height: 20),
ElevatedButton(
onPressed: _startAROverlay,
style: ElevatedButton.styleFrom(
padding: const EdgeInsets.symmetric(vertical: 20, horizontal: 40),
textStyle: const TextStyle(fontSize: 18),
),
child: const Text("Start the AR overlay"),
),
],
),
),
);
}
void _startBarcodeScanning() async {
try {
// Create the default configuration object.
var configuration = BarcodeScannerConfiguration();
// Initialize the use case for single scanning.
var scanningMode = SingleScanningMode();
// Enable and configure the confirmation sheet.
scanningMode.confirmationSheetEnabled = true;
scanningMode.sheetColor = ScanbotColor("#FFFFFF");
// Hide/unhide the barcode image.
scanningMode.barcodeImageVisible = true;
// Configure the barcode title of the confirmation sheet.
scanningMode.barcodeTitle.visible = true;
scanningMode.barcodeTitle.color = ScanbotColor("#000000");
// Configure the barcode subtitle of the confirmation sheet.
scanningMode.barcodeSubtitle.visible = true;
scanningMode.barcodeSubtitle.color = ScanbotColor("#000000");
// Configure the cancel button of the confirmation sheet.
scanningMode.cancelButton.text = "Close";
scanningMode.cancelButton.foreground.color = ScanbotColor("#C8193C");
scanningMode.cancelButton.background.fillColor = ScanbotColor("#00000000");
// Configure the submit button of the confirmation sheet.
scanningMode.submitButton.text = "Submit";
scanningMode.submitButton.foreground.color = ScanbotColor("#FFFFFF");
scanningMode.submitButton.background.fillColor = ScanbotColor("#C8193C");
// Configure other parameters, pertaining to single-scanning mode as needed.
configuration.useCase = scanningMode;
// Set an array of accepted barcode types.
// configuration.recognizerConfiguration.barcodeFormats = [
// scanbotV2.BarcodeFormat.AZTEC,
// scanbotV2.BarcodeFormat.PDF_417,
// scanbotV2.BarcodeFormat.QR_CODE,
// scanbotV2.BarcodeFormat.MICRO_QR_CODE,
// scanbotV2.BarcodeFormat.MICRO_PDF_417,
// scanbotV2.BarcodeFormat.ROYAL_MAIL,
/// .....
// ];
// Configure other parameters as needed.
var result = await ScanbotBarcodeSdk.startBarcodeScanner(configuration);
if(result.operationResult == OperationResult.SUCCESS)
{
// TODO: present barcode result as needed
print(result.value?.items.first.type?.name);
}
} catch (e) {
print('Error: $e');
}
}
void _startBarcodeMultiScanning() async {
try {
// Create the default configuration object.
var configuration = BarcodeScannerConfiguration();
// Initialize the use case for multiple scanning.
var scanningMode = MultipleScanningMode();
// Set the counting mode.
scanningMode.mode = MultipleBarcodesScanningMode.COUNTING;
// Set the sheet mode for the barcodes preview.
scanningMode.sheet.mode = SheetMode.COLLAPSED_SHEET;
// Set the height for the collapsed sheet.
scanningMode.sheet.collapsedVisibleHeight = CollapsedVisibleHeight.LARGE;
// Enable manual count change.
scanningMode.sheetContent.manualCountChangeEnabled = true;
// Set the delay before same barcode counting repeat.
scanningMode.countingRepeatDelay = 1000;
// Configure the submit button.
scanningMode.sheetContent.submitButton.text = "Submit";
scanningMode.sheetContent.submitButton.foreground.color =
ScanbotColor("#000000");
// Configure other parameters, pertaining to multiple-scanning mode as needed.
configuration.useCase = scanningMode;
// Set an array of accepted barcode types.
// configuration.recognizerConfiguration.barcodeFormats = [
// BarcodeFormat.AZTEC,
// BarcodeFormat.PDF_417,
// BarcodeFormat.QR_CODE,
// BarcodeFormat.MICRO_QR_CODE,
// BarcodeFormat.MICRO_PDF_417,
// BarcodeFormat.ROYAL_MAIL,
/// .....
// ];
// Configure other parameters as needed.
var result = await ScanbotBarcodeSdk.startBarcodeScanner(configuration);
if(result.operationResult == OperationResult.SUCCESS)
{
// TODO: present barcode result as needed
print(result.value?.items.first.type?.name);
}
} catch (e) {
print('Error: $e');
}
}
void _startAROverlay() async {
try {
// Create the default configuration object.
var configuration = new BarcodeScannerConfiguration();
// Configure the usecase.
var usecase = new MultipleScanningMode();
usecase.mode = MultipleBarcodesScanningMode.UNIQUE;
usecase.sheet.mode = SheetMode.COLLAPSED_SHEET;
usecase.sheet.collapsedVisibleHeight = CollapsedVisibleHeight.SMALL;
// Configure AR Overlay.
usecase.arOverlay.visible = true;
usecase.arOverlay.automaticSelectionEnabled = false;
// Set the configured usecase.
configuration.useCase = usecase;
// Set an array of accepted barcode types.
// configuration.recognizerConfiguration.barcodeFormats = [
// BarcodeFormat.AZTEC,
// BarcodeFormat.PDF_417,
// BarcodeFormat.QR_CODE,
// BarcodeFormat.MICRO_QR_CODE,
// BarcodeFormat.MICRO_PDF_417,
// BarcodeFormat.ROYAL_MAIL,
/// .....
// ];
var result = await ScanbotBarcodeSdk.startBarcodeScanner(configuration);
if (result.operationResult == OperationResult.SUCCESS) {
// TODO: present barcode result as needed
print(result.value?.items.first.type?.name);
}
} catch (e) {
print('Error: $e');
}
}
}
Now let’s build and run the app again so we can try out our new scanning modules.
5. Scanning some barcodes!
Now you can go ahead and scan 1D and 2D barcodes – one after the other, many at the same time, and even with an AR overlay that lets you preview their values!

And if you’re in need of some sample barcodes for testing purposes, we’ve got you covered:
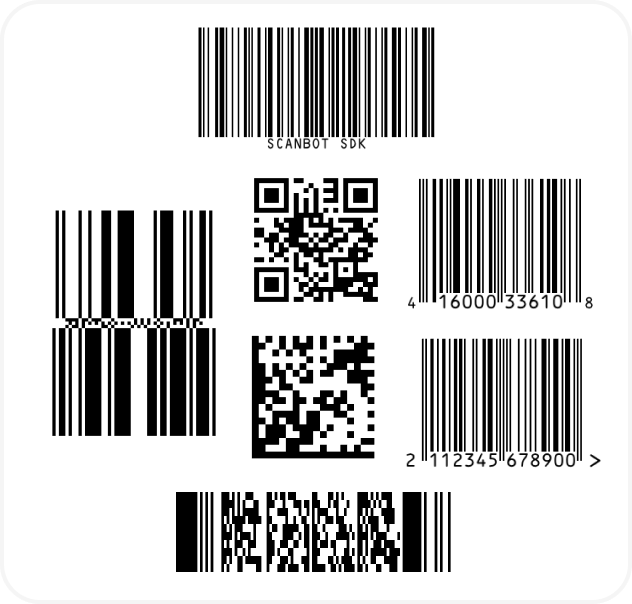

If this tutorial has piqued your interest in integrating barcode scanning functionalities into your Flutter app, make sure to take a look at our SDK’s other neat features in our documentation.
Should you have questions about this tutorial or ran into any issues, we’re happy to help! Just shoot us an email via tutorial-support@scanbot.io.
Happy coding!







