In this tutorial, you’ll learn how to build a cross-platform mobile app for scanning barcodes using Capacitor and Google’s ML Kit.
To integrate the scanning functionalities, you’ll use @capacitor-mlkit/barcode-scanning, a wrapper around ML Kit that streamlines its integration into Capacitor projects.
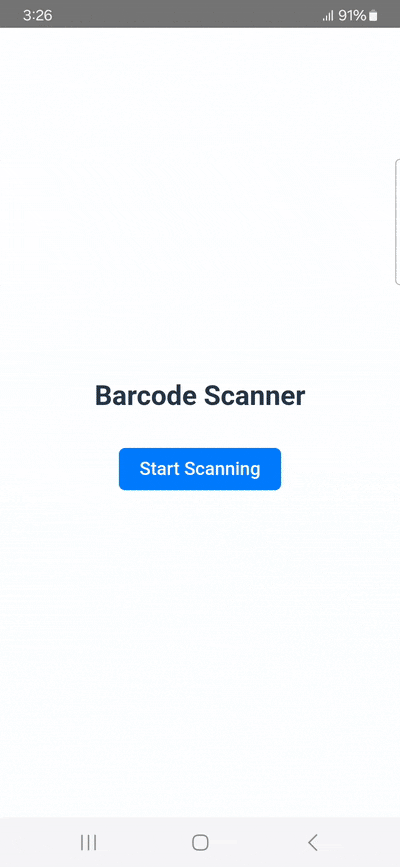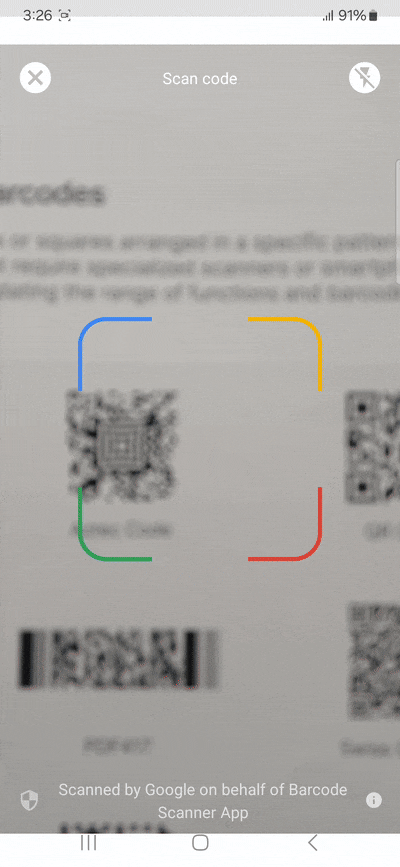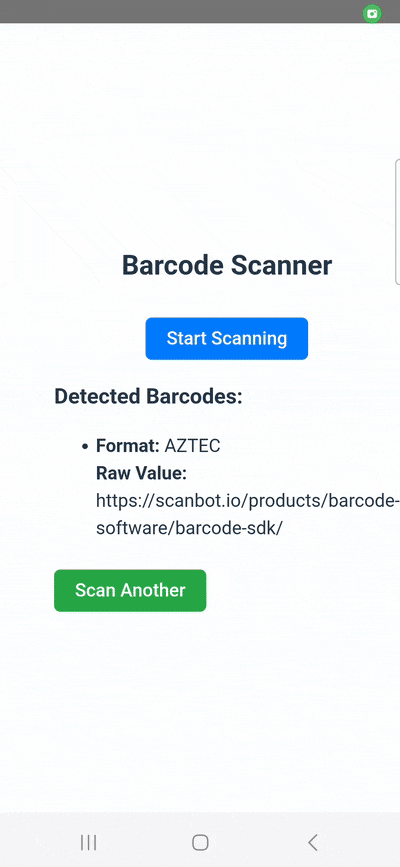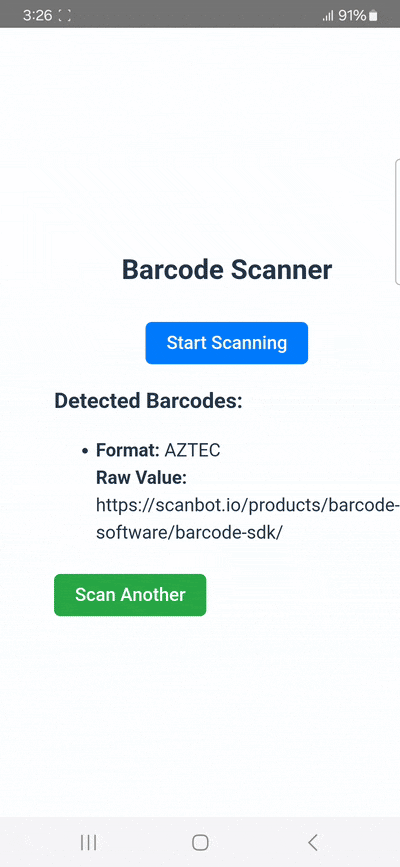
Building the app requires the following steps:
- Setting up the project
- Installing the barcode scanning plugin
- Setting up permissions
- Implementing the barcode scanning feature
Prerequisites
Before getting started, make sure your environment is ready.
Core requirements:
- Node.js version 20.19 or higher
For Android development:
- Android Studio Jellyfish (2024.2.1) or higher
- Android SDK (API 22 or higher), Platforms and Developer Tools
For iOS development:
- macOS with Xcode 16 or higher
- Homebrew
- CocoaPods (
brew install cocoapods) - Xcode Command Line Tools (
xcode-select --install)
Since scanning barcodes requires camera access, we recommend testing the app on a physical device.
Developing Capacitor applications can be done via the CLI or using the VS Code extension. You also have the option to use Capacitor with different frameworks. In this tutorial, we’ll use CLI commands and Capacitor with React. However, feel free to follow along using whatever option suits you best.
Step 1: Set up the project
First, create a new React project using Vite.
npm create vite@latest barcode-scanner-app -- --template reactThen navigate into your project directory.
cd barcode-scanner-appNext, install the Capacitor core JavaScript runtime and Command Line Interface:
npm install @capacitor/core @capacitor/cliAnd initialize the Capacitor configuration:
npx cap initEnter your app’s name (e.g., “Barcode Scanner App”) and App package ID (e.g., “com.barcodescanner.app”) when prompted.
Now, add Android and iOS:
npm install @capacitor/android @capacitor/ios
npx cap add android
npx cap add iosStep 2: Install the barcode scanning plugin
Now you can install the @capacitor-mlkit/barcode-scanning package via npm.
npm install @capacitor-mlkit/barcode-scanningStep 3: Set up Android & iOS permissions
To configure camera access for Android, open android/app/src/main/AndroidManifest.xml and add this line to the <manifest> tag:
<uses-permission android:name="android.permission.CAMERA" />For iOS, open ios/App/Podfile and set the deployment target to at least 15.5 (this prevents CocoaPods version issues).
platform :ios, '15.5'Then open ios/App/App/Info.plist and add the camera permission description inside the <dict> block.
<key>NSCameraUsageDescription</key>
<string>The app enables the scanning of various barcodes.</string>Step 4: Implement the barcode scanning feature
Create a new file src/components/BarcodeScannerView.jsx and paste the following code to set up a barcode scanner component:
import React, { useState } from 'react';
import { BarcodeScanner } from '@capacitor-mlkit/barcode-scanning';
export default function BarcodeScannerView() {
const [barcodes, setBarcodes] = useState([]);
const [scanning, setScanning] = useState(false);
const startScan = async () => {
try {
setScanning(true);
setBarcodes([]);
// Request camera permission
const perm = await BarcodeScanner.requestPermissions();
if (perm.camera !== 'granted') {
alert('Camera permission not granted');
setScanning(false);
return;
}
// Start scanning
const { barcodes } = await BarcodeScanner.scan();
setBarcodes(barcodes);
} catch (err) {
console.error(err);
alert('Error while scanning: ' + err.message);
} finally {
setScanning(false);
}
};
return (
<div style={{ textAlign: 'center', padding: 20 }}>
<h2>Barcode Scanner</h2>
{!scanning && (
<button
onClick={startScan}
style={{
background: '#007bff',
color: 'white',
padding: '10px 20px',
border: 'none',
borderRadius: '6px',
cursor: 'pointer',
marginTop: 10,
}}
>
Start Scanning
</button>
)}
{scanning && <p>📷 Scanning in progress... hold still.</p>}
{barcodes.length > 0 && (
<div style={{ marginTop: 20, textAlign: 'left' }}>
<h3>Detected Barcodes:</h3>
<ul>
{barcodes.map((code, i) => (
<li key={i}>
<strong>Format:</strong> {code.format}<br />
<strong>Raw Value:</strong> {code.rawValue}
</li>
))}
</ul>
<button
onClick={startScan}
style={{
background: '#28a745',
color: 'white',
padding: '10px 20px',
border: 'none',
borderRadius: '6px',
cursor: 'pointer',
marginTop: 10,
}}
>
Scan Another
</button>
</div>
)}
</div>
);
}This component uses React’s useState hook to manage its behavior, tracking whether it is currently scanning and storing any barcodes that are detected.
When the user clicks the “Start Scanning” button, the asynchronous startScan function is called. This function first checks and requests camera permissions using BarcodeScanner.requestPermissions(). If permission is denied, it alerts the user and stops. If permission is granted, it calls BarcodeScanner.scan(), which opens the camera, performs the scan, and then returns the detected data. The component then updates the state with the raw value and format of the new barcodes.
Now, import and use the component in your App.jsx file by replacing its contents with the following code:
import './App.css'
import BarcodeScannerView from './components/BarcodeScannerView.jsx'
function App() {
return (
<>
<BarcodeScannerView />
</>
)
}
export default AppNow build your app and sync the native projects.
npm run build
npx cap syncFinally, run the app on Android and iOS using the following commands:
Android:
npx cap run androidiOS:
npx cap run ios
Common issues & fixes
| Issue | Cause | Fix |
|---|---|---|
GoogleMLKit/BarcodeScanning requires higher iOS target | iOS target below 15.5 | Set platform :ios, '15.5' in Podfile and run pod install. |
Unable to read property list | Malformed Info.plist | Keep everything inside <dict>. Make sure tags follow each other. |
Camera permission not granted | iOS or Android permission missing | Refer to step 3 of this tutorial. |
Signing for "App" requires a development team... | Xcode requires every iOS app to be signed with a valid development team certificate before it can be built or run on a real device. | Open your project in Xcode, select the App Target → Signing & Capabilities tab → under Team, choose your Apple ID or development team. If you don’t have one, go to Xcode → Settings → Accounts and add your Apple ID first. |
Conclusion
This concludes our tutorial on how to set up a simple barcode scanning app using the Capacitor ML Kit barcode scanning plugin.
Free solutions like this one can be great for prototyping and personal projects. However, they have their drawbacks.
Since barcode scanning plugin is a wrapper for Google’s ML Kit, its functionality depends entirely on this third-party library. Companies relying on ML Kit for their scanning needs won’t be able to submit feature requests nor count on help when things don’t work as expected.
We developed the Scanbot Barcode Scanner SDK to help companies overcome these hurdles. Our goal was to provide a developer-friendly solution for a wide range of platforms that consistently delivers high-quality results, even in challenging circumstances – enterprise-grade support included.
In the following tutorial, we’ll show you how to set up a powerful cross-platform barcode scanner using Capacitor, Ionic, and the Scanbot SDK.
Building an Ionic Capacitor barcode scanner app with the Scanbot SDK
To set up our app, we’ll follow these steps:
- Preparing the project
- Installing the SDK
- Initializing the SDK
- Implementing the scanning modules
Thanks to the SDK’s Ready-to-Use UI Components, we’ll have an intuitive user interface out of the box.


Developing Capacitor applications can be done via CLI or using the VS Code extension. In this tutorial we will use CLI commands. However, feel free to follow along using whatever option suits you best.
Capacitor can be used with different frameworks. In this tutorial, we will use Capacitor with Ionic and Angular. Again, these choices depend on your needs and prior knowledge.
Since we’ll use Ionic in this tutorial, you also need to install the Ionic CLI if you haven’t already:
npm install -g @ionic/cliStep 1: Prepare the project
To start creating your Capacitor app with Ionic using the CLI, run the following command in the terminal, which will create a blank project with some recommended Capacitor dependencies:
ionic start CapacitorTutorial blank --capacitor --type angular-standalone --package-id io.scanbot.tutorial.capacitor⚠️ When using your own license, make sure that the package-id is the same as the application/bundle ID associated with it.
Generate the native projects
Now, let’s add the Android and iOS platforms to our project.
Navigate into the project directory:
cd CapacitorTutorialAdd Android and iOS as platforms:
npm i @capacitor/android @capacitor/iosRun the following commands to create the native Android and iOS projects:
npx cap add android
npx cap add iosStep 2: Install the SDK
To install the Scanbot Capacitor Barcode Scanner SDK, run:
npm i capacitor-plugin-scanbot-barcode-scanner-sdk💡 This will install the latest Scanbot SDK version. You can find more information about each version in our changelog.
Now that the npm package has been installed, we need to make some changes to the native projects.
Android
For Android, we need to add the camera permission and feature in android/app/src/main/AndroidManifest.xml:
<uses-permission android:name="android.permission.CAMERA" />
<uses-feature android:name="android.hardware.camera" />iOS
For iOS, we need to include a description for the camera permission in ios/App/App/Info.plist anywhere inside the <dict> element:
<key>NSCameraUsageDescription</key>
<string>Camera permission is needed to scan barcodes</string>Now that the project is set up, we can start integrating the barcode scanning functionalities.
Step 3: Initialize the SDK
Before using any feature of the Capacitor Barcode Scanner SDK, we need to initialize it. Ideally, initialization should be done once, as soon as the app is fully launched.
In this tutorial, we’re going to initialize the SDK inside the ngOnInit callback in the src/app/app.component.ts file and make sure that we import the ScanbotBarcodeSDK. Your app.component.ts should then look like this:
import { Component, OnInit } from '@angular/core';
import { IonApp, IonRouterOutlet } from '@ionic/angular/standalone';
import { ScanbotBarcodeSDK } from 'capacitor-plugin-scanbot-barcode-scanner-sdk';
@Component({
selector: 'app-root',
templateUrl: 'app.component.html',
standalone: true,
imports: [IonApp, IonRouterOutlet],
})
export class AppComponent implements OnInit {
constructor() { }
ngOnInit(): void {
ScanbotBarcodeSDK.initializeSdk({
licenseKey: ""
}).then(result => console.log(result))
.catch(err => console.log(err));
}
}💡 Without a license key, our SDK only runs for 60 seconds per session. This is more than enough for the purposes of our tutorial, but if you like, you can generate a license key using the application/bundle ID.
Step 4: Implement the scanning modes
The SDK’s RTU UI components make it easy to deploy different scanning modes in your app. Let’s start with the simplest use case: single-barcode scanning.
In your project folder, go to src/app/home/home.page.ts, add the necessary imports, and create a method that will start the single-barcode scanning use case. The result should look something like this:
import { Component } from '@angular/core';
import { IonHeader, IonToolbar, IonTitle, IonContent, IonButton } from '@ionic/angular/standalone';
import { ScanbotBarcodeSDK } from 'capacitor-plugin-scanbot-barcode-scanner-sdk';
import { startBarcodeScanner, BarcodeScannerConfiguration, SingleScanningMode } from 'capacitor-plugin-scanbot-barcode-scanner-sdk/ui_v2';
@Component({
selector: 'app-home',
templateUrl: 'home.page.html',
styleUrls: ['home.page.scss'],
standalone: true,
imports: [IonHeader, IonToolbar, IonTitle, IonContent, IonButton],
})
export class HomePage {
constructor() {}
async startSingleBarcodeScan() {
try {
/** Check license status and return early if the license is not valid */
if (!(await ScanbotBarcodeSDK.getLicenseInfo()).data?.isLicenseValid) {
return;
}
/**
* Instantiate a configuration object of BarcodeScannerConfiguration and
* start the barcode scanner with the configuration
*/
const config = new BarcodeScannerConfiguration();
/** Initialize the use case for single scanning */
config.useCase = new SingleScanningMode();
/** Start the BarcodeScanner */
const result = await startBarcodeScanner(config);
/** Handle the result if there are scanned barcodes */
if (result.data && result.data?.items.length > 0) {
alert(
'Barcode Scanning successfully! \n' +
`Value: ${result.data.items[0].text} \n` +
`Type: ${result.data.items[0].type}`
);
}
} catch (e: any) {
console.error("An error has occurred while running Barcode Scanner", e.message);
}
}
}Next, go to src/app/home/home.page.html and add a button that calls our startSingleBarcodeScan method when clicked. Your home.page.html should look something like this:
<ion-header [translucent]="true">
<ion-toolbar>
<ion-title>
Capacitor Tutorial
</ion-title>
</ion-toolbar>
</ion-header>
<ion-content [fullscreen]="true">
<ion-header collapse="condense">
<ion-toolbar>
<ion-title size="large">Capacitor Tutorial</ion-title>
</ion-toolbar>
</ion-header>
<div id="container">
<ion-button (click)="startSingleBarcodeScan()">Start single barcode scanning</ion-button>
</div>
</ion-content>We can add our multi-scanning and AR overlay use cases in a similar manner.
Just add MultipleScanningMode to the import:
import { startBarcodeScanner, BarcodeScannerConfiguration, SingleScanningMode, MultipleScanningMode } from 'capacitor-plugin-scanbot-barcode-scanner-sdk/ui_v2';And create two more methods:
async startMultiBarcodeScan() {
try {
/** Check license status and return early if the license is not valid */
if (!(await ScanbotBarcodeSDK.getLicenseInfo()).data?.isLicenseValid) {
return;
}
/**
* Instantiate a configuration object of BarcodeScannerConfiguration and
* start the barcode scanner with the configuration
*/
const config = new BarcodeScannerConfiguration();
/** Initialize the use case for multi-scanning */
config.useCase = new MultipleScanningMode();
/** Start the BarcodeScanner */
const result = await startBarcodeScanner(config);
/** Handle the result */
if (result.data && result.data?.items.length > 0) {
alert(
'Barcode Scanning successfully! \n' +
`${result.data.items.map(barcode =>
`Barcode value: ${barcode.text} and type: ${barcode.type}`
).join("\n")}`);
}
} catch (e: any) {
console.error("An error has occurred while running Barcode Scanner", e.message);
}
}
async startAROverlayBarcodeScan() {
try {
/** Check license status and return early if the license is not valid */
if (!(await ScanbotBarcodeSDK.getLicenseInfo()).data?.isLicenseValid) {
return;
}
/**
* Instantiate a configuration object of BarcodeScannerConfiguration and
* start the barcode scanner with the configuration
*/
const config = new BarcodeScannerConfiguration();
/** Initialize the use case for multi-scanning */
config.useCase = new MultipleScanningMode();
/** Configure AR Overlay. */
config.useCase.arOverlay.visible = true;
config.useCase.arOverlay.automaticSelectionEnabled = false;
/** Start the BarcodeScanner */
const result = await startBarcodeScanner(config);
/** Handle the result */
if (result.data && result.data?.items.length > 0) {
alert(
'Barcode Scanning successfully! \n' +
`${result.data.items.map(barcode =>
`Barcode value: ${barcode.text} and type: ${barcode.type}`
).join("\n")}`);
}
} catch (e: any) {
console.error("An error has occurred while running Barcode Scanner", e.message);
}
}Next, go back to src/app/home/home.page.html and add buttons for the multi-scanning and AR overlay use cases:
<ion-button (click)="startMultiBarcodeScan()">Start multi-barcode scanning</ion-button>
<ion-button (click)="startAROverlayBarcodeScan()">Start AR Overlay barcode scanning</ion-button>We’re now ready to build and run the app!
In the terminal, run these commands to build and sync the native projects:
npm run build
npx cap syncTo run the app on Android and iOS, use the following commands:
For Android:
npx cap run androidFor iOS:
To run the app on a real iOS device, you need to adjust the Provisioning and Signing settings. Open ios/App/App.xcworkspace with Xcode, manage the signing and provisioning settings, and run the project from Xcode or with this command:
npx cap run iosNow you can go ahead and scan 1D and 2D barcodes – one after the other, many at the same time, and even with an AR overlay that lets you preview their values!

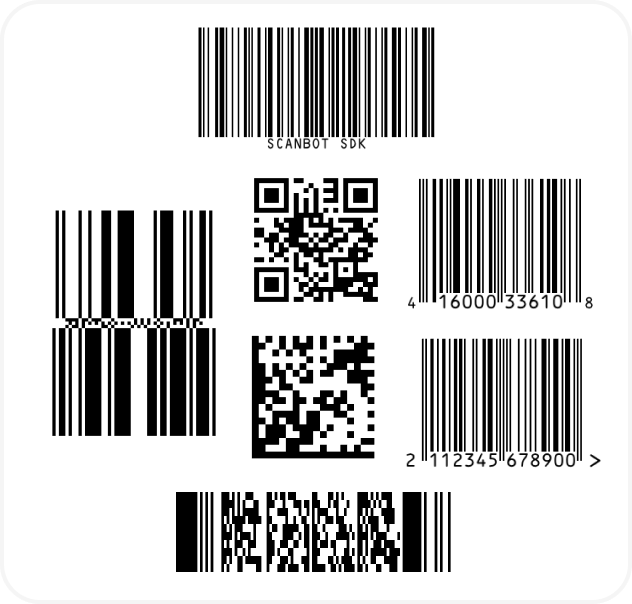
And if you’re in need of some sample barcodes for testing purposes, we’ve got you covered:

Conclusion
If this tutorial has piqued your interest in integrating barcode scanning functionalities into your Ionic Capacitor app, make sure to take a look at the other neat features in the SDK’s documentation.
Furthermore, you can take a look at and run our example project.
Should you have questions about this tutorial or ran into any issues, we’re happy to help! Just shoot us an email via tutorial-support@scanbot.io.
Happy scanning! 🤳







