In this tutorial, we’ll use Flutter to build a cross-platform app for Android and iOS that recognizes and extracts text from a live camera stream.
To implement the text recognition functionalities, we’ll use the Scanbot Text Pattern Scanner SDK.
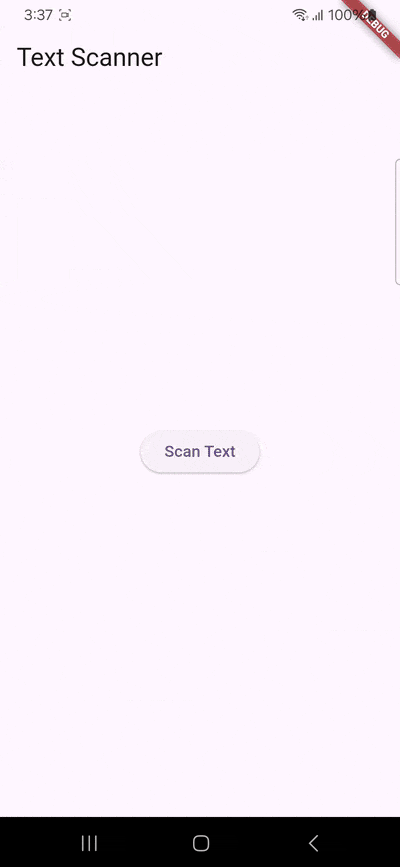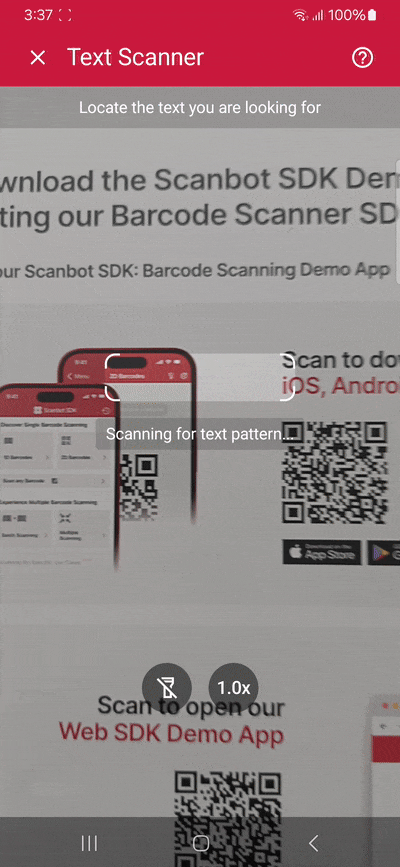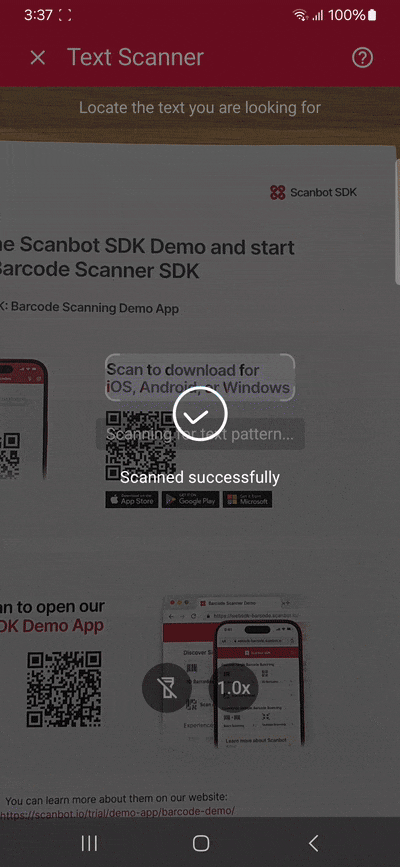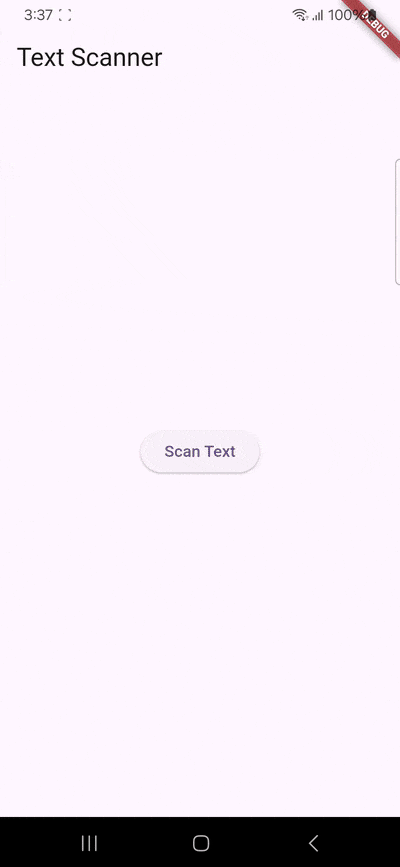
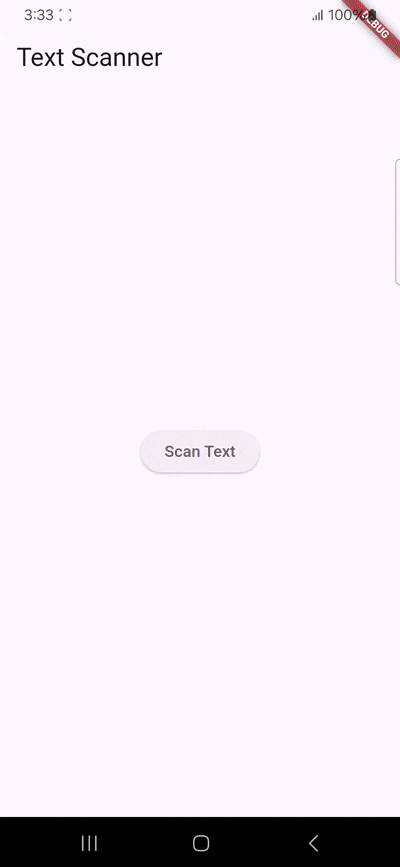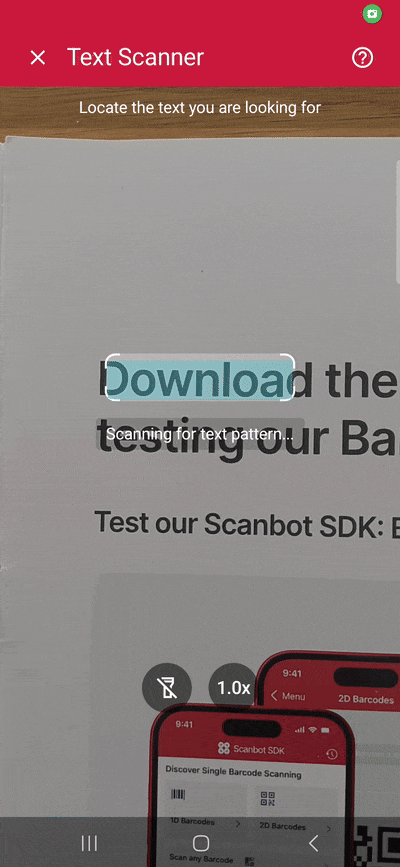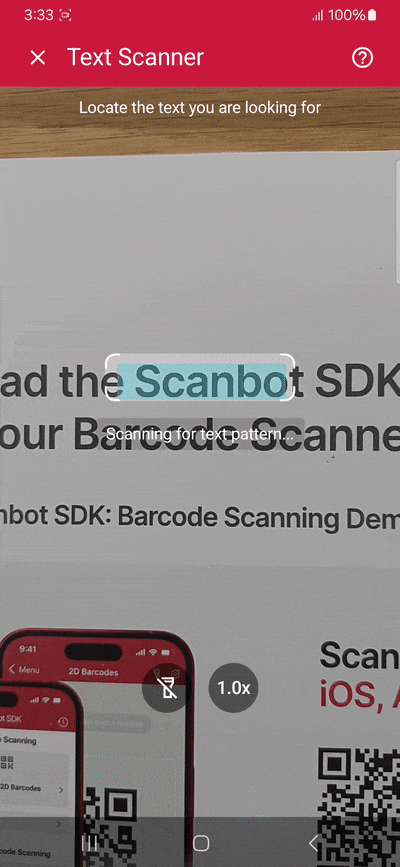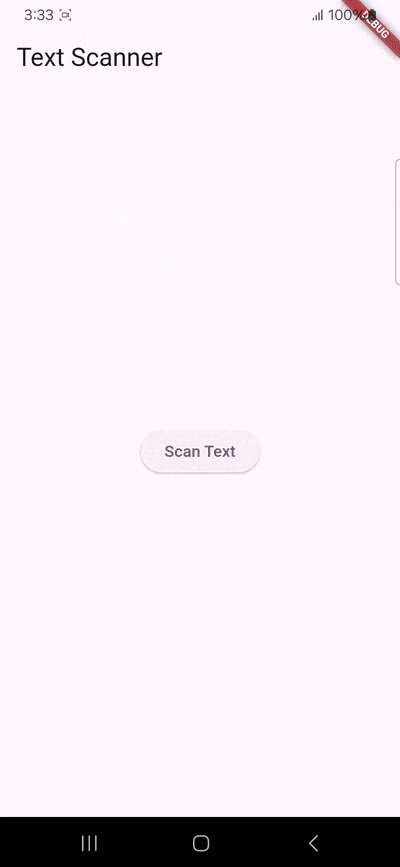
Building our app involves the following steps:
- Preparing the project
- Initializing the SDK
- Setting up the main widget
- Implementing the text scanning feature
Prerequisites
- Flutter SDK: Ensure you have the latest version installed.
- Development tools:
- For Android: Android Studio with the Android SDK.
- For iOS: macOS with the latest Xcode and CocoaPods installed.
- Optional: Visual Studio Code with the Flutter and Dart extensions.
Step 1: Prepare the project
Open your terminal and execute:
flutter create text_scanner_app
cd text_scanner_appThen open pubspec.yaml and add the scanbot_sdk dependency.
dependencies:
flutter:
sdk: flutter
scanbot_sdk: ^7.0.1Then, fetch the package.
flutter pub get💡 We use SDK version 7.0.1 in this tutorial. You can find the latest version in the changelog.
We need to access the device camera to scan text, so open android/app/src/main/AndroidManifest.xml and add the necessary permissions for Android:
<uses-permission android:name="android.permission.CAMERA" />
<uses-feature android:name="android.hardware.camera" />For iOS, open ios/Runner/Info.plist and add:
<key>NSCameraUsageDescription</key>
<string>Grant camera access to text.</string>Step 2: Initialize the SDK
Before we can use the Scanbot SDK, we need to initialize it. Make sure to call the initialization after entering the main widget creation. This ensures the SDK is correctly initialized.
In lib/main.dart, import the Scanbot SDK package:
import 'package:scanbot_sdk/scanbot_sdk.dart';
import 'package:scanbot_sdk/scanbot_sdk_ui_v2.dart';Within your main widget, initialize the Scanbot SDK. This is typically done in the initState method of your main widget’s state class:
class _MyHomePageState extends State<MyHomePage> {
@override
void initState() {
super.initState();
_initScanbotSdk();
}
Future<void> _initScanbotSdk() async {
var config = ScanbotSdkConfig(
licenseKey: "",
loggingEnabled: true,
);
try {
await ScanbotSdk.initScanbotSdk(config);
print('Scanbot SDK initialized successfully');
} catch (e) {
print('Error initializing Scanbot SDK: $e');
}
}
//...💡 Without a license key, our SDK only runs for 60 seconds per session. This is more than enough for the purposes of our tutorial, but if you like, you can generate a license key using your app identifier.
Step 3: Set up the main widget
Next, we’ll create a simple user interface that includes a button to initiate the scanning process.
Still in lib/main.dart, and in your main widget’s state class, define a widget with a button labeled “Scan Text”:
class _MyHomePageState extends State<MyHomePage> {
// ... (existing code)
@override
Widget build(BuildContext context) {
return Scaffold(
appBar: AppBar(
title: Text('Text Scanner'),
),
body: Center(
child: ElevatedButton(
onPressed: _startTextPatternScanner,
child: Text('Scan Text'),
),
),
);
}
Future<void> _startTextPatternScanner() async {
// To be implemented in the next step
}
}Next, we’ll connect the button with our RTU UI’s scanning screen.
Step 4: Implement the text scanning feature
Within the _startTextPatternScanner method, configure and launch the scanning UI. This involves creating a TextPatternScannerScreenConfiguration and starting the scanner:
Future<void> _startTextPatternScanner() async {
try {
final licenseInfo = await ScanbotSdk.getLicenseStatus();
if (!licenseInfo.isLicenseValid) {
return;
}
final configuration = TextPatternScannerScreenConfiguration();
final result = await ScanbotSdkUiV2.startTextPatternScanner(
configuration,
);
if (result.status == OperationStatus.OK) {}
} catch (e) {
print('Error: $e');
}
}
}We can then extract the recognized text and show it in an alert like this:
Future<void> _startTextPatternScanner() async {
try {
final licenseInfo = await ScanbotSdk.getLicenseStatus();
if (!licenseInfo.isLicenseValid) {
return;
}
final configuration = TextPatternScannerScreenConfiguration();
final result = await ScanbotSdkUiV2.startTextPatternScanner(
configuration,
);
if (result.status == OperationStatus.OK) {
if (Navigator.of(context).mounted) {
showDialog(
context: context,
builder: (BuildContext context) {
return AlertDialog(
title: const Text("Scanned text:"),
content: Text(result.data!.rawText),
actions: <Widget>[
TextButton(
child: const Text("OK"),
onPressed: () {
Navigator.of(context).pop();
},
),
],
);
},
);
}
}
} catch (e) {
print('Error: $e');
}
}
}Feel free to run the app using flutter run.

Optional: Set a text pattern
As it is now, our scanner will extract any text inside the viewfinder. But we can also pre-define the text we’re looking for, e.g., using regular expressions.
In this example, we’re only extracting seven-letter words beginning with “S” and ending in “t” (regex pattern \bS\w{5}t\b plus escape characters).
Future<void> _startTextPatternScanner() async {
try {
final licenseInfo = await ScanbotSdk.getLicenseStatus();
if (!licenseInfo.isLicenseValid) {
return;
}
final configuration = TextPatternScannerScreenConfiguration();
// Configure the pattern content validator here
final patternValidator = PatternContentValidator(
pattern: r"\bS\w{5}t\b",
allowedCharacters:
"ABCDEFGHIJKLMNOPQRSTUVWXYZabcdefghijklmnopqrstuvwxyz",
matchSubstring: false,
patternGrammar: PatternGrammar.REGEX,
);
configuration.scannerConfiguration.validator = patternValidator;
final result = await ScanbotSdkUiV2.startTextPatternScanner(
configuration,
);
if (result.status == OperationStatus.OK) {
if (Navigator.of(context).mounted) {
showDialog(
context: context,
builder: (BuildContext context) {
return AlertDialog(
title: const Text("Scanned text:"),
content: Text(result.data!.rawText),
actions: <Widget>[
TextButton(
child: const Text("OK"),
onPressed: () {
Navigator.of(context).pop();
},
),
],
);
},
);
}
}
} catch (e) {
print('Error: $e');
}
}Now run the app again to test the text recognition with pattern matching.

Conclusion
And that’s it! You’ve successfully built a cross-platform text scanning app with Flutter 🎉
If this tutorial has piqued your interest in integrating scanning functionalities into your Flutter app, make sure to take a look at the SDK’s other neat features in the documentation – or run our example project for a more hands-on experience.
Should you have questions about this tutorial or run into any issues, we’re happy to help! Just shoot us an email via tutorial-support@scanbot.io.
Happy scanning! 🤳





